Introduction
The low-carbohydrate diet has gained significant attention as an effective strategy for weight management and overall health improvement. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing the consumption of proteins and healthy fats, individuals can shift their metabolism from burning glucose to utilizing fat for energy.
This article delves into the fundamentals of a low-carb diet, providing practical steps for those looking to embark on this dietary journey. From identifying suitable low-carb foods to meal planning and monitoring progress, readers will find a comprehensive guide that highlights the benefits, challenges, and essential strategies for maintaining a successful low-carb lifestyle.
With an emphasis on informed choices and nutritional transparency, this exploration aims to empower individuals to achieve their health goals through a structured and sustainable approach to eating.
1. Understanding the Basics of a Low-Carb Diet
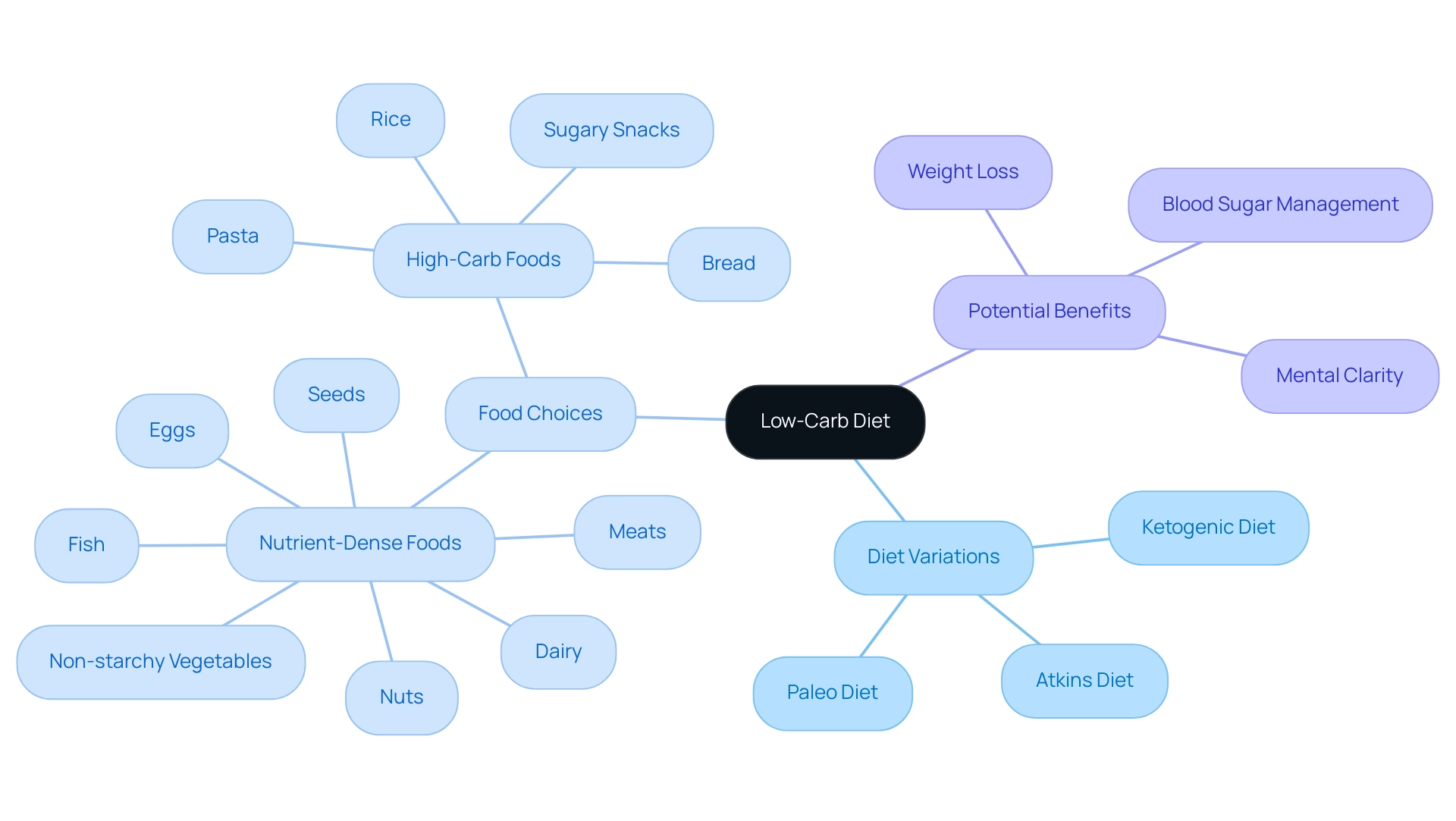
A low carb diet primarily entails a significant reduction in carbohydrate intake, along with an increase in the consumption of proteins and healthy fats. This nutritional approach aims to shift the body's metabolic process from utilizing glucose derived from carbohydrates to burning fat for energy. Among the popular reduced-carbohydrate diets are:
- The ketogenic diet
- Atkins diet
- Paleo diet
Each varies in the degree of carbohydrate limitation.
