Introduction
Stuttering is a multifaceted speech disorder that presents significant challenges for individuals of all ages. Characterized by disruptions in the flow of speech, stuttering can lead to not only communication difficulties but also emotional and psychological distress. As research continues to evolve, understanding the nuances of stuttering—its definitions, characteristics, and treatment options—has never been more crucial.
This article delves into the complexities of stuttering, exploring:
- Effective treatment techniques
- The vital role of speech-language pathologists
- The integration of counseling and emotional support in therapy
Furthermore, it highlights recent innovations that are reshaping the landscape of stuttering treatment, ensuring that individuals receive comprehensive and tailored care. Through this exploration, the importance of a holistic approach to managing stuttering becomes clear, paving the way for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for those affected.
1. Understanding Stuttering: Definition and Characteristics
Stuttering is a complex communication disorder characterized by interruptions in the flow of talk. These disruptions can manifest as repetitions of sounds, syllables, or words, prolonged phonemes, or blocks where a person struggles to produce sounds. The disorder not only affects the rhythm of talking but may also be accompanied by physical tension and anxiety, further complicating communication.
Research indicates that nearly one-third of individuals who stutter may also exhibit symptoms of cluttering, highlighting the multifaceted nature of communication disorders. A preliminary study suggests a prevalence rate of 1.1% to 1.2% among school-age children, indicating a need for further research in this area. Moreover, the crude prevalence of developmental disorders of speech and language has increased from 2015 to 2018, emphasizing a growing concern in this field, while the occurrence of speech disfluency has remained stable.
The severity of stuttering can vary significantly, influenced by factors such as genetics, developmental stages, and environmental pressures. Beilby et al. note,
Most people who stutter exhibit both noticeable disfluency and adverse life effects,
highlighting the importance of comprehending these traits for effective care.
highlighting the importance of comprehending these traits for effective care.
Additionally, Luterman's work on counseling individuals with communication disorders offers valuable insights into methods that can be tailored to individual needs. Identifying appropriate strategies is critical, especially given the limited engagement of fewer than 1% of adults who stutter with supportive communities, which highlights the importance of fostering such connections for better management and treatment outcomes.
2. Exploring Treatment Techniques for Stuttering: From Children to Adults
Stuttering treatment encompasses a range of approaches, including fluency shaping, modification techniques, and cognitive-behavioral therapy for addressing speech disruptions. Fluency shaping techniques aim to enhance verbal fluency by modifying communication patterns, allowing people to express themselves more smoothly. In contrast, stuttering treatment emphasizes assisting people in managing their speech difficulties by altering their reactions and responses to them.
Importantly, therapy modalities can differ significantly based on age; for instance, children often benefit from play-based interventions that engage their natural communication styles, while adults may prefer more structured therapy sessions focusing on specific speech objectives. Recent advancements in these techniques have demonstrated promising outcomes, including emerging evidence for telehealth delivery of stuttering treatment, which provides accessible options for many individuals. Furthermore, a case study named 'Clinical Practice Guidelines for Speech Fluency Disorders' underscores a consensus-based strategy created by seventeen expert societies in Germany, stressing the significance of standardized care protocols.
Engagement in self-help groups is likewise advised according to clinical agreement, highlighting its importance in the care landscape. According to Angela Morgan, an international leader in childhood speech impairments, 'her extensive research has significantly contributed to understanding the neurobiology of speech, language, and literacy issues in children.' This highlights the significance of choosing the appropriate therapeutic method customized to a person's specific needs and situations, ensuring the most effective results in managing speech difficulties.
