Introduction
Introduction
Introduction
Nasal breathing, often overlooked in discussions about respiratory health, plays a crucial role in enhancing overall well-being. This natural method of inhaling and exhaling through the nose not only filters and conditions the air but also stimulates the production of nitric oxide, which is vital for oxygen uptake and cardiovascular function.
Research reveals a compelling link between nasal breathing and:
- Improved energy levels
- Reduced anxiety
- Better sleep quality
As individuals increasingly recognize the physiological advantages of this practice, it becomes essential to explore the techniques that can enhance nasal breathing and its impact on sleep disorders. Understanding the connection between nasal breathing and health can pave the way for effective management strategies, ultimately leading to a healthier, more restorative sleep and a better quality of life.
1. Understanding Nasal Breathing: The Basics and Benefits
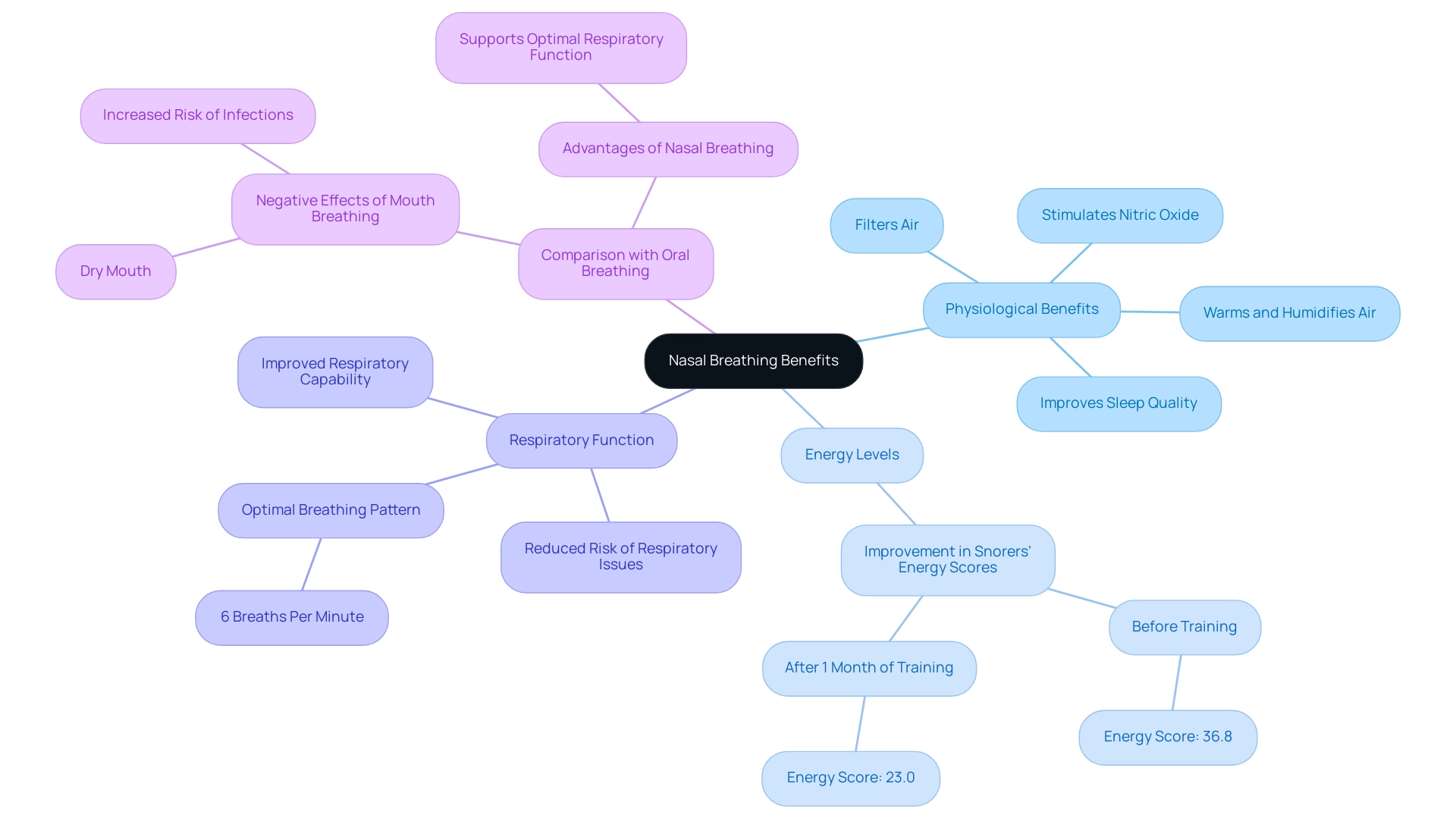
Nasal respiration, defined by the intake and release of air through the nose, is explored in The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep, highlighting various physiological benefits that are crucial for sustaining optimal well-being. This method effectively filters, warms, and humidifies the air, ensuring that only clean and appropriately conditioned air reaches the lungs. According to The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep, one of the essential advantages of inhaling through the nose is its stimulation of nitric oxide production, a crucial molecule that improves oxygen absorption and supports cardiovascular wellness.
