Introduction
The rise of matcha as a health staple has transformed how individuals approach nutrition and wellness. This finely ground powder, derived from specially cultivated green tea leaves, offers a wealth of benefits that extend beyond its vibrant color and unique flavor.
From its impressive antioxidant profile to its potential for enhancing mental clarity and physical vitality, matcha stands out as a formidable superfood. However, its integration into daily diets requires an understanding of both its advantages and potential drawbacks.
This article delves into the multifaceted world of matcha, exploring its health benefits, culinary versatility, and the environmental implications of its production, providing a comprehensive guide for those looking to embrace this green powerhouse responsibly.
1. What is Matcha and Why is it Considered a Superfood?
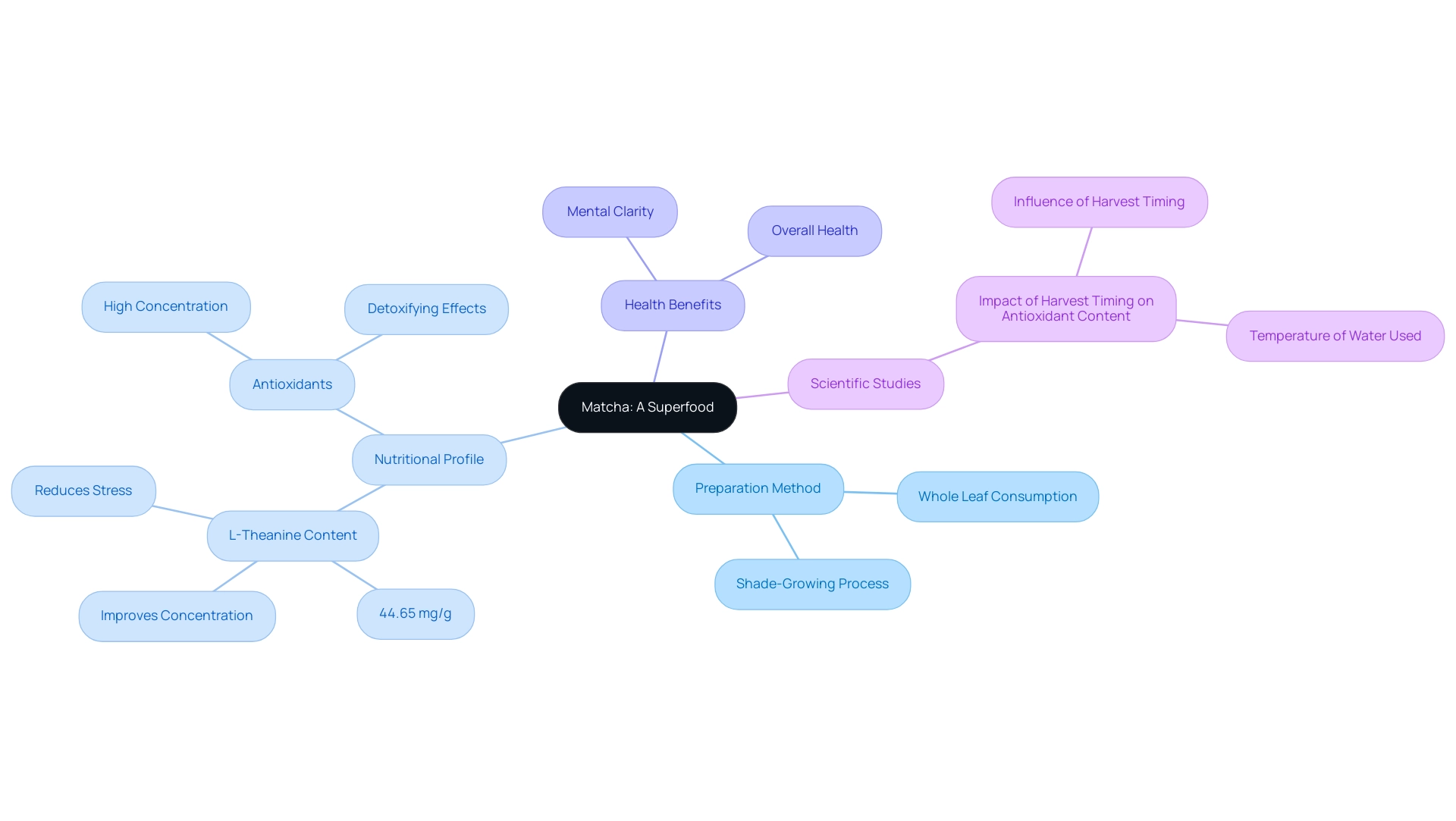
Matcha is a finely ground powder obtained from specially cultivated tea leaves, primarily from Japan. Unlike traditional green tea, which involves steeping leaves and discarding them, this powdered variety requires the consumption of the entire leaf, significantly enhancing its nutritional profile. This preparation method is pivotal to understanding what makes matcha a superfood, attributed to its rich composition of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Notably, this green tea boasts a remarkable
