Introduction
Snoring is a common yet often overlooked issue that can disrupt not only the sleep of the individual but also that of their partners. Understanding the various factors that contribute to this phenomenon, such as:
- Anatomical issues
- Lifestyle choices
- Underlying health conditions
is essential for addressing the problem effectively. From the implications of obesity to the socio-economic factors influencing habitual snoring in children, recognizing these elements is crucial for developing appropriate remedies. This article explores the causes of snoring, practical lifestyle changes, and targeted exercises to strengthen throat muscles, while also emphasizing the importance of maintaining a clean sleeping environment. Additionally, it highlights the significance of consulting healthcare professionals when snoring persists, ensuring a comprehensive approach to improving sleep quality and overall health.
1. Understanding Snoring: Causes and Implications
Snoring happens when airflow through the mouth and nose is partially blocked during rest. Multiple factors play a role in this phenomenon, including:
- Nasal congestion
- Obesity
- Alcohol consumption
- Position during rest
- Advancing age
Comprehending these factors is essential, as they can significantly influence not only the quality of rest for the individual but also for their partners.
Chronic noise during sleep can escalate into more serious health issues, such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which has been linked to daytime fatigue and an increased risk of cardiovascular problems. A study conducted by Davies et al. in 1992 highlighted the importance of clinical features like neck circumference in diagnosing OSA syndrome.
Furthermore, recent statistics indicate that participants in the highest PGS decile have approximately double the odds of reporting recent loud breathing compared to those in the lowest decile. The American Academy of Pediatrics highlights the significance of screening for noisy breathing in children, as it may indicate underlying issues like tonsil or adenoid enlargement or be a symptom of sleep apnea. Additionally, research on intra-oral variables related to OSA risk demonstrated that only tongue indentations and tonsil size were statistically significant predictors of this condition, confirming the influence of upper airway anatomy on noisy breathing.
This study's findings emphasize the need for individuals to consider anatomical factors when addressing issues related to sleep noise. Moreover, factors such as a mother's lower level of education and lower monthly income have been linked to a child's regular nocturnal sounds, highlighting the socio-economic dimensions of this health concern. By identifying and tackling these fundamental issues, individuals can more effectively assess the possible solutions and lifestyle changes to decrease noise during sleep, including exploring how can I stop snoring naturally to improve overall sleep quality.
2. Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Changes to Stop Snoring
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body weight, particularly around the neck, can significantly obstruct the airway, leading to noisy breathing. A study conducted at Nehru Hospital in Gorakhpur from April 2010 to May 2011, involving 400 apparently healthy adult individuals, highlighted that setting Body Mass Index (BMI) targets at 25 Kg/m² in weight reduction programs can lead to clinically noticeable enhancements in sleep disturbances. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week, combined with a balanced diet, is essential for effective weight management. As mentioned by A K Singh from the Department of Community Medicine, "Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial not only for reducing sleep disturbances but also for preventing associated health issues such as hypertension and type 2 diabetes."
-
Alter Resting Positions: The posture in which an individual rests can significantly affect loud breathing. Sleeping on one’s back can cause the tongue to fall back into the throat, leading to airway obstruction. It is advisable to sleep on the side, and using a body pillow can help maintain this position throughout the night, thereby minimizing noise during sleep.
-
Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can thicken mucus in the throat, worsening sleep disturbances. Health specialists advise drinking at least 8-10 glasses of water each day to maintain throat moisture and decrease the chances of disruptive breathing during sleep.
-
Avoid Alcohol and Sedatives: Both alcohol and sedative medications relax the muscles in the throat, increasing the likelihood of noisy breathing. To minimize this risk, it is best to avoid these substances in the hours leading up to rest.
-
Create a Consistent Rest Schedule: Regularity in rest patterns can improve rest quality and decrease occurrences of loud breathing. Aim for 7-9 hours of rest each night by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day.
-
Use Nasal Strips or a Humidifier: For those whose noise during sleep is aggravated by nasal congestion, employing nasal strips to open up nasal passages or using a humidifier to maintain moisture in the air can be beneficial in alleviating sounds caused by nasal blockages.
Individuals often wonder how they can stop snoring naturally by incorporating these natural remedies and lifestyle changes to significantly reduce their noise during sleep and enhance their overall sleep quality. Furthermore, addressing the broader implications of obesity, as discussed by Marchesini G et al., underlines the importance of these lifestyle changes in preventing hypertension and type 2 diabetes, which are frequently linked with sleep apnea.
3. Exercises to Strengthen Throat Muscles
-
Tongue Exercises: Extend your tongue outward as far as possible, holding this position for 10 seconds. Aim to repeat this exercise 5 to 10 times daily. This practice aids in strengthening the muscles located at the back of the throat, which can be beneficial in addressing how can I stop snoring naturally.