Research suggests that individuals who inhale through their noses can experience a notable enhancement in their energy levels; for example, a study discovered that the energy dimension score for snorers dropped significantly from 36.8 to 23.0 after just one month of training in nose inhalation. Moreover, sustaining a respiration pattern of approximately 6 breaths per minute might alleviate anxiety and enhance blood pressure, which aligns with The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep. In stark contrast, oral respiration can lead to a range of issues, including dry mouth and an increased risk of infections, while inhaling through the nose supports optimal respiratory function.
A case study titled Nasal vs. Oral Breathing in Exercise highlights the prevalence of mouth inhalation among children and its potential negative health effects, emphasizing the advantages of respiratory function through the nose, such as improved respiratory capability and reduced risk of respiratory issues. John Doe, a researcher, notes, "This study does not show that any of the respiration regimen is more effective; however, it also points out that the most commonly used respiration regimens (NM, MM) are not more effective than Ann regimen." A thorough comprehension of these principles is crucial for understanding the significant advantages highlighted in the science of nasal breathing and why it improves sleep quality and general wellness.
2. The Connection Between Nasal Breathing and Sleep Quality
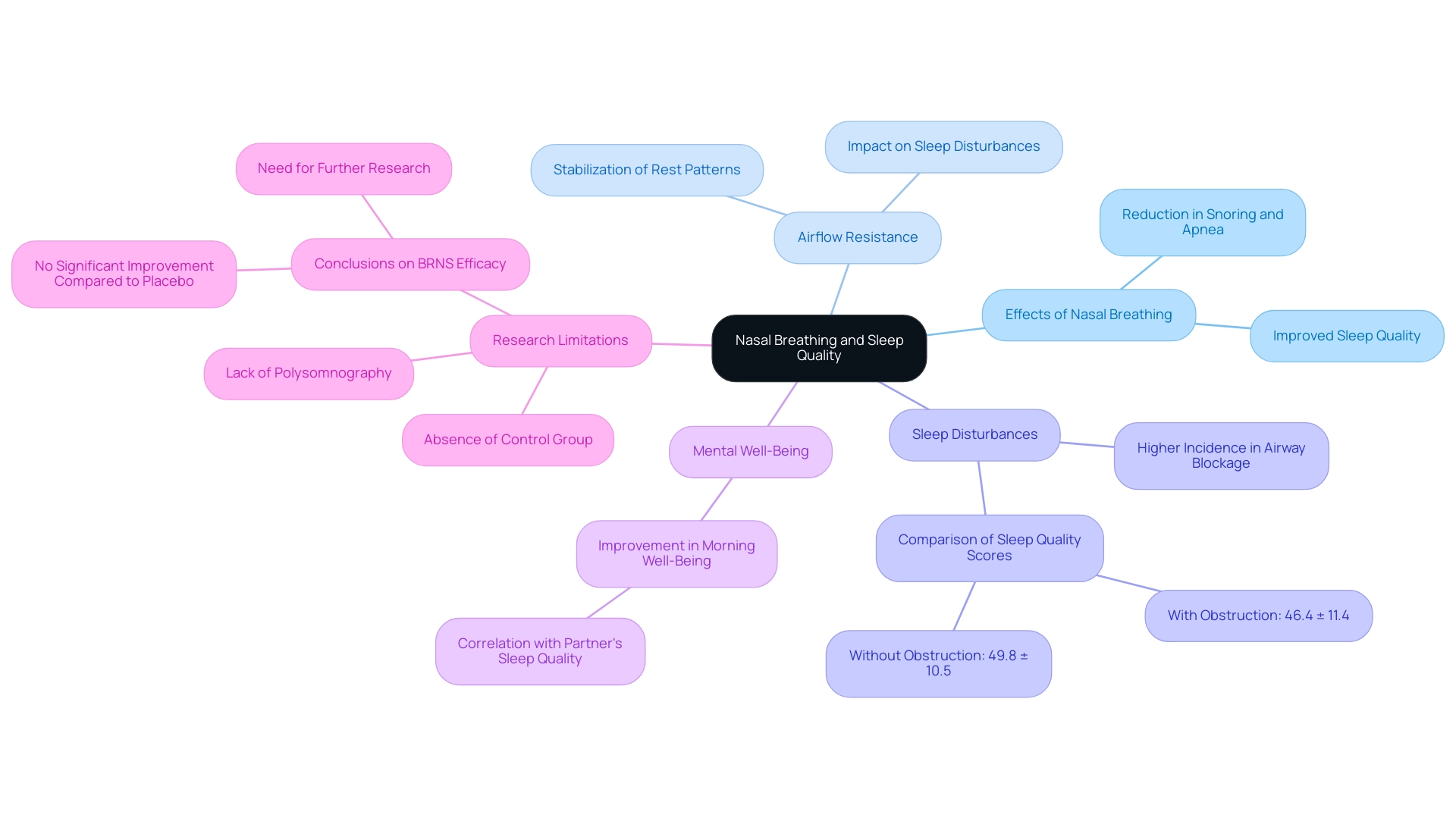
Studies have consistently emphasized The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep, highlighting the strong connection between breathing through the nose and improved rest quality. Individuals who breathe through their noses often experience increased airflow resistance, a factor known to help stabilize rest patterns and diminish occurrences of snoring and apnea. Significantly, data shows that patients with airway blockage experience a considerably higher proportion of sleep-related disturbances compared to those without such blockages.
Moreover, research indicates that individuals who practice the science of nasal breathing and why it improves sleep at night experience fewer interruptions, leading to a more rejuvenating rest. This practice not only promotes deeper stages of sleep, essential for physical recovery and cognitive clarity, but is also supported by The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep, which links it to an improved mental quality of life. For instance, one study noted a marked difference in mental well-being between groups with and without nocturnal airway obstruction (46.4 ± 11.4 vs. 49.8 ± 10.5, p < 0.001).
Dr. Steen Löth, an MD, notes that the female partners who shared a bed experienced a decrease in disturbances during rest that corresponded with an enhancement in their own rest and sense of well-being in the morning. Despite these promising findings, it is important to recognize the limitations of the current research, such as the absence of polysomnography for insomnia evaluation and the lack of a control group of healthy individuals. Furthermore, the case study named 'Conclusions on BRNS Efficacy' suggests that although techniques involving the nose were assessed, they did not notably enhance subjective assessments of rest quality and congestion compared to placebo over 14 nights of use.
These constraints emphasize the necessity for additional investigation into the connection between respiratory ventilation and rest quality, particularly in the context of The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep, especially in alleviating the negative impacts linked to sleep apnea and other respiratory issues.