l-theanine content, reaching up to 44.65 mg/g, which is linked to improved concentration and stress reduction, particularly due to the shade-growing process that enhances its flavor and nutritional properties. According to Rebecca Jaspan, MPH, RD, "Matcha's unique composition not only supports mental clarity but also provides a rich source of antioxidants that contribute to overall health." The vibrant green hue of the powdered tea indicates a high concentration of chlorophyll, recognized for its potential detoxifying effects, which can aid in cleansing the body of toxins.
Furthermore, a recent study titled 'Impact of Harvest Timing on Antioxidant Content' revealed that the concentration of antioxidant compounds in green tea is influenced by the timing of the harvest and the temperature of the water used for infusion. This reinforces the understanding of what makes matcha a superfood, as this green tea embodies the characteristics of a superfood while also showcasing versatility in culinary applications, making it a valuable addition to a health-conscious lifestyle. In contrast to conventional matcha, matcha provides improved wellness advantages because of its greater antioxidant levels and the distinct method of consumption.
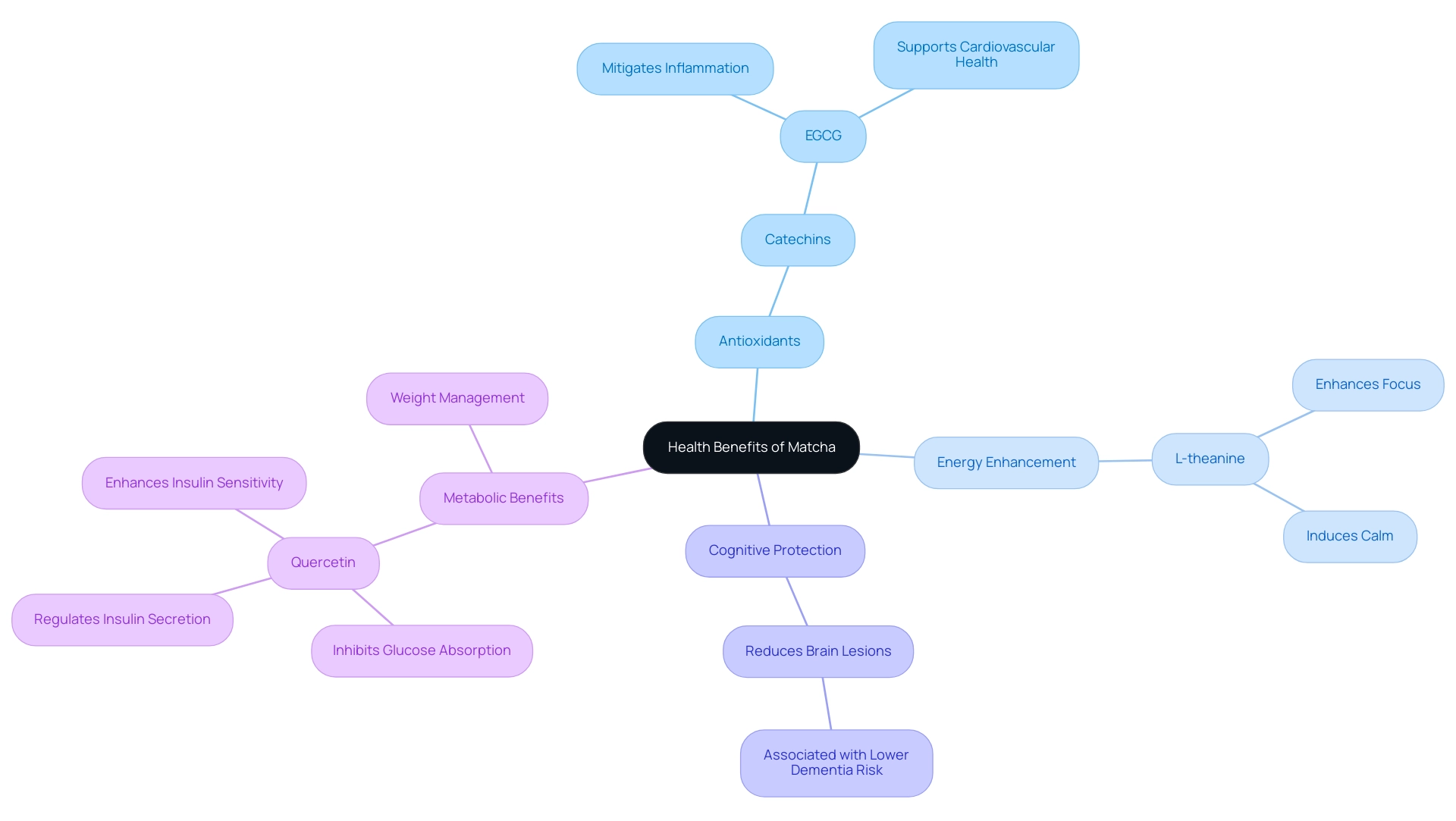
2. Exploring the Health Benefits of Matcha: Antioxidants, Energy, and More
Matcha is widely celebrated for its remarkable antioxidant levels, particularly its rich concentration of catechins, which play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals within the body. Among these catechins, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) stands out due to its potential to mitigate inflammation and support cardiovascular health. Recent studies have indicated that regular green tea consumption is associated with
fewer brain lesions characteristic of dementia, suggesting a protective effect on cognitive function.
Furthermore, green tea contains L-theanine, an amino acid renowned for its ability to enhance focus while inducing a state of calm, free from the jittery feelings often linked to caffeine. This synergistic combination of compounds not only provides a sustained energy boost but also positions this beverage as a preferred choice for individuals aiming to enhance both physical and mental vitality. Moreover, quercetin present in green tea inhibits glucose absorption, regulates insulin secretion, and enhances insulin sensitivity, further adding to its advantages.
Current studies indicate that regular consumption of this green tea may assist in weight management and enhance metabolic well-being, raising the question of what makes matcha a superfood. Findings from an extensive study titled 'Antioxidant Properties and Nutritional Composition of Green Tea,' carried out by specialists from the Department of Human Nutrition and Metabolomics, clarified these advantages, highlighting the potential of this tea in enhancing well-being. As Jon Johnson noted, 'What makes matcha a superfood is its unique blend of antioxidants and amino acids, which makes it a powerhouse for health-conscious individuals looking to enhance their overall vitality.