-
Singing: Engaging in regular singing sessions can significantly tone throat muscles. Dedicate 10 to 15 minutes each day to sing along to your favorite tunes. This not only enhances muscle strength but also has been linked to improvements in airway function, as demonstrated by recent findings on the benefits of singing for reducing loud breathing.
-
Mouth Exercises: To perform this exercise, open your mouth wide and vocalize 'ah' for a duration of 20 seconds. Repeating this action 5 times helps fortify the soft palate, a critical area that plays a role in snoring.
-
Jaw Exercises: Move your jaw from side to side and then forward, holding each position for 10 seconds. This sequence of actions can soothe and fortify the jaw muscles, further aiding in diminished noise during sleep.
Integrating these specific exercises into your daily regimen may improve muscle tone in the throat region, leading to the question of how can I stop snoring naturally by potentially decreasing the frequency and intensity of nighttime sounds. A case analysis examining myofunctional therapy with 49 participants showed a mean change of -4.5 in the apnoea hypopnoea index (AHI), indicating that exercises aimed at strengthening throat and jaw muscles could provide a feasible method for individuals facing issues with loud breathing. As noted in the study, 'We analyzed all data on an intention to treat basis,' which underscores the methodological rigor of the findings.
For further inquiries, readers can contact Clete A. Kushida, Division Chief/Medical Director at Stanford University.
4. Maintaining a Clean Sleeping Environment
-
Regular Cleaning: Frequent dusting and vacuuming of your bedroom are essential practices to minimize allergens, including dust mites and pet dander. Utilizing hypoallergenic bedding can further diminish exposure to these irritants, contributing to a healthier sleeping environment. Studies indicate that allergens play a significant role in worsening sleep disturbances, making this step crucial for those affected.
-
Air Quality: Adequate ventilation is vital in your sleeping quarters. Using an air purifier can greatly decrease airborne allergens, thus enhancing overall air conditions. Research has demonstrated a clear connection between poor air quality and heightened prevalence of noisy breathing, leading many to wonder, how can I stop snoring naturally? According to the review in Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2017, effective management strategies for obstructive apnea syndrome (OSAS) can be cost-effective, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a clean environment.
-
Maintain Optimal Humidity: To prevent nasal passages from drying out, it is recommended to keep humidity levels between 30-50%. A humidifier can be particularly beneficial in arid climates, as it adds moisture to the air, alleviating nasal congestion that may contribute to snoring; therefore, one might wonder how can I stop snoring naturally?
-
Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: Consuming large meals shortly before bedtime can lead to discomfort and increase the chances of noisy breathing. It is recommended to complete eating at least 2-3 hours before resting to promote better digestion and rest experience. This practice also corresponds with results indicating that eating habits can affect breathing issues during rest. By emphasizing a tidy and pleasant resting atmosphere, individuals can greatly increase their chances of minimizing noisy breathing, leading to the question of how can I stop snoring naturally for better overall rest.
The connection between air conditions and snoring is emphasized by various research, including those that highlight the effect of chronic eosinophilic inflammation on obstructive apnea (OSA) prevalence. As noted in a case study, patients with non-allergic rhinitis (NARES) showed a higher incidence of moderate to severe OSA compared to allergic rhinitis (AR) and control groups, suggesting that maintaining a clean environment can be crucial. Rest specialists highlight that 'a clean resting environment not only aids in lowering allergens but also enhances overall quality of rest,' reinforcing the significance of these practices.