3. Techniques to Enhance Nasal Breathing for Better Sleep
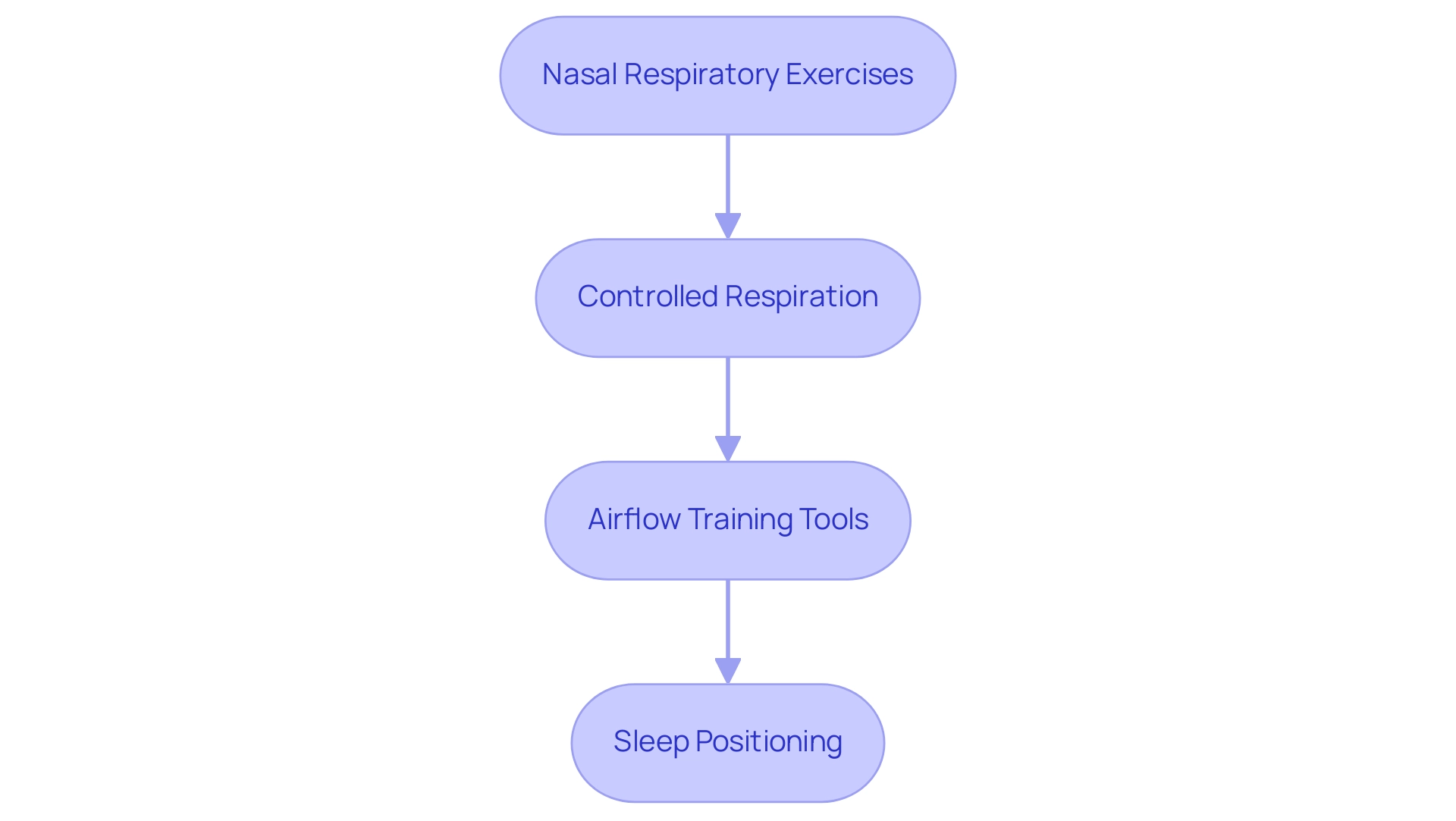
To improve airflow through the nose for better sleep quality, consider incorporating the following techniques into your daily routine:
- Nasal Respiratory Exercises: Engage in deep inhalation exercises throughout the day, concentrating on inhaling and exhaling solely through the nose. This practice helps prepare your respiratory system for breathing through the nose.
- Controlled Respiration: Implement controlled respiration techniques such as the Buteyko method, which emphasizes slow and gentle inhalation through the nose. Research has indicated this approach can greatly improve respiratory efficiency, especially in individuals facing exercise-induced shortness of breath, as evidenced in the Breathe-HF trial sub-study, which concentrated on enhancing exercise respiratory efficiency through slow inhalation training.
- Airflow Training Tools: Use passage expanders or inhalation strips created to maintain the airways open while sleeping. These devices can relieve airway blockage, enabling a more regular airflow pattern during the night.