3. How to Incorporate Matcha into Your Diet
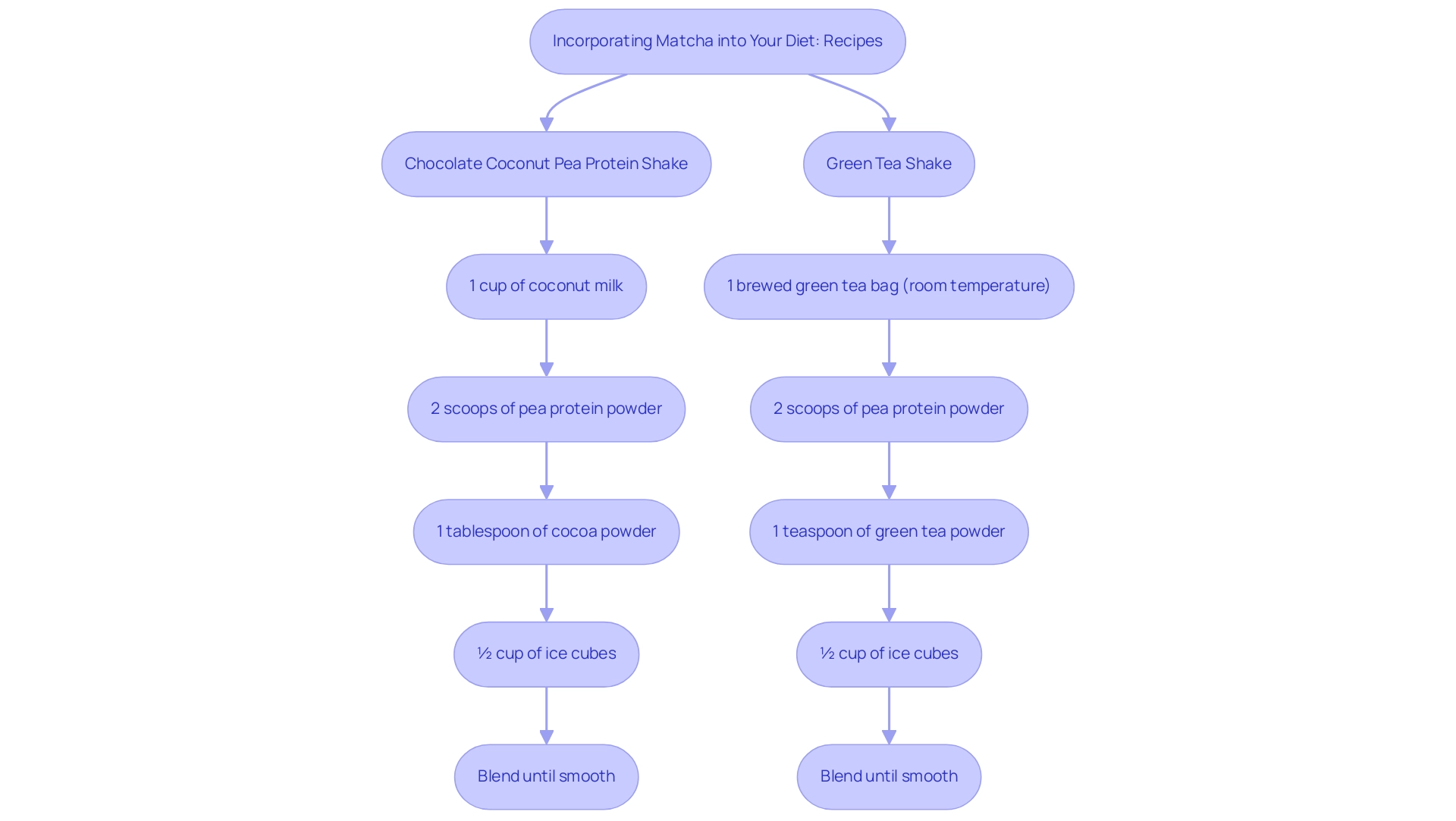
Including powdered green tea in your diet leads to the question, what makes matcha a superfood, as it provides both pleasure and various health advantages. A classic method is to prepare green tea by whisking the powder with hot water until it achieves a frothy consistency, resulting in a refreshing beverage rich in antioxidants. For those seeking indulgent plant-based shake recipes, consider blending green tea powder into smoothies featuring pea protein.
For the Chocolate Coconut Pea Protein Shake, blend:
- 1 cup of coconut milk
- 2 scoops of pea protein powder
- 1 tablespoon of cocoa powder
- ½ cup of ice cubes
until smooth.
For the Green Tea Shake, combine:
- 1 brewed green tea bag (room temperature)
- 2 scoops of pea protein powder
- 1 teaspoon of green tea powder
- ½ cup of ice cubes
blending until smooth. You can also add honey or maple syrup if you prefer your shakes on the sweeter side.
Research indicates that a safe daily intake level for adults is approximately 338 mg of catechin and EGCG, which raises the question: What makes matcha a superfood when it is equivalent to about 4 g of powdered green tea or 2 level teaspoons? Incorporating green tea powder into smoothies raises the question of what makes matcha a superfood, offering an extra nutritional enhancement while enhancing the flavor profile. Furthermore, this unique flavor and vibrant color make it an excellent choice for baking, featuring in recipes for green tea cookies or cakes.
