Introduction
In the realm of child development, speech delays pose a significant challenge that can impact a child's ability to communicate effectively. Recognizing the early signs of speech delays is crucial for caregivers, as timely intervention can lead to improved outcomes. This article delves into the indicators of speech delay, the underlying causes, and the importance of proactive diagnosis and treatment.
It also highlights the vital role of speech therapy and offers practical strategies for supporting speech development at home. Understanding these elements empowers caregivers to take informed actions that can foster their child's communicative abilities and overall development.
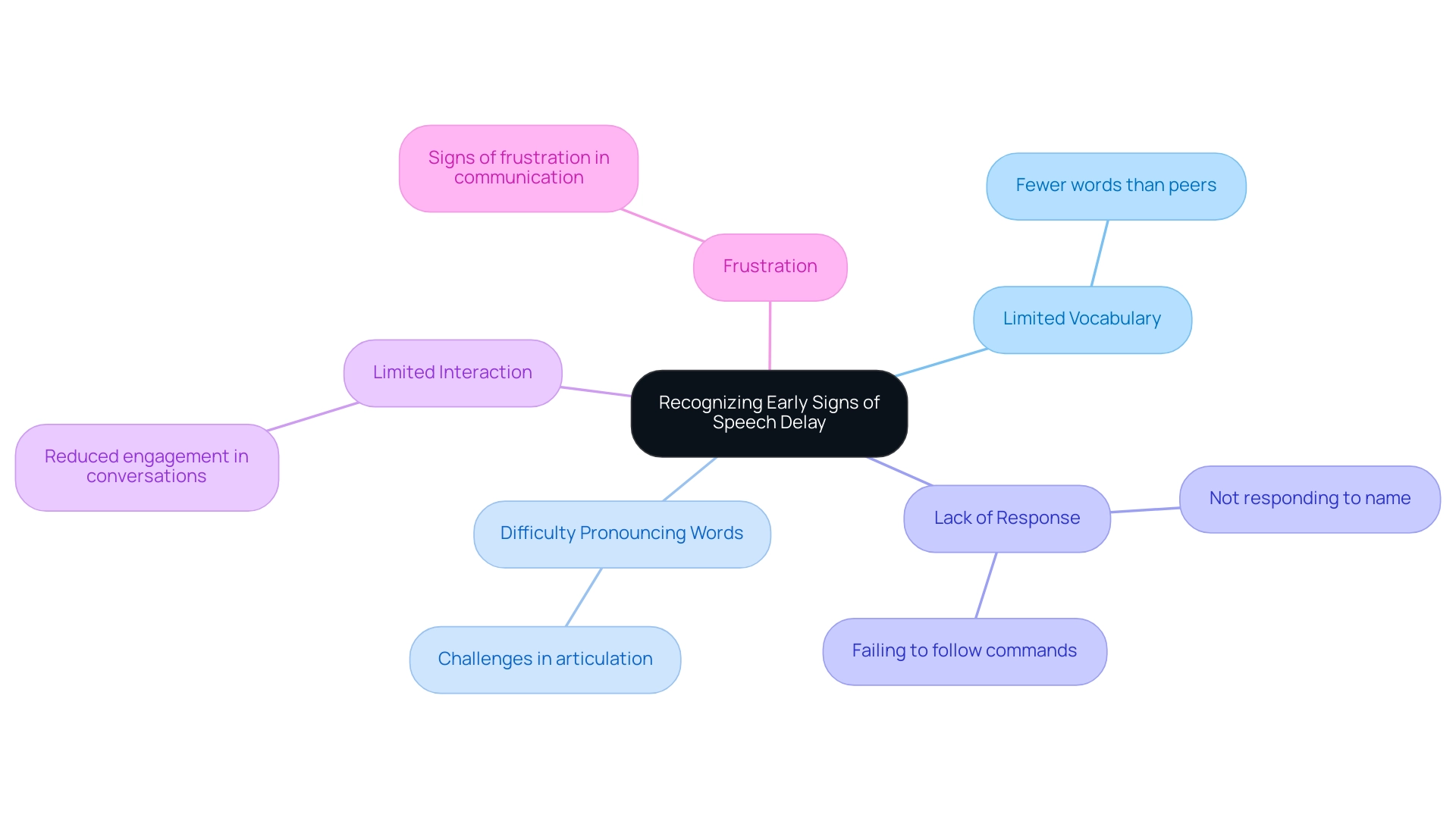
1. Recognizing Early Signs of Speech Delay
Caregivers should be vigilant in observing several key indicators that may suggest a speech delay in youngsters. These indicators include:
-
Limited Vocabulary: A young individual exhibiting fewer words than peers of the same age.