It is crucial to prioritize nutrient-dense foods such as:
- Meats
- Fish
- Eggs
- Dairy
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Non-starchy vegetables
While limiting or avoiding high-carbohydrate products like:
- Bread
- Pasta
- Rice
- Sugary snacks
These can impede weight loss and hinder health improvements. The FDA has indicated that brands not accurately quantifying their products’ net carbohydrate content per serving might be subject to enforcement actions, underscoring the importance of transparency in food choices. Noteworthy instances of plant-based keto foods encompass:
- Love Lava Yogurt
- Octonuts Almond Protein Powder
- Sir Kensington’s Vegan Mayo
These can be outstanding choices for individuals adhering to a reduced carbohydrate diet.
The possible advantages of following a low carb diet, such as weight loss, enhanced blood sugar management, and increased mental clarity, can serve as major incentives for individuals contemplating this nutritional approach. Recent studies, including a cutting-edge review titled '
Ketogenic Nutrition and Cardiovascular Risk,' have highlighted the effectiveness of a low carb diet, with many participants reporting positive health outcomes; however, long-term adherence to this dietary approach can be challenging and warrants further investigation.
2. Practical Steps to Start Your Low-Carb Journey
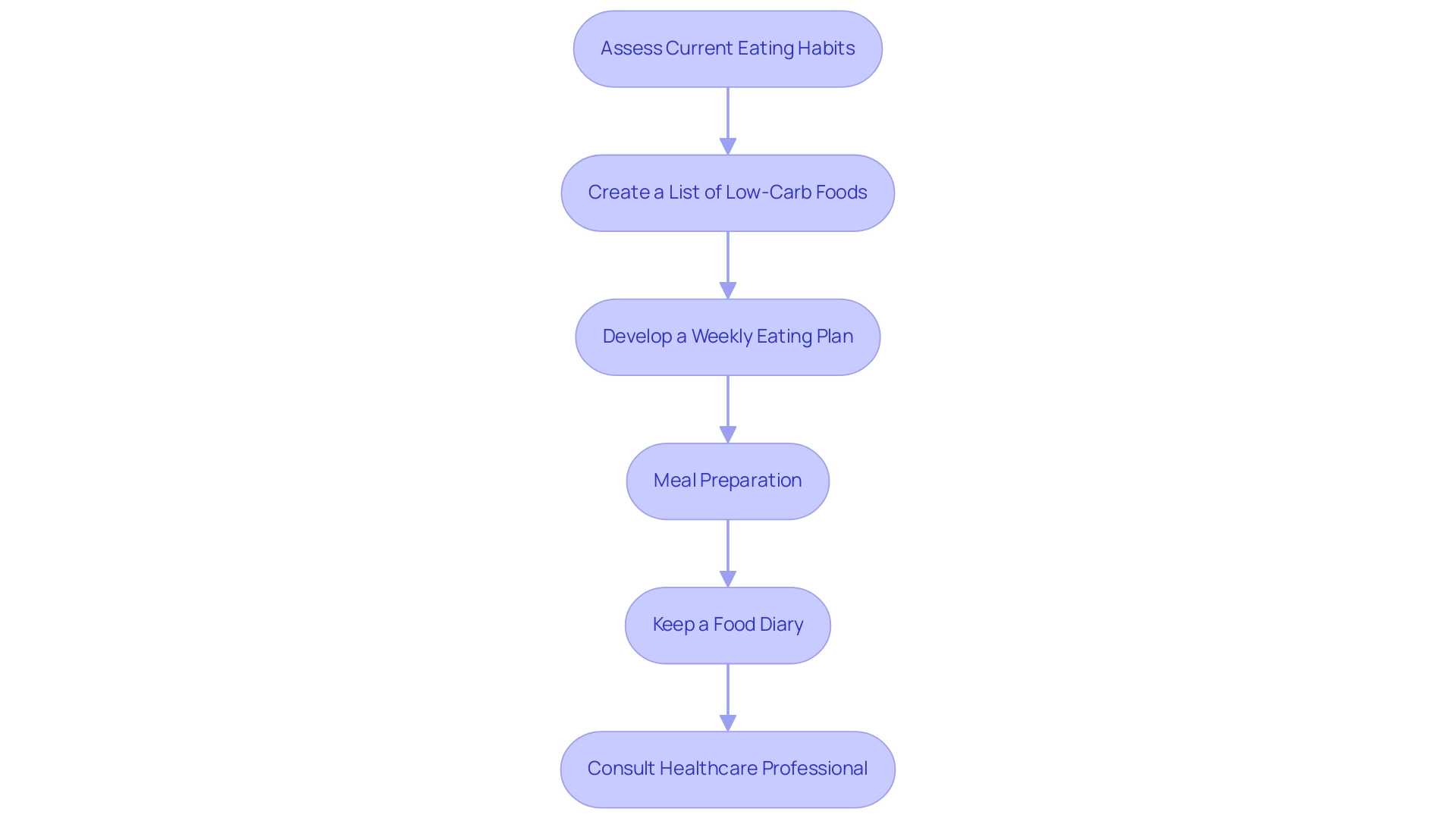
Embarking on a low-carbohydrate eating plan requires a thoughtful assessment of your current eating habits and the identification of areas for improvement. Start by creating a list of foods with minimal carbohydrates that appeal to you, such as:
- Leafy greens
- Avocados
- Lean meats
Research indicates that
eighty-eight percent of participants in a two-phase diet program were compliant with the entire regimen, emphasizing the effectiveness of planning in adhering to a low carb diet.
Afterward, create a weekly eating plan that includes:
- A protein source
- Healthy fats