Beyond sweet applications, green tea powder can also be creatively used in savory dishes; for instance, it can be blended into salad dressings or lightly sprinkled over popcorn, transforming it into a nutritious snack. However, it's important to consume green tea in moderation; despite its wellness advantages, excessive intake may lead to adverse effects due to its caffeine content. A case study titled 'Moderation in Matcha Consumption' emphasizes this point, recommending 1–2 cups per day and the choice of organic varieties.
The versatility of this green tea raises the question, what makes matcha a superfood, as it enhances diverse dietary preferences and culinary styles, making it a favored component among wellness enthusiasts and culinary specialists alike. As Amy Richter, RD, notes, 'Salads are great sources of veggies, but they're not the only way to consume veggies.' Recent trends indicate that green tea's culinary uses are broadening, with creative recipes appearing in 2024 that cater to various preferences and wellness objectives.
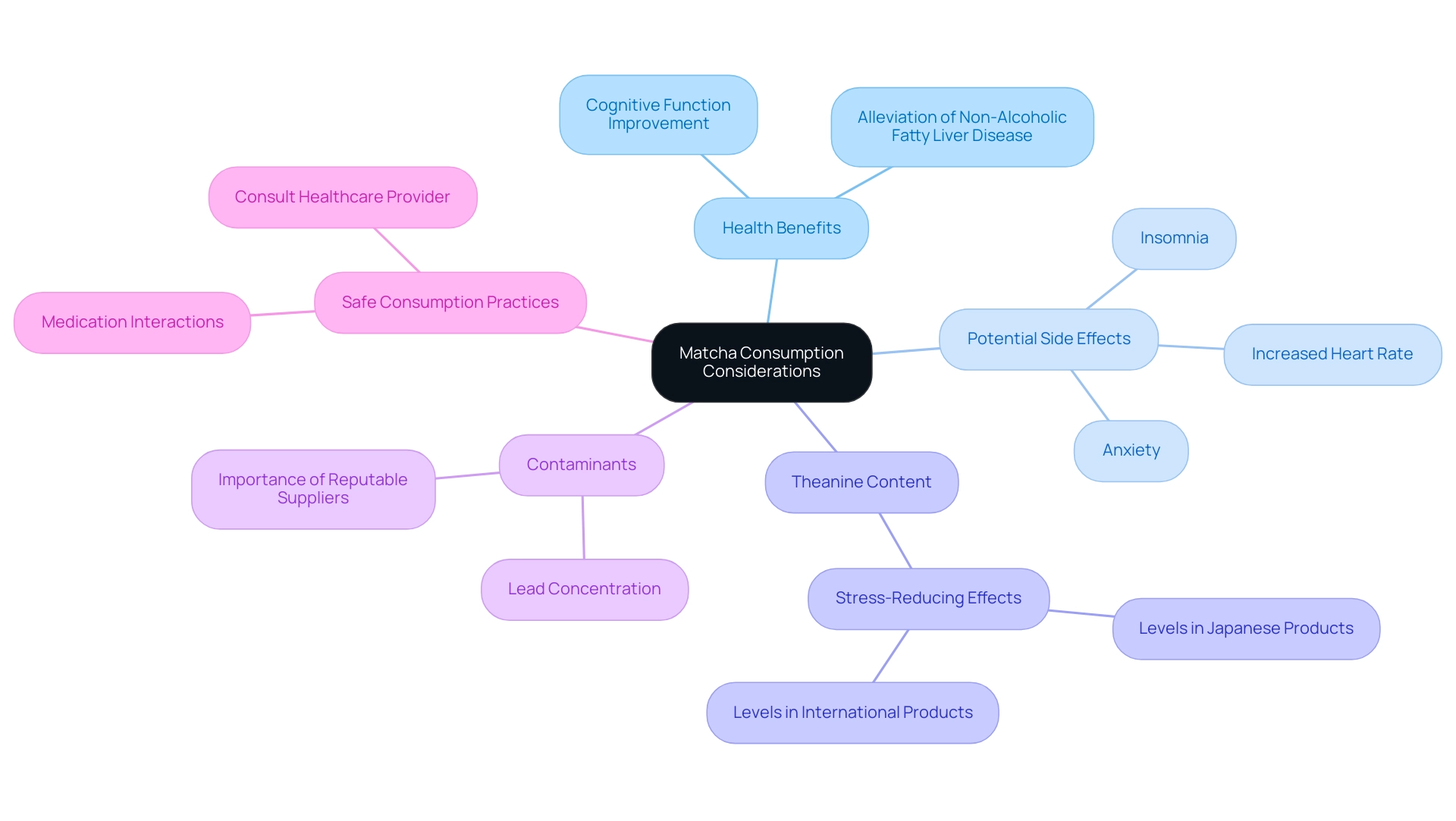
4. Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While this green tea is celebrated for its numerous health benefits, what makes matcha a superfood is the crucial importance of moderation in consumption. The caffeine content in this green tea can lead to side effects such as insomnia, increased heart rate, and anxiety, particularly for those who are sensitive to caffeine. Recent studies indicate that green tea powder may
alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese mice, as reported by Zhou et al., but excessive intake can exacerbate caffeine-related issues.