-
Difficulty Pronouncing Words: Challenges in articulating sounds or words clearly, which can hinder effective communication.
-
Lack of Response: Not responding to their name or failing to follow simple commands, indicating potential auditory processing issues.
-
Limited Interaction: Reduced engagement in conversations or play with peers, which is essential for developing social skills.
-
Frustration: Displaying signs of frustration when attempting to communicate, often stemming from an inability to express needs or feelings.
Not recognizing these signs early is crucial, as timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Research indicates that 1.4% of U.S. youth experience a voice disorder lasting a week or longer, emphasizing the importance of awareness among caregivers. Moreover, environmental risk factors, such as inadequate stimulation, have been shown to correlate with speech-language delay. A study analyzing these factors found that inadequate stimulation was a statistically significant risk factor, highlighting the need for caregivers to provide enriching environments.
Furthermore, it is important to note that the limitations of this study include a small, hospital-based sample, which could introduce bias in the findings. By recognizing these indicators swiftly, caregivers can promote effective support and treatment for their offspring's communication progress, including speech delay treatment. Furthermore, conditions such as spasmodic dysphonia, which can influence voice quality, remind us of the wider framework of voice disorders and their potential effect on communication growth.
2. Understanding the Causes of Speech Delay
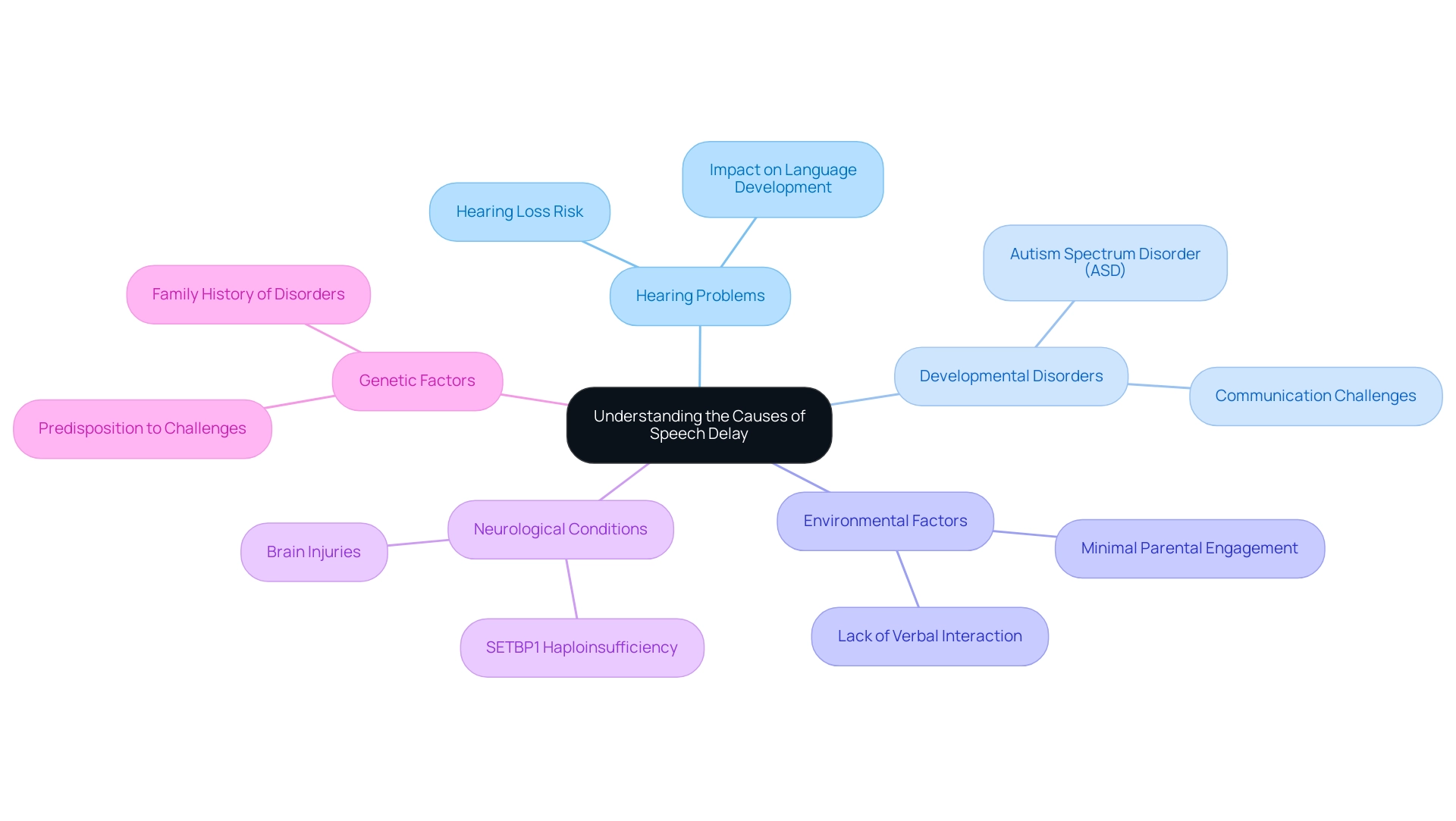
Speech delays in young ones can stem from numerous underlying factors, each contributing significantly to the progress of communication abilities. Key contributors include:
- Hearing Problems: Reduced hearing is one of the most crucial factors affecting a young person's language development. Research indicates that children with hearing loss are at a heightened risk for delayed communication and language skills, as they may struggle to hear and process sounds accurately.