- Plenty of non-starchy vegetables in each dish
Preparing meals in advance can significantly reduce the temptation to stray from your dietary goals, thereby enhancing adherence to the regimen. Keeping a food diary can further reinforce this commitment, as it allows individuals to meticulously track their carbohydrate intake and monitor their progress.
As noted by the Healthline Medical Network, a consistent keto approach should lead to ketosis, identified by signs like bad breath and weight loss. Moreover, consider gradually lowering your carbohydrate consumption over several days to mitigate potential withdrawal symptoms, such as fatigue and cravings. Staying hydrated throughout this process is crucial for overall well-being.
A case study by Guldbrand et al. demonstrated that while there was no significant difference in weight loss between low-carb and low-fat eating plans, the low-carb group showed significant improvement in glycemic control at six months. For a tailored approach, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist, ensuring that your eating habits align with your unique nutritional needs.
By following these steps, you will be well-equipped to initiate and sustain your low carb diet journey.
3. Identifying Low-Carb Foods
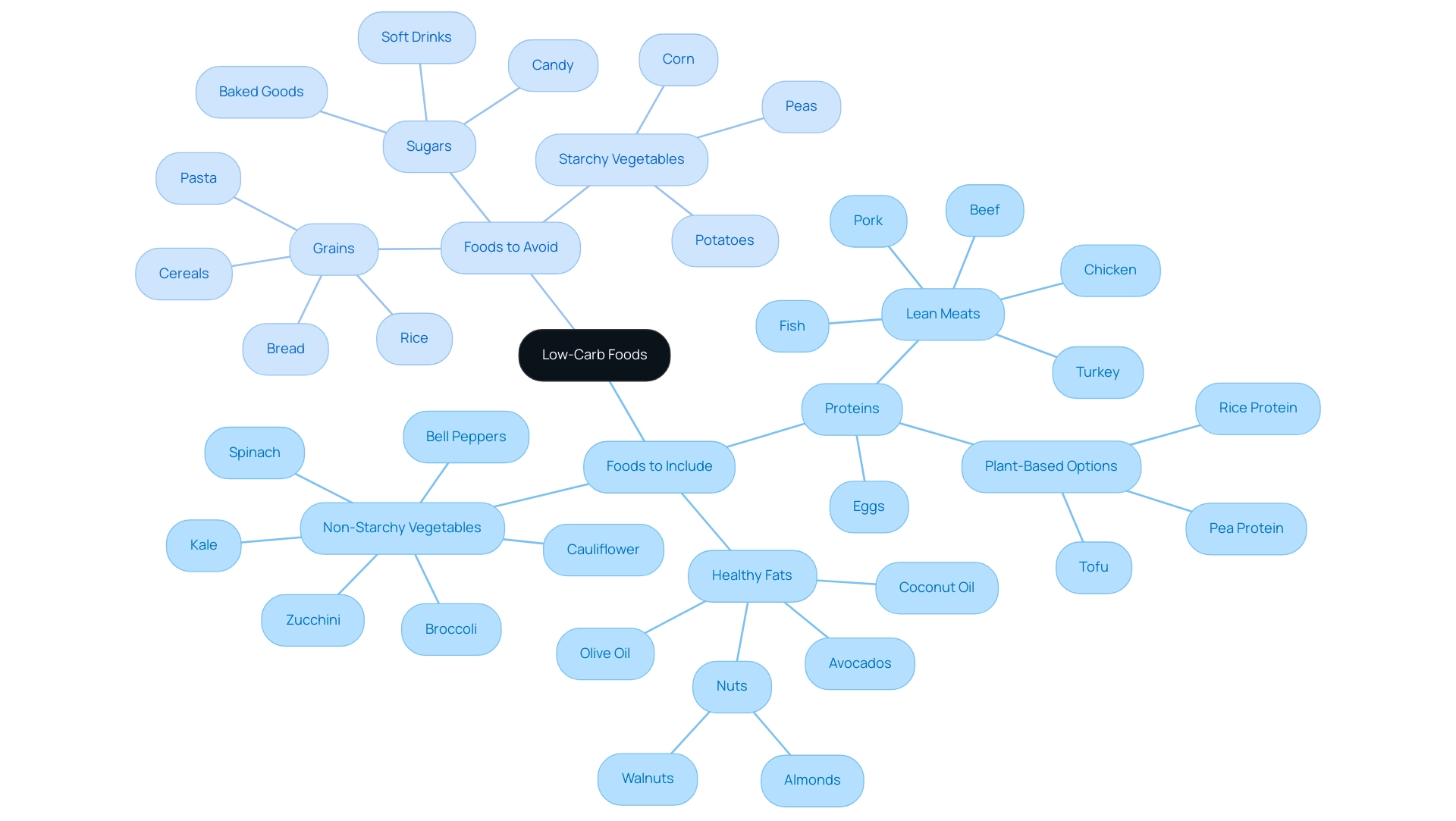
When starting a low carb diet, it is crucial to prioritize the inclusion of specific food categories that align with your nutritional goals. Recommended foods include:
-
Proteins: Opt for lean sources such as chicken, turkey, beef, pork, fish, eggs, and plant-based options like tofu, pea protein, and rice protein, which are excellent choices for vegans and vegetarians seeking high-quality protein alternatives. Pea protein, derived from dried peas that are processed into a fine powder, is particularly beneficial because of its high essential amino acid content, making it an ideal addition to a low carb diet.