According to research conducted by Unno et al. (2018):
- "50 out of 76 product samples bought from Japan contained levels of theanine expected to have a stress-reducing effect (>17 mg/g), while only 6 exceeded that limit in the ones purchased from the international market."
- Moreover, as this green tea is derived from whole leaves, it may also contain higher concentrations of substances, such as lead, which can vary based on the growing conditions.
Consequently, it is prudent to procure green tea powder from reputable suppliers who rigorously test their products for contaminants. Additionally, to safely consume the green tea powder, individuals should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they take to prevent possible interactions and side effects. As with any dietary adjustment, individuals should discuss their green tea consumption with healthcare professionals, especially if they have existing health concerns or are wary of caffeine-related side effects.
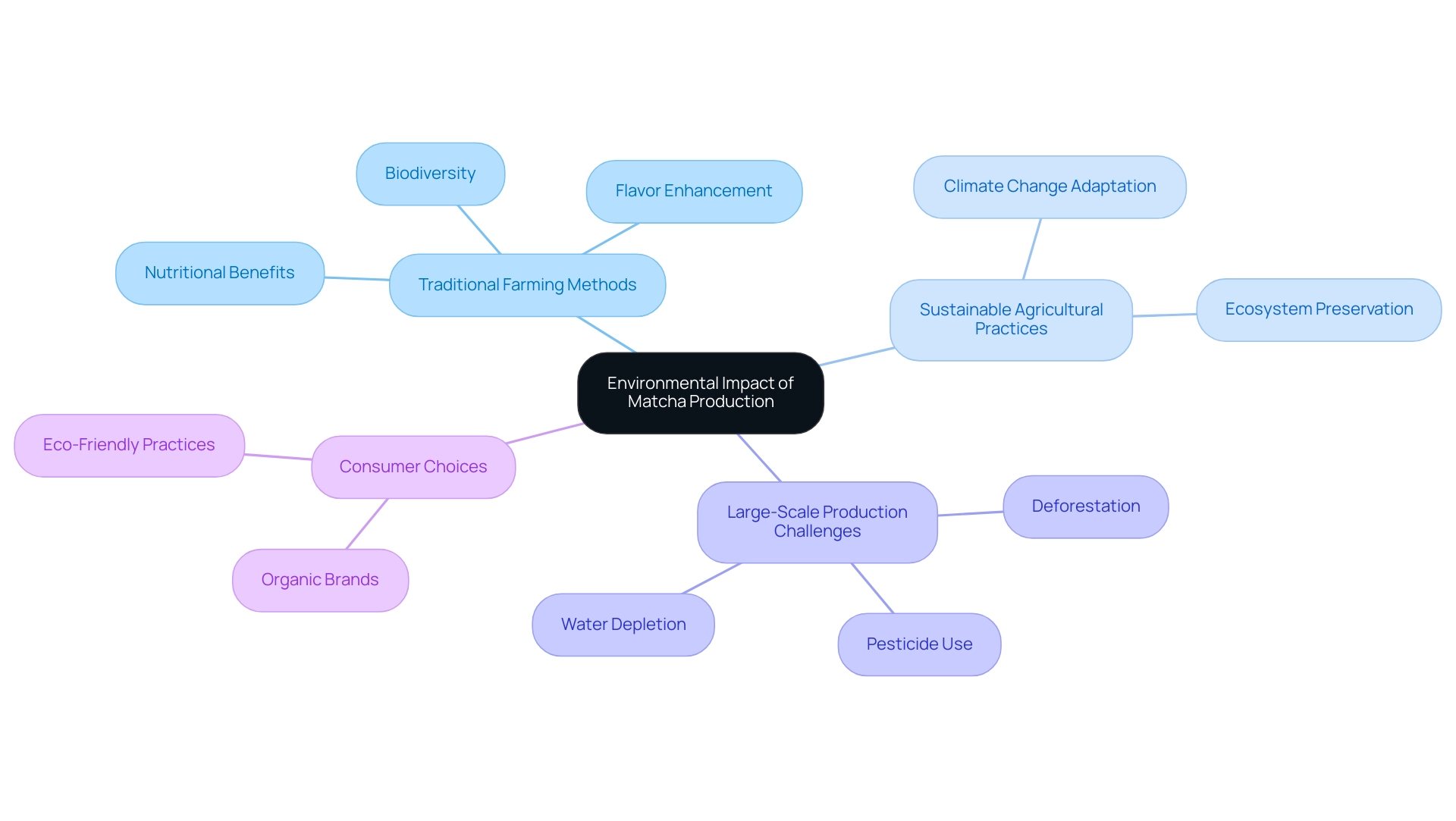
5. The Environmental Impact of Matcha Production
The environmental impact of green tea production varies significantly based on the farming practices employed. Traditional cultivation methods, which often utilize shade-growing techniques, are beneficial not only for enhancing the flavor and nutritional profile of the tea but also for promoting biodiversity. These techniques provide essential habitats for various species, contributing to a more balanced ecosystem.
As Gopalakrishnan et al. discussed, sustainable agricultural practices are crucial in the face of climate change, highlighting the importance of adapting farming methods to preserve coastal and agricultural ecosystems. Conversely, large-scale green tea production presents several environmental challenges, including deforestation, excessive pesticide use, and the depletion of vital water resources.
According to research, the cultivation of green tea can yield l-theanine levels as high as 44.65 mg/g, making it a nutritionally advantageous choice; however, the farming methods must be sustainable to preserve these benefits. Furthermore, a safety assessment of green tea catechins indicates that while green tea infusions are presumed safe, concentrated extracts require caution, particularly at doses above 800 mg EGCG/day, which have been associated with liver injury. Dekant et al. proposed a