- Developmental Disorders: Conditions such as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often lead to communication challenges. Children with ASD may have difficulty with verbal expression and social interactions, which can contribute to delays in communication.
- Environmental Factors: The home environment significantly influences language development. A lack of verbal interaction, such as minimal parental engagement or exposure to rich language experiences, can hinder a child's ability to develop adequate communication skills.
- Neurological Conditions: Neurological disorders, including brain injuries or conditions like SETBP1 haploinsufficiency, can severely affect communication abilities. Recent studies have indicated that individuals with such neurological impairments often encounter language delays, emphasizing the significance of timely intervention.
- Genetic Factors: A family background of communication or language disorders may predispose youngsters to similar challenges. Understanding these genetic influences can better inform caregivers about potential risks.
Statistics indicate that early intervention is strongly advised as a form of speech delay treatment to enhance a young one's communication growth potential, highlighting the necessity for prompt action. Additionally, many early years development programs exclude individuals with developmental disabilities, creating a significant gap in necessary services that can lead to further challenges in speech development.
As noted by Maura R McLaughlin, there is good evidence that speech delay treatment, particularly through speech-language therapy, is helpful for youngsters with expressive language disorder. Furthermore, a case study titled "Importance of Early Intervention" illustrates that speech delay treatment and addressing developmental concerns early is crucial to prevent escalation into more severe issues. Proactive early intervention programs facilitate better outcomes, assisting young individuals in reaching their full potential by utilizing developmental screening tools.
Recognizing these causes enables caregivers and educators to take proactive steps toward effective intervention, ensuring that young individuals receive the necessary support to thrive.
3. Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Speech Delay
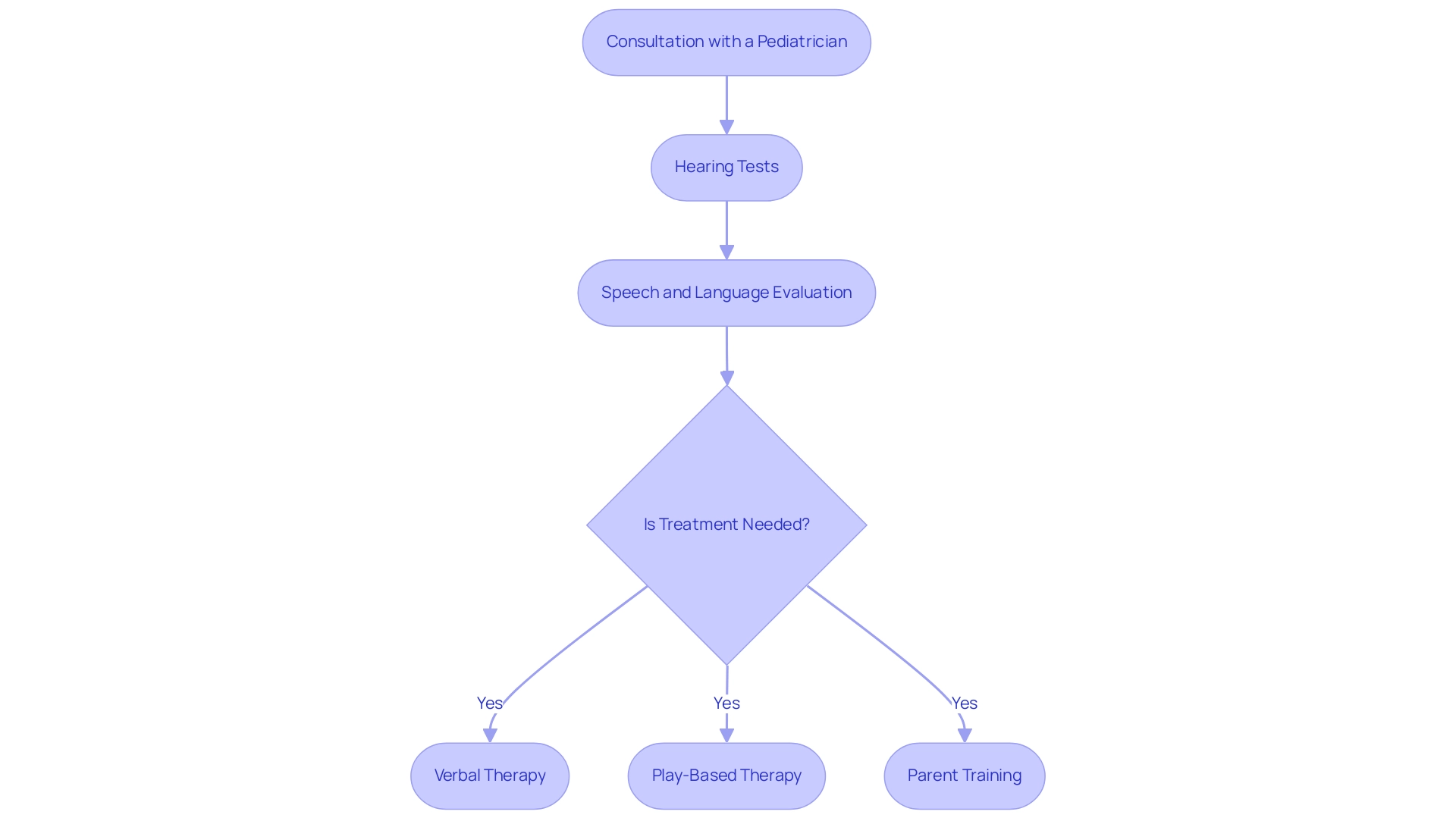
The assessment of language development issues in youngsters generally occurs through a systematic procedure intended to guarantee thorough evaluation and efficient early support. Key steps include:
-
Consultation with a Pediatrician: The initial assessment often begins with a healthcare provider, who evaluates the individual's overall development and development history.
-
Hearing Tests: Experts may perform hearing evaluations to eliminate auditory problems that might lead to communication challenges.
-
Speech and Language Evaluation: A speech-language pathologist (SLP) will conduct a thorough assessment to evaluate the individual's communication skills, identifying specific areas of concern. The available treatment options for addressing communication delays, including speech delay treatment, are varied and should be customized to the unique needs of the individual. These include:
- Verbal Therapy: Targeted sessions designed to enhance verbal skills, utilizing evidence-based techniques to promote effective communication.
- Play-Based Therapy: This approach uses play as an engaging medium to foster communication skills, making learning both effective and enjoyable.
- Parent Training: Educating parents on strategies and techniques to support their offspring's language development at home is crucial for reinforcing therapy outcomes.
Recent data shows that speech-language issues were identified in 2.53% of youngsters visiting pediatric outpatient departments, a statistic that highlights the necessity for prompt interventions. With pediatric communication challenges in youngsters aged 12 and younger more than doubling since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, early diagnosis and customized speech delay treatment are essential. As pointed out by Sujata V Kanhere, timely recognition of setbacks by primary care physicians can enable early intervention and diminish disability. By identifying the indicators of communication issues early, parents and caregivers can greatly boost a youngster's potential for progress, ultimately resulting in improved developmental results. A case study named 'Early Intervention for Communication Issues' demonstrates how addressing communication challenges through speech delay treatment can greatly impact a young person's developmental path. This case study highlights the significance of early assistance and recognizes the indicators of communication issues in young ones, reinforcing the essential need for prompt intervention. For further inquiries, readers can reach out via email at nidcdinfo@nidcd.nih.gov.