- Sleep Positioning: Choose side sleeping rather than back sleeping to encourage respiratory function and reduce the risk of airway obstruction. This arrangement not only promotes improved airflow but also enhances overall rest quality.
Integrating these methods into your evening routine can enhance respiratory function during slumber, as explained in The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep, ultimately aiding better recuperation. Furthermore, research indicates that the effect size of breathwork on stress ranges from -0.27 to -0.39, highlighting its potential benefits. As noted by Heber et al., respiratory techniques not only impact stress but also show moderate effects on anxiety and depression, making nasal inhalation a valuable practice for enhancing overall well-being.
4. Nasal Breathing as a Solution for Sleep Disorders
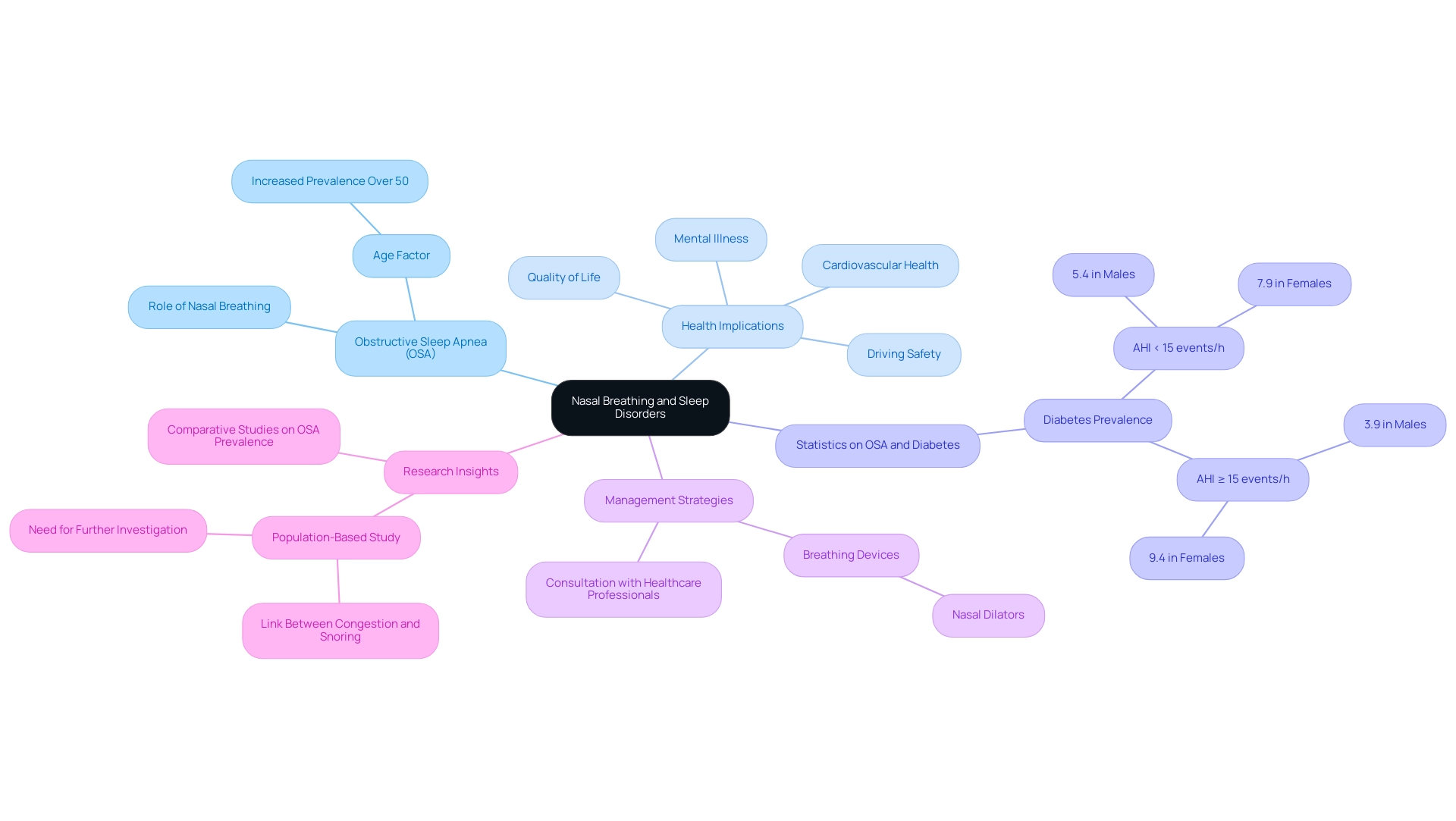
Nasal breathing plays a crucial role in managing disorders of rest, which is supported by The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep, especially in cases of obstructive apnea (OSA). The science of nasal breathing and why it improves sleep facilitates improved airflow, reducing the risk of airway collapse, which can significantly decrease the frequency and severity of apnea episodes. Evidence suggests that the prevalence of OSA increases with age, particularly among individuals over 50 years old, highlighting the necessity for effective management strategies.