tolerable upper intake of 300 mg EGCG/person and day based on clinical trials that did not report liver effects.
Therefore, consumers who prioritize sustainability should actively seek out organic brands that adhere to eco-friendly farming practices. By choosing sustainably sourced matcha, individuals not only enjoy its numerous health benefits, which leads to the question of what makes matcha a superfood, but also contribute to the protection of the environment, reinforcing the importance of responsible consumption in today's market.
Conclusion
The exploration of matcha reveals its status as a superfood backed by a wealth of health benefits. Rich in antioxidants, particularly catechins like EGCG, matcha supports everything from heart health to cognitive function. Its unique combination of L-theanine and caffeine offers a balanced energy boost, enhancing focus without the jittery side effects typically associated with caffeine consumption. With various methods to incorporate matcha into daily diets, from teas to smoothies and baked goods, it proves to be a versatile ingredient that can enrich both flavor and nutrition.
However, moderation is key. Consumers must be mindful of matcha's caffeine content, which can lead to side effects if consumed excessively. Ensuring the quality of matcha by sourcing from reputable suppliers is also crucial to avoid potential contaminants. Furthermore, understanding the environmental implications of matcha production highlights the importance of choosing sustainably sourced options, promoting both personal health and ecological responsibility.
In summary, matcha offers a powerful array of health benefits while also posing certain risks if not consumed judiciously. By integrating matcha thoughtfully into a balanced diet, individuals can harness its potential while supporting sustainable practices that benefit the planet. Embracing this green powerhouse responsibly is essential for maximizing its advantages and ensuring a healthier future for both consumers and the environment.