3. The Role of Speech-Language Pathologists in Stuttering Treatment
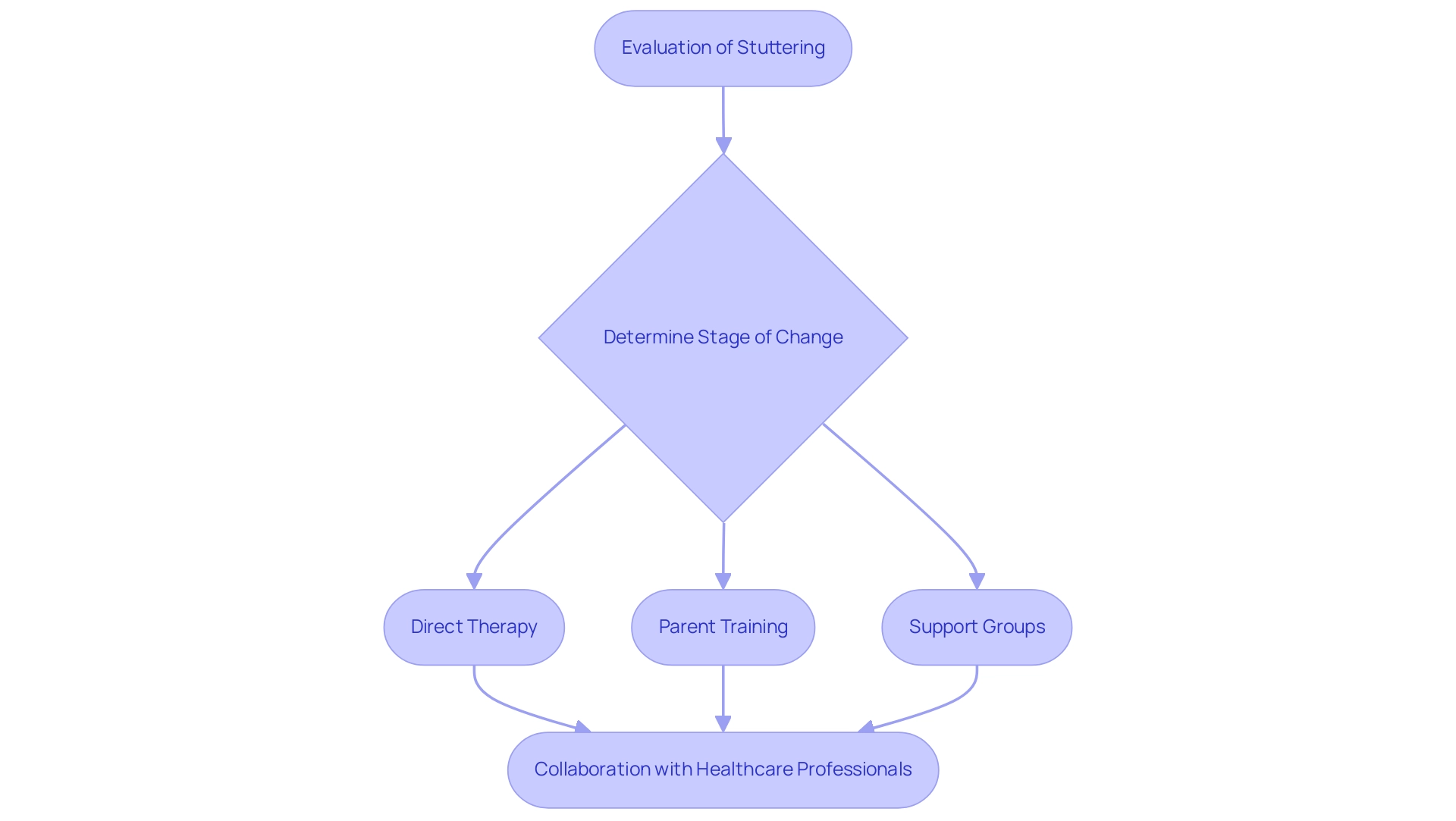
Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) play an essential role in the evaluation and management of stuttering treatment. With approximately 234,000 members, certificate holders, and affiliates as reported by the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA), SLPs are equipped to conduct comprehensive evaluations that determine the nature and severity of stuttering in people. These evaluations are guided by the transtheoretical model of change, which assesses an individual's preparedness for addressing fluency disorders.
For instance, SLPs may identify which stage a client is in, allowing for tailored interventions that match their readiness for change. Following the assessment, SLPs develop individualized treatment plans that cater to the unique needs of each client for stuttering treatment. Their methodologies include:
- Direct therapy
- Parent training
- Support groups
All designed to foster effective communication skills.
Risk factors for ongoing speech difficulties include:
- Being male
- Having a family history of these issues
- Experiencing slower language development
As highlighted by ASHA, speech therapy can significantly improve a child's communication skills, which can positively affect their emotional health, academic performance, and social interactions.
Furthermore, case studies, like the management of communication difficulties in adults who did not overcome childhood challenges, highlight the significance of teamwork between healthcare professionals and language pathologists to address ongoing developmental communication issues effectively, which impacts less than 1% of the population.
This collaboration is essential in addressing both the communication disorder and associated psychological issues. Through these personalized methods, SLPs are crucial in assisting people with speech difficulties, including stuttering treatment, ultimately improving their quality of life.
4. Incorporating Counseling and Emotional Support in Stuttering Therapy
Incorporating counseling and emotional support into stuttering treatment is essential for effectively tackling the psychological challenges often linked to speech disorders. Research indicates that people who stutter often encounter heightened levels of anxiety, frustration, and embarrassment, which can complicate their condition and make effective stuttering treatment essential. Notably, a study on adolescents who stutter found that the intricate relationship between stuttering and anxiety often leads to social anxiety and a fear of judgment, which highlights the importance of effective stuttering treatment in significantly impacting their quality of life and social interactions.
This complexity is underscored by the statistic that 4 (8.9%) of participants believe self-help groups should be developed, highlighting the demand for emotional support structures. Counseling serves as an essential tool in stuttering treatment, offering coping mechanisms and fostering emotional resilience. It creates a safe environment for people to articulate their feelings and experiences.
Techniques such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises can be beneficial additions to stuttering treatment, providing individuals with strategies to manage anxiety and enhance their overall communication skills. As Charles Van Riper, a pioneer in the field of speech-language pathology, noted from his own experiences, the importance of addressing these emotional dimensions cannot be overstated. This comprehensive method not only supports results but also emphasizes the importance of addressing emotional health in stuttering treatment.
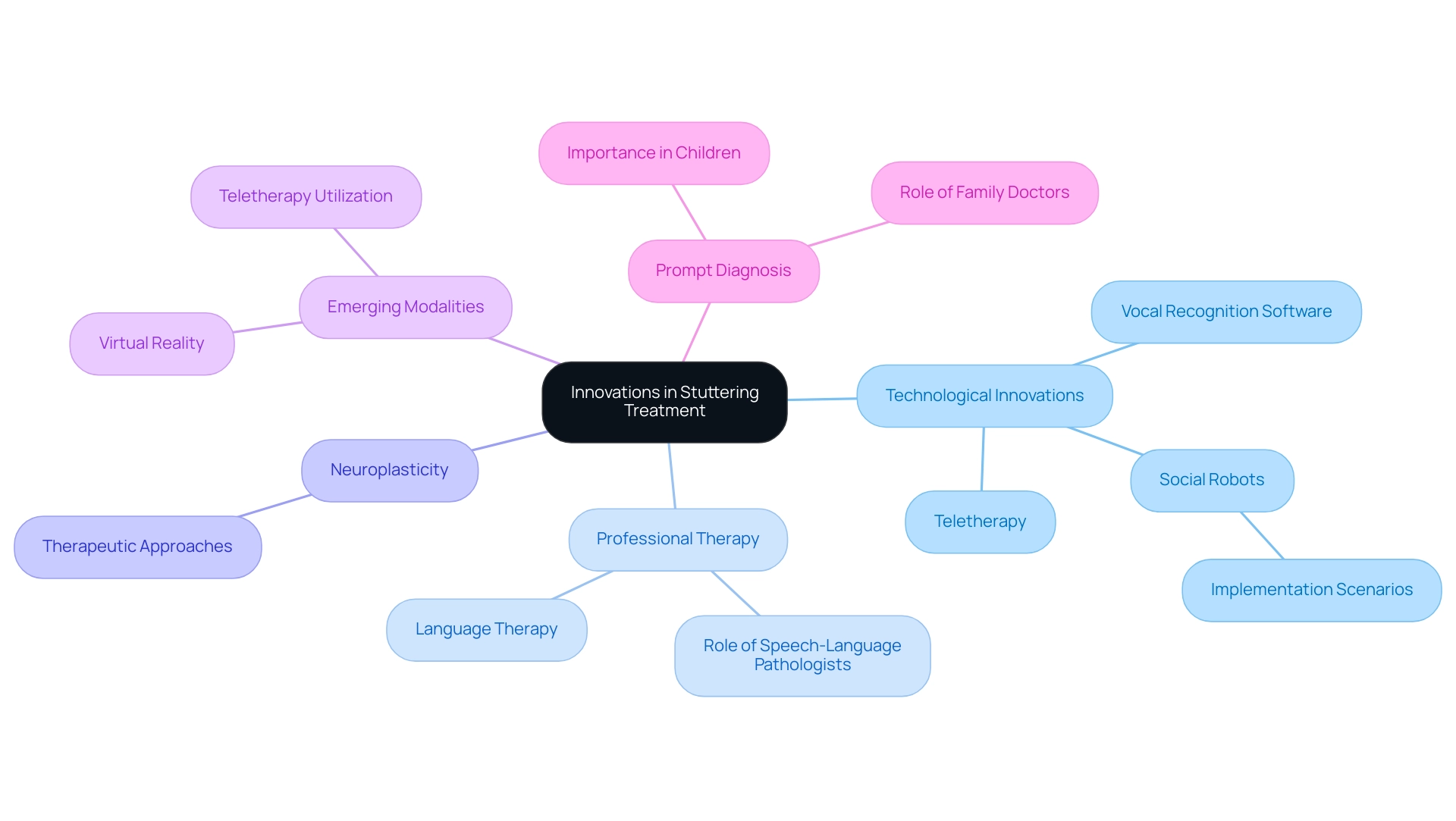
5. Innovations in Stuttering Treatment: What’s New in Therapy?
Recent advancements in stuttering treatment are significantly influenced by technological innovations, including vocal recognition software and specialized applications aimed at enhancing fluency training. These tools not only offer prompt feedback but also enable practice within a controlled setting, which is especially advantageous for individuals aiming to enhance their communication. Significantly, stuttering treatment through language therapy conducted by a specially qualified communication pathologist remains the cornerstone of care at any age, highlighting the importance of professional guidance in utilizing these technological advancements.
Furthermore, the exploration of neuroplasticity has led to novel therapeutic approaches that target and modify the brain pathways essential to verbal expression. Emerging modalities, such as virtual reality and teletherapy, are gaining prominence as they provide flexible and accessible stuttering treatment options for diverse populations. In fact, teletherapy has seen a marked increase in utilization, reflecting a broader trend towards integrating technology into speech therapy.
Abdulaziz Al mudhi, an author in the field, aptly notes,
The advent of technology has revolutionized speech therapy.
Moreover, innovative research, including the proposed use of social robots in speech intervention, illustrates the potential for integrating human-robot interaction into therapy. The research outlines eight scenarios for the implementation of social robots, showcasing their versatility in therapeutic settings.
Moreover, innovative research, including the proposed use of social robots in speech intervention, illustrates the potential for integrating human-robot interaction into therapy. The research outlines eight scenarios for the implementation of social robots, showcasing their versatility in therapeutic settings.
Additionally, prompt diagnosis in children is critical for effective stuttering treatment, as highlighted by the case study titled 'Diagnosis and Treatment of Stuttering.' A robust understanding of speech disruptions among physicians and speech pathologists can improve identification and management of the disorder and its associated psychological issues. For practitioners and individuals affected by stuttering, remaining informed about these advancements is essential to leveraging the best available stuttering treatment.
Conclusion
Stuttering is a complex disorder that impacts not only the ability to communicate but also emotional well-being and social interactions. The exploration of effective treatment techniques reveals a variety of approaches tailored to meet the needs of individuals across different age groups. Fluency shaping, stuttering modification, and cognitive-behavioral therapy are key methods that have shown promise in enhancing speech fluency and managing the psychological aspects of stuttering. Importantly, the role of speech-language pathologists is crucial in providing comprehensive assessments and personalized treatment plans that address the unique challenges faced by each individual.
Incorporating counseling and emotional support into stuttering therapy further emphasizes the necessity of a holistic approach. Addressing the psychological challenges associated with stuttering can significantly improve quality of life, as individuals learn to cope with anxiety and frustration. Recent technological innovations, including teletherapy and speech recognition tools, are transforming the landscape of stuttering treatment, offering new avenues for support and practice in a controlled environment.
Ultimately, the integration of these various strategies—effective treatment techniques, the expertise of speech-language pathologists, emotional support, and technological advancements—underscores the importance of a comprehensive and individualized approach to managing stuttering. By fostering a deeper understanding of stuttering and its complexities, individuals affected by this disorder can achieve improved communication skills and enhanced emotional resilience, paving the way for a better quality of life.




