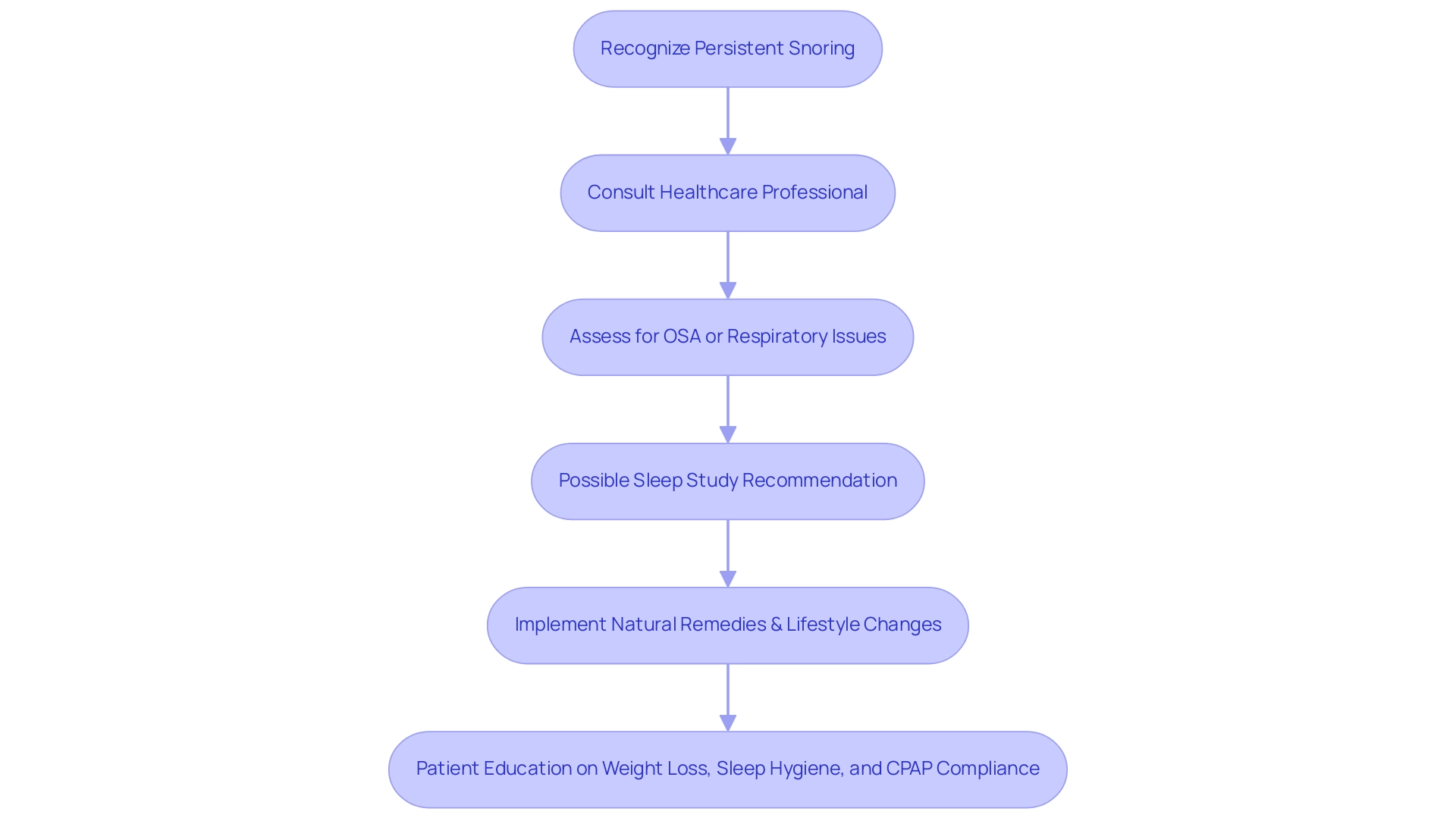
5. Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If snoring continues despite the implementation of natural remedies and lifestyle modifications, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. This step is crucial for assessing potential underlying conditions, such as obstructive apnea (OSA) or other respiratory issues that may necessitate medical intervention. Significantly, men are at heightened risk of experiencing symptoms of apnea compared to women, and the prevalence of OSA rises with age, especially in individuals over 50 years.
Therefore, seeking expert evaluation becomes essential as one ages. A healthcare provider may suggest a rest study to monitor breathing patterns during slumber, which can offer essential insights into noise issues. Dr. Won emphasizes the significance of sound rest by stating,
Attaining quality rest is a fundamental part of a healthy lifestyle.
Individuals may wonder, 'How can I stop snoring naturally?' by identifying and addressing any underlying health concerns to effectively manage their snoring and enhance their overall health and well-being. Moreover, informing patients about the importance of weight reduction, sleep hygiene, and compliance with treatments like CPAP can reduce risks linked to OSA and enhance treatment results, as illustrated in the case analysis titled 'Patient Education and Deterrence.' This study emphasizes that proper education can lead to better adherence to recommended treatments, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected by OSA.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Addressing snoring requires a comprehensive understanding of its various causes, ranging from anatomical issues and lifestyle choices to underlying health conditions. This article has explored the significant factors contributing to snoring, emphasizing the importance of recognizing these elements for effective management.
Maintaining a healthy weight, adjusting sleep positions, staying hydrated, and establishing a consistent sleep routine are practical lifestyle changes that can help mitigate the issue. Additionally, targeted exercises for strengthening throat muscles can further reduce snoring frequency and intensity.
Creating a clean sleeping environment is equally crucial, as allergens and poor air quality can exacerbate snoring. Regular cleaning, optimal humidity levels, and avoiding heavy meals before bedtime all contribute to a healthier sleep space. For those who continue to struggle with snoring despite making these adjustments, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. This step ensures that any underlying conditions, such as obstructive sleep apnea, are properly assessed and managed.
In summary, tackling snoring involves a multifaceted approach that encompasses lifestyle modifications, environmental considerations, and professional guidance. By implementing these strategies, individuals can significantly improve their sleep quality and overall health, paving the way for a more restful night and a healthier life.



