Rice protein, another plant-based option, provides a complete amino acid profile and can be combined with pea protein for enhanced nutritional benefits.
-
Healthy Fats: Incorporate nutrient-dense fats such as avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, and a variety of nuts including almonds and walnuts. In a low carb diet, it is important to focus on non-starchy vegetables like spinach, kale, broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, and bell peppers, which provide essential vitamins and minerals without the excess carbohydrates.
In contrast, it is essential to avoid foods that are high in carbohydrates, which can undermine your dietary efforts. These include:
-
Grains: Steer clear of bread, pasta, rice, and cereals, as they are typically high in carbs.
-
Sugars: Eliminate sources of refined sugars such as candy, soft drinks, and baked goods to prevent health issues associated with excessive sugar intake, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
The health risks of consuming 50 grams of sugar a day can be significant, leading to long-term health consequences.
-
Starchy Vegetables: Limit intake of potatoes, corn, and peas, which can add unnecessary carbohydrates to your meals. For instance, the overall
carbohydrate total for a sample menu on the third day of a reduced-carb eating plan is roughly 54.7 grams, demonstrating how to efficiently control carbohydrate consumption.
By making informed food choices, such as incorporating plant-based proteins and reducing added sugars, you can successfully maintain a low carb diet, which can potentially lead to enhanced health outcomes associated with decreased carbohydrate intake. As noted by Thomas M. Holland, MD, a plant-based eating plan emphasizing high-quality, whole foods is generally superior for cardiovascular health due to its higher fiber and phytochemical content. Additionally, incorporating high-intensity exercise, as highlighted in the case study 'High-Intensity Exercise and Cardiovascular Risk,' may further lower the risk of major cardiