Introduction
- Characteristics
- Health benefits
- Dosage recommendations
- Potential side effects
- Strategies for choosing the right magnesium supplement
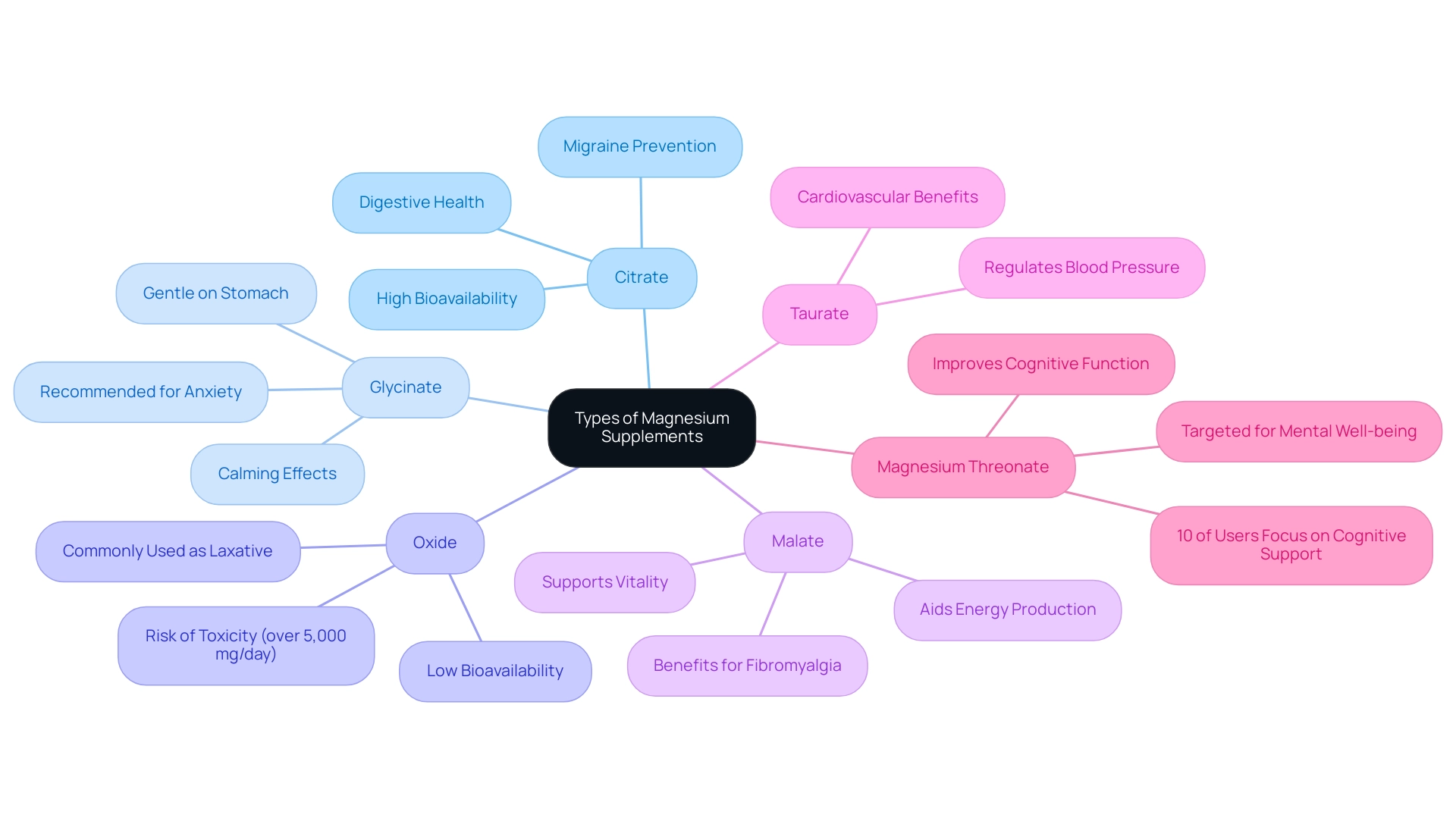
1. Exploring the Different Types of Magnesium Supplements
-
Citrate: Recognized for its high bioavailability, citrate is an excellent choice for individuals looking to swiftly increase their levels of this essential mineral.
It is frequently utilized to promote digestive health and alleviate constipation, making it a practical choice for many. In fact, the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society concluded that this therapy is probably effective for migraine prevention, which adds to its appeal. -
Glycinate: Acknowledged for its calming effects, glycinate is frequently recommended for those facing anxiety and sleep issues.
This form is less likely to induce gastrointestinal discomfort compared to others, making it a gentle option for supplementation. -
Oxide: Among the most commonly utilized forms due to its affordability, oxide has lower bioavailability.
It is generally used as a laxative instead of a method to tackle mineral deficiency, which restricts its efficacy in supplementation scenarios.
It's important to note that very large doses of laxatives and antacids containing this element (more than 5,000 mg/day) have been linked to toxicity, highlighting the need for careful dosage management. -
Malate: This type combines a mineral with malic acid and is reputed to aid energy production.
It may offer benefits to individuals suffering from fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome, supporting overall vitality. -
Taurate: Bound to the amino acid taurine, this compound may provide cardiovascular benefits and assist in regulating blood pressure, which is critical for heart health.
-
Magnesium Threonate: As a relatively recent addition to the nutritional market, this compound has shown promise in improving cognitive function, making it a hopeful choice for brain wellness.
Significantly, approximately 10% of product users consume items targeted at mental well-being and cognitive function, with Omega-3 fatty acids being the best-selling item, reflecting a rising interest in cognitive support.
As the market for mineral supplements continues to grow, remaining informed about the latest research and statistics for 2024 becomes crucial for effective wellness management.
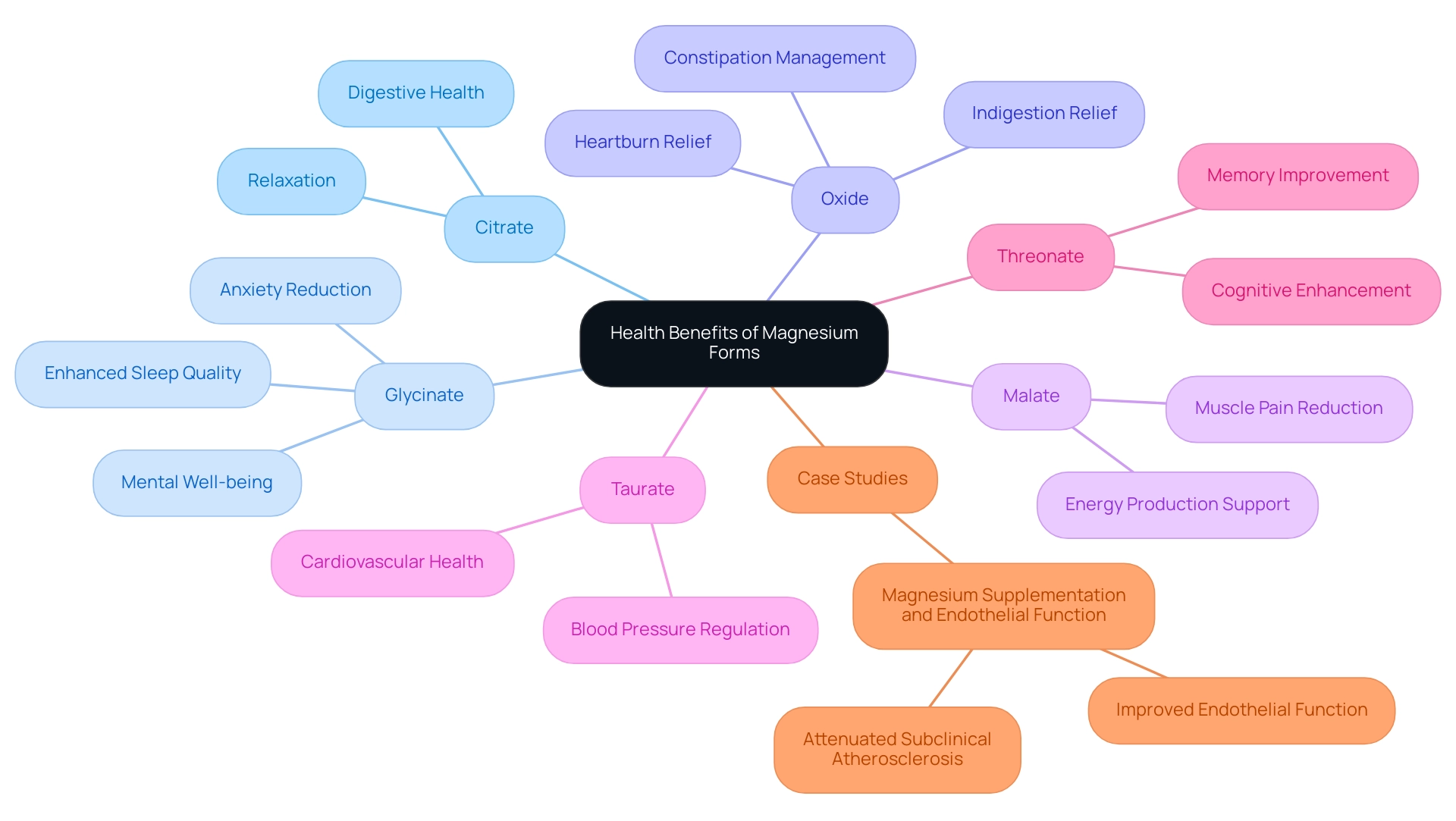
2. Health Benefits of Various Magnesium Forms
-
Citrate: This highly bioavailable form supports digestive health, effectively relieving constipation, and is known for its potential to promote relaxation and enhance sleep quality. Recent findings suggest that participants in the sulfate group reported gastrointestinal complaints, highlighting the importance of selecting the right form of this mineral for digestive support.
-
Glycinate: Renowned for its calming effects, this supplement assists in reducing anxiety and enhancing sleep quality, making it particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing stress-related issues. Recent studies have indicated that this form may yield significant improvements in overall mental well-being. Notably, health professionals emphasize its effectiveness, stating that 'glycinate is a preferred choice for those looking to manage anxiety.'
-
Oxide: Although it has lower bioavailability, this compound can still be effective in alleviating heartburn and indigestion. It is often utilized in higher doses to help manage constipation symptoms.
-
Malate: This form is recognized for its ability to reduce muscle pain and support energy production, making it particularly advantageous for individuals suffering from fatigue syndromes.
-
Taurate of magnesium supports cardiovascular well-being, with potential advantages such as the regulation of blood pressure and improvement of heart function.
-
Threonate: Recent studies indicate that this compound may enhance cognitive ability and memory, providing encouraging assistance for brain wellness, particularly in seniors.
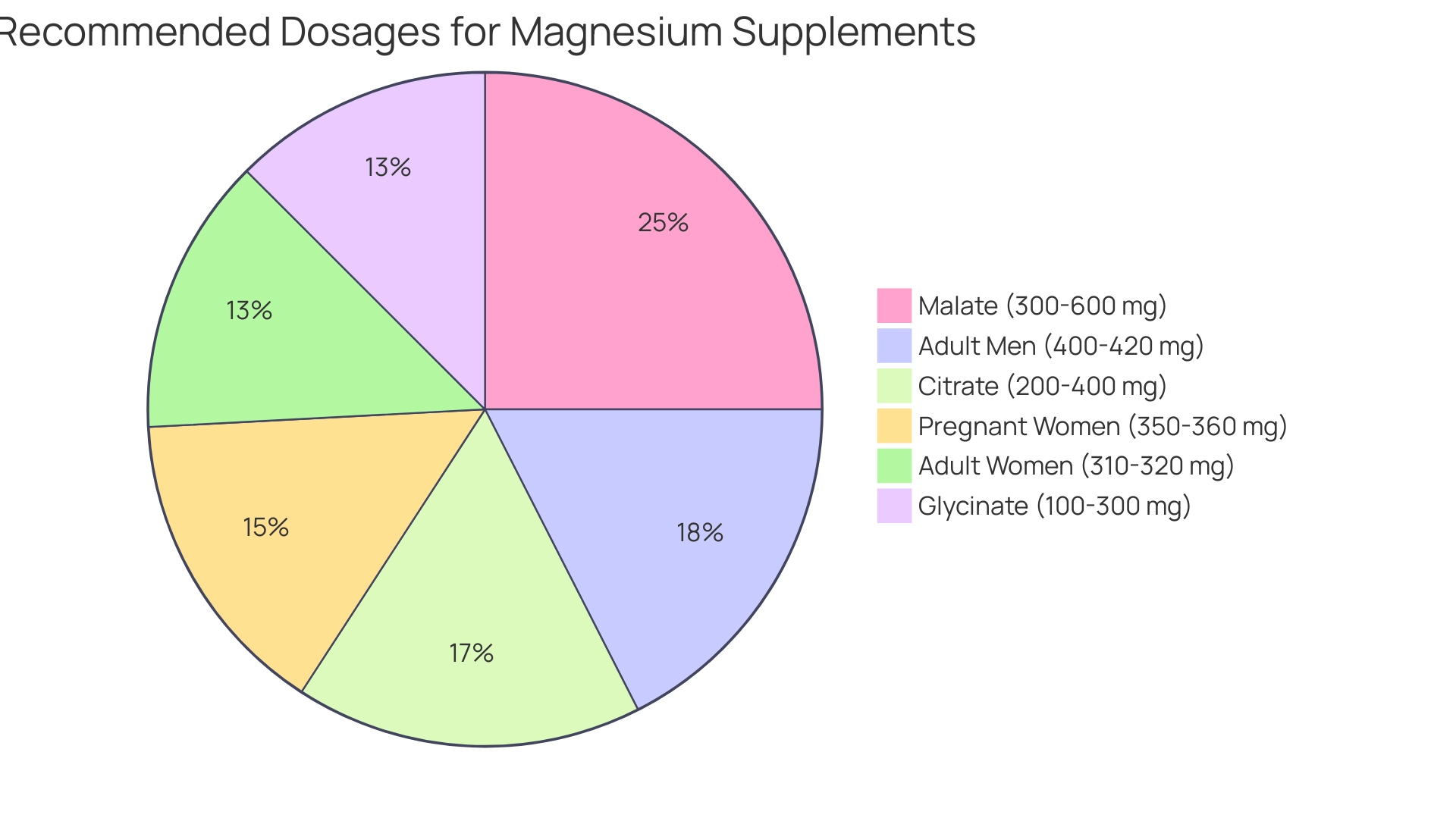
3. Dosage Recommendations for Magnesium Supplements
- Adult men: 400-420 mg per day
- Adult women: 310-320 mg per day
- Pregnant women: 350-360 mg per day
- Citrate: 200-400 mg daily
- Glycinate: 100-300 mg daily
- Malate: 300-600 mg daily
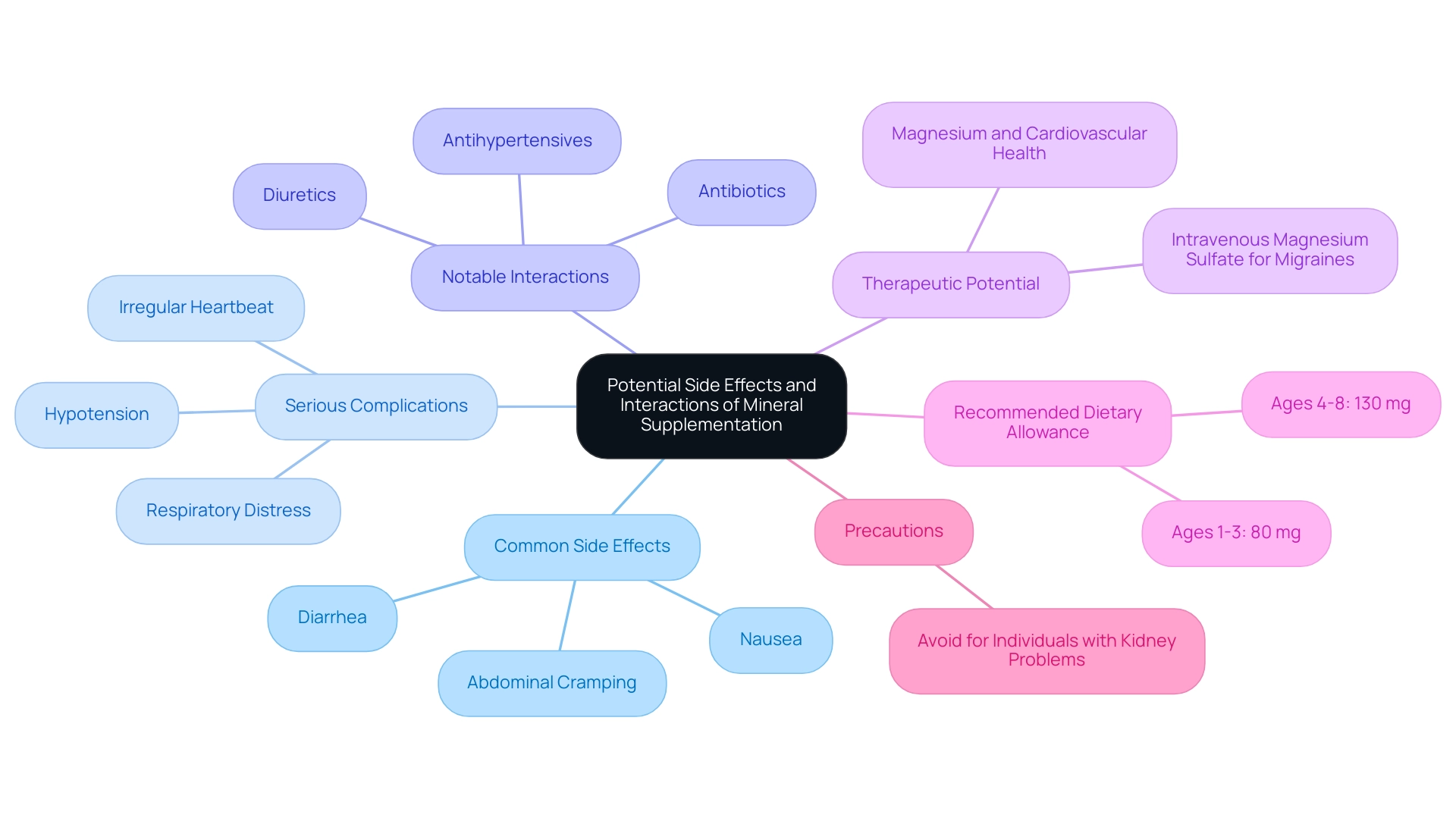
4. Potential Side Effects and Interactions
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Abdominal cramping
- Irregular heartbeat
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Respiratory distress
- Diuretics: These medications can increase the excretion of this mineral, potentially leading to deficiency.
- Antibiotics: Certain classes may exhibit reduced efficacy when taken concurrently with supplements of this mineral.
- Antihypertensives: The combination may result in additive effects, risking excessively low blood pressure.
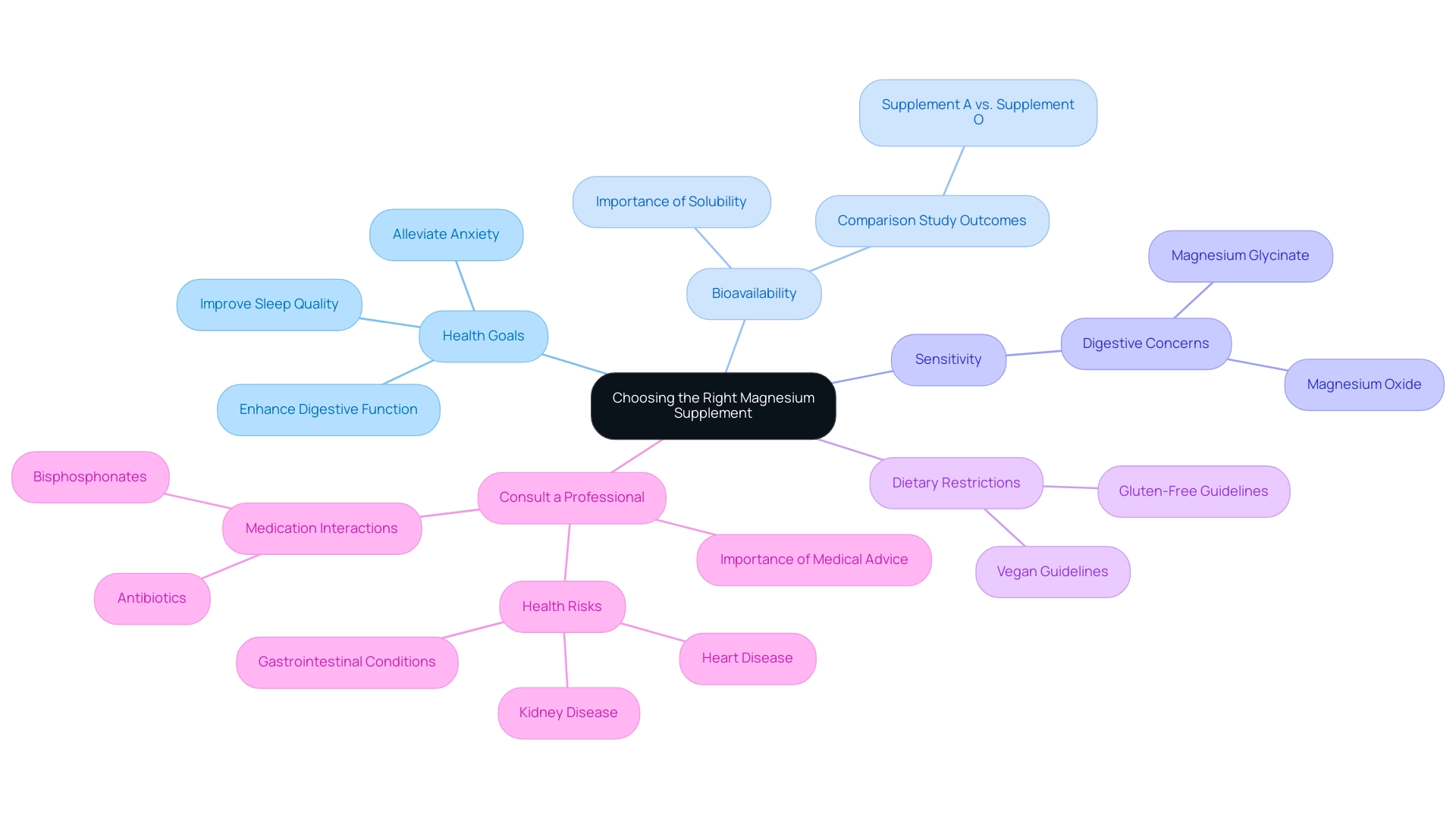
5. Choosing the Right Magnesium Supplement for Your Needs
-
Health Goals: Clearly define your health objectives. Whether aiming to improve sleep quality, alleviate anxiety, or enhance digestive function, different types of magnesium may provide specific benefits suited to these concerns.
- Bioavailability: Opt for forms of this mineral with higher bioavailability, such as Citrate or Glycinate, especially if rapid absorption is essential. A recent comparison study, Phase B: Comparison of Products A and O, highlighted significant differences in serum mineral levels based on the solubility of the products. This study concluded that bioavailability is more crucial than the total elemental magnesium content, emphasizing that a product containing 1,000 mg of its magnesium compound may only contain 50 mg of magnesium itself.
- Sensitivity: Take into account any sensitivities or digestive concerns. For instance, individuals with sensitive stomachs might find Magnesium Glycinate more tolerable than Magnesium Oxide, which can cause gastrointestinal discomfort.
-
Dietary Restrictions: Ensure the chosen product aligns with any dietary restrictions, such as vegan or gluten-free guidelines, to maintain overall dietary integrity.
-
Consult a Professional: Always engage with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation. Krista Elkins, BA, RN, CRFN, NRP, CCP-C, advises,Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on the site.
This step is essential for customizing the product selection to your particular wellness requirements and circumstances. Additionally, be aware that certain medications, like bisphosphonates and antibiotics, can interact with these supplements, affecting absorption.
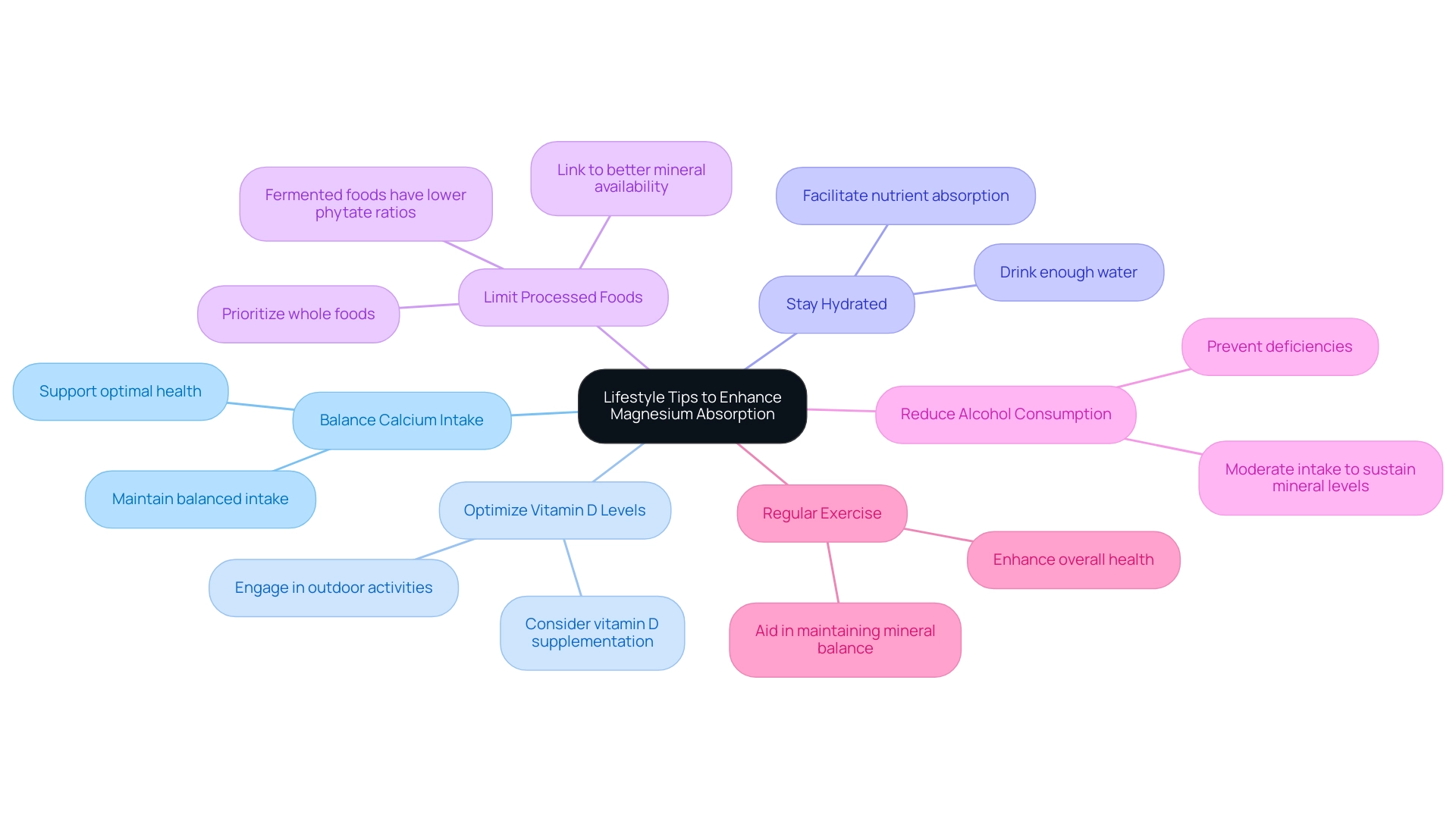
6. Lifestyle Tips to Enhance Magnesium Absorption
-
Balance Calcium Intake: An excessive intake of calcium can hinder the absorption of another essential mineral. It's crucial to maintain a balanced intake of both minerals to support optimal health.
-
Optimize Vitamin D Levels: Adequate vitamin D is crucial for enhancing the absorption of minerals. Engaging in outdoor activities to soak up sunlight or considering vitamin D supplementation can be beneficial.
-
Stay Hydrated: Sufficient hydration plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption, including minerals. Ensure to drink enough water throughout the day to facilitate this process.
-
Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods typically have reduced amounts of essential minerals. Prioritize a diet rich in whole foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains to enhance mineral intake. As noted in the OBENUTIC-Mineral study, diets emphasizing raw and minimally processed foods are linked to better mineral availability, further supporting this approach. Additionally, Bhavana Vishwas Mohite highlights that the ratios of phytate to Zn, Fe, Ca, and Mg in fermented products are lower than in raw foods, indicating increased mineral availability from fermented foods.
-
Reduce Alcohol Consumption: High alcohol intake can contribute to depletion of essential minerals. Moderating alcohol intake can help sustain healthy mineral levels and prevent deficiencies.
-
Regular Exercise: Engaging in consistent physical activity not only enhances overall health but also aids in maintaining mineral balance, thus improving the body’s ability to utilize this essential nutrient effectively.