Furthermore, diabetes prevalence is notably higher among individuals with OSA, with rates of:
- 5.4% in males and 7.9% in females with an apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) of less than 15 events per hour
- 3.9% in males and 9.4% in females with AHI of 15 events per hour or greater
This underscores the serious health implications associated with OSA. Devices such as breathing dilators play a vital role in The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep by widening the nostrils and enhancing airflow, thus promoting better sleep quality.
A population-based study involving 1,001 men demonstrated a link between congestion and habitual snoring, emphasizing the importance of addressing blockage in the context of sleep-disordered respiration. While prior research indicated limited support for airway blockage worsening sleep-related disorders, these findings suggest a need for further investigation into its impact. Consulting with healthcare professionals is essential for integrating respiratory techniques into personalized treatment plans, as their expertise can provide substantial relief from symptoms and enhance overall sleep hygiene.
According to Jennifer M. Slowik,
, underscoring the importance of addressing this condition through effective management strategies. Recent studies also aim to compare current OSA prevalence with previous estimates, highlighting the evolving understanding of this condition.
1OSA has significant implications for cardiovascular well-being, mental illness, quality of life, and driving safety
5. Long-Term Health Benefits of Nasal Breathing for Sleep
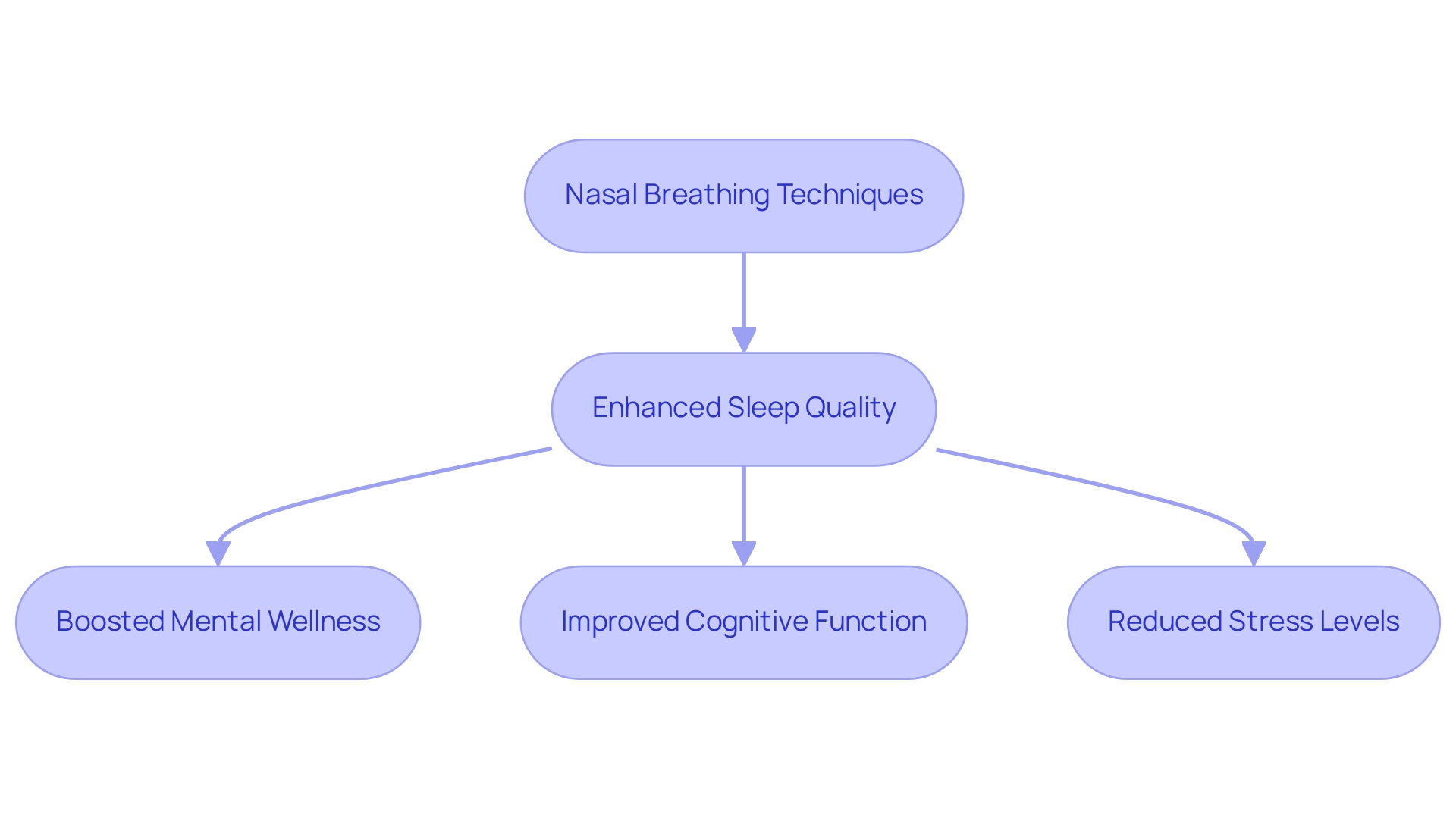
Adopting nasal inhalation techniques can result in a range of long-term wellness benefits. One of the primary advantages, highlighted in The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep, is enhanced sleep quality, which subsequently boosts mental wellness and cognitive function, contributing to overall well-being. As Niraj Naik, the creator of Soma Breath, notes, "Soma Breath is a system of respiration developed based on traditional yoga techniques," emphasizing the significance of these time-honored practices.
Research shows that sustaining a respiration rate of around six breaths per minute—recommended to alleviate anxiety and enhance blood pressure—can greatly improve overall well-being. Additionally, a case study titled Resting Respiratory Rate, Brachial Blood Pressure, and Hemodynamics found that mean and diastolic blood pressure were significantly lower during airway respiration, suggesting a physiological benefit. Moreover, individuals who incorporate The Science of Nasal Breathing and Why It Improves Sleep into their sleep practices may encounter reduced stress levels and enhanced emotional well-being.
Overall, by understanding and integrating these breathing techniques into daily routines, individuals can substantially enhance their health and quality of life.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Nasal breathing is a powerful yet often underestimated practice that offers significant physiological benefits, particularly in enhancing overall health and sleep quality. By filtering and conditioning the air, stimulating nitric oxide production, and stabilizing sleep patterns, nasal breathing stands out as a vital component for those seeking improved energy levels, reduced anxiety, and better rest. The stark contrast between nasal and mouth breathing underscores the importance of adopting nasal breathing techniques to mitigate various health issues, including sleep disorders.
The evidence linking nasal breathing to improved sleep quality is compelling. Individuals who engage in nasal breathing experience fewer sleep disturbances and deeper stages of sleep, which are essential for physical recovery and cognitive clarity. While the research highlights promising outcomes, it also reveals the need for further exploration to fully understand the nuances of this relationship, especially concerning conditions like obstructive sleep apnea.
Implementing techniques to enhance nasal breathing, such as specific exercises, controlled breathing methods, and proper sleep positioning, can lead to substantial improvements in sleep and overall well-being. By integrating these practices into daily routines, individuals not only support better sleep hygiene but also pave the way for long-term health benefits, including reduced stress and improved cardiovascular function. Embracing nasal breathing is more than just a trend; it is a proactive step towards achieving optimal health and a higher quality of life.



