In 2024, the newest treatment alternatives for communication challenges, including speech delay treatment, feature innovative methods such as teletherapy and tailored language programs that adjust to a young person's specific needs, ensuring that interventions are both effective and accessible.
4. The Role of Speech Therapy in Treatment
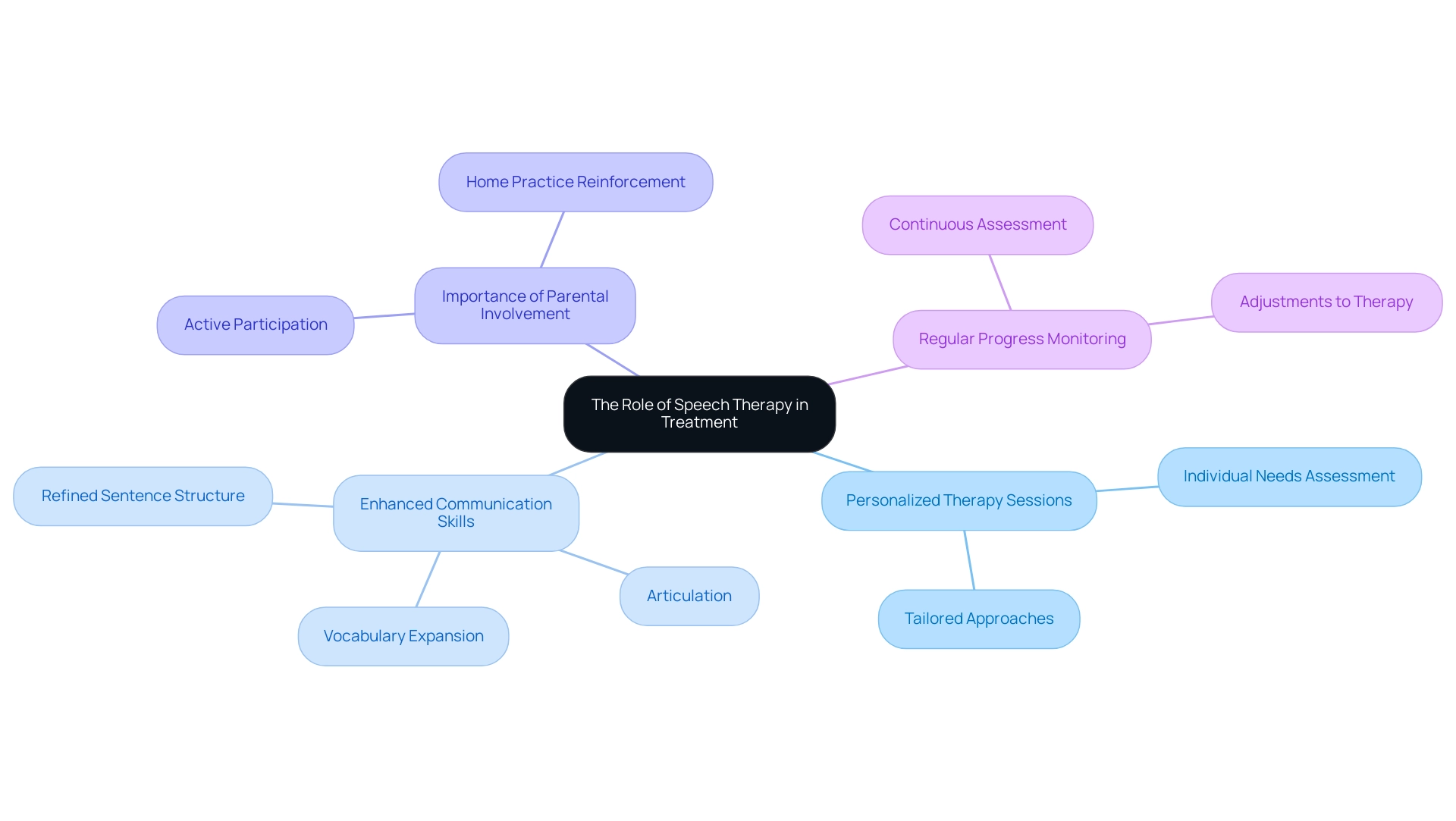
Speech therapy plays an essential role in providing effective speech delay treatment, offering a range of significant benefits that can enhance an individual's communicative abilities. Key components include:
-
Personalized Therapy Sessions: These sessions are specifically tailored to meet the individual needs and challenges of each young person, ensuring that the therapy is relevant and effective.
-
Enhanced Communication Skills: The focus of therapy is on improving articulation, expanding vocabulary, and refining sentence structure, which collectively contribute to more effective communication.
-
Importance of Parental Involvement: Engaging parents and caregivers in the therapy process is crucial. Their active participation reinforces the skills learned during therapy and facilitates practice at home, leading to better outcomes.
-
Regular Progress Monitoring: Continuous assessment enables therapists to track a young person's development and make necessary adjustments to the therapy approach, optimizing the effectiveness of the treatment. Research has demonstrated that early intervention is essential; for instance, developmental language disorder impacts roughly 7% of youth, equating to 1 in 14. Moreover, almost 180,000 Americans develop aphasia annually, emphasizing the significance of tackling communication issues early.
Additionally, statistics indicate that 1.4% of U.S. youths have a voice disorder lasting for a week or longer, underscoring the range of speech-related challenges faced by young individuals. Effective communication therapy, including speech delay treatment, not only nurtures communication skills but also fosters academic success by enhancing reading comprehension, vocabulary skills, and listening abilities. With consistent therapy sessions, individuals can develop the skills necessary to communicate effectively, paving the way for future success.
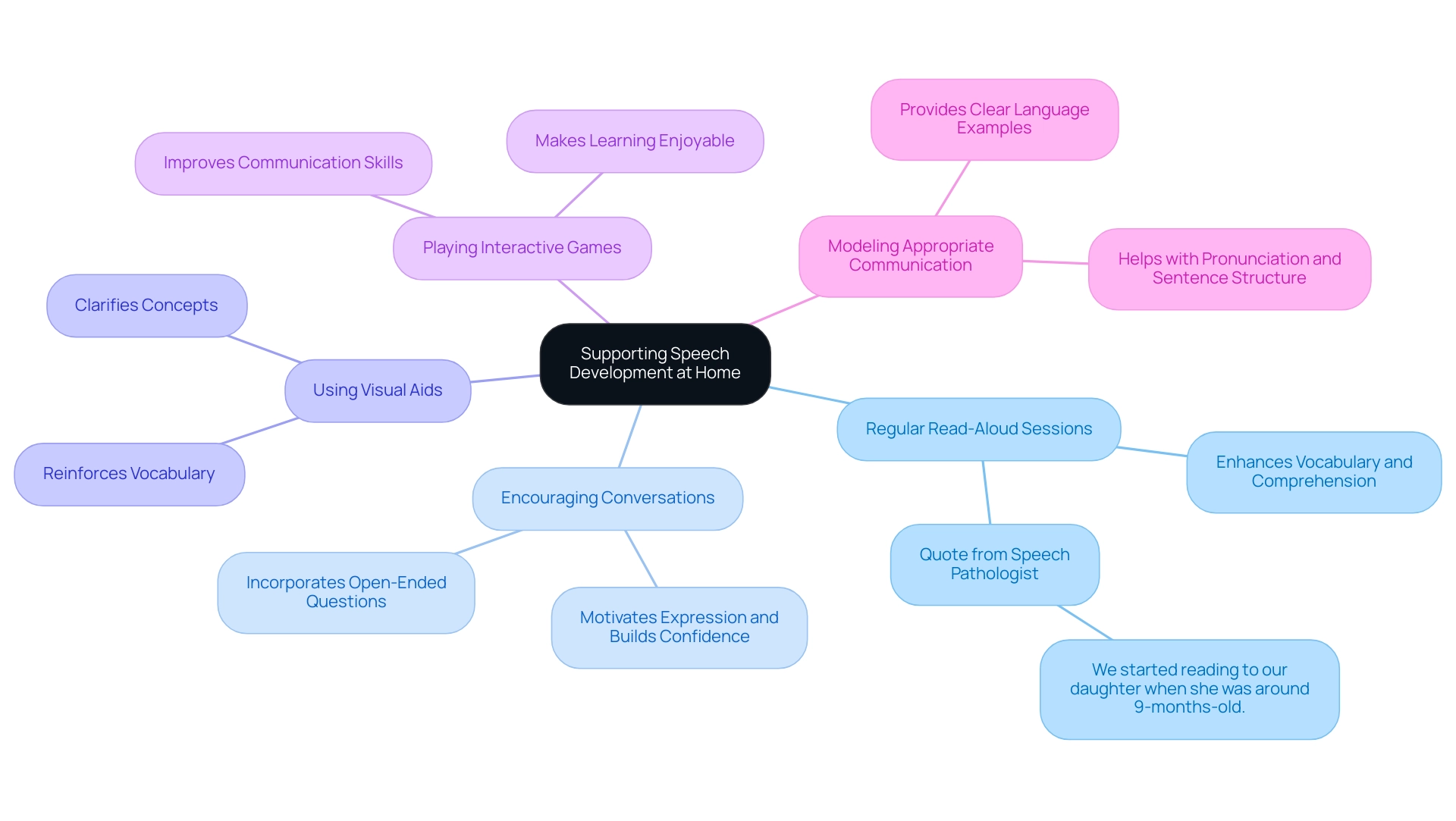
5. Practical Strategies for Supporting Speech Development at Home
Caregivers can adopt a multitude of strategies at home to foster their child's communication development effectively. These methods include:
-
Regular Read-Aloud Sessions: Engaging in frequent reading sessions significantly enhances vocabulary and comprehension.An unnamed language pathologist emphasizes the importance of this practice, noting,We started reading to our daughter when she was around 9-months-old, and we read as many books as possible until she finished her nighttime bottle.
This consistent exposure to language is critical in establishing a strong foundation for verbal communication. -
Encouraging Conversations: Daily dialogues that incorporate open-ended questions motivate young individuals to express themselves and develop their conversational skills. This approach not only nurtures language but also builds confidence in communication.
-
Using Visual Aids: Incorporating pictures or tangible objects during discussions can reinforce vocabulary and clarify concepts for young learners. Visual aids serve as effective tools for making abstract ideas more concrete.
-
Playing Interactive Games: Involving kids in games that require verbal interaction not only makes learning enjoyable but also significantly improves communication skills. Recent studies indicate that such interactive play can have a substantial impact on a young person's linguistic development.
-
Modeling Appropriate Communication: Caregivers should consistently use clear and accurate language, providing a model for youngsters to imitate. This practice is essential in helping young learners acquire proper pronunciation and sentence structure.
In addition to these strategies, it is essential to recognize the broader context of early intervention.
For example, the identification of postnatal depression, as established through the 10-item Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale, emphasizes the necessity of prompt assistance for caregivers, which can ultimately enhance the infant's language skills. Furthermore, a case study of an early intervention therapist working with a bilingual 2-year-old girl illustrates the effectiveness of reading in improving language skills. After adding reading to her routine, the young one started to express herself in short phrases by the age of three, showcasing considerable language progress through regular exposure to books.
Additionally, surveys indicate that about half of adolescents and young adults with criminal records have reading difficulties, underscoring the long-term implications of fostering literacy from a young age. Implementing these strategies creates a rich and stimulating environment that is conducive to speech delay treatment, ultimately leading to greater language advancement by 24 months, as supported by current research in child development.
Conclusion
Recognizing and addressing speech delays in children is crucial for their communication development and overall well-being. Early signs such as:
- Limited vocabulary
- Difficulty in pronunciation
- Lack of response to social cues
can indicate the need for intervention. Caregivers must remain vigilant, as timely recognition can lead to significant improvements in a child’s speech capabilities.
Understanding the underlying causes of speech delays—ranging from hearing issues to environmental factors—is essential in formulating an effective response. It is imperative that caregivers consult with healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive evaluations and tailored treatment plans. Speech therapy, in particular, offers a structured approach to improving communication skills, with personalized sessions and parental involvement enhancing the effectiveness of the therapy.
Implementing practical strategies at home can further support speech development. Regular reading, encouraging conversations, and using visual aids are just a few methods that can create a rich linguistic environment for children. By actively engaging in their child’s speech development and seeking timely intervention when necessary, caregivers can significantly enhance their child’s communicative abilities, setting the stage for future success.
In conclusion, early intervention and proactive support are key to fostering effective communication skills in children with speech delays. By being informed and involved, caregivers can play a pivotal role in their child's developmental journey, ensuring they reach their full potential.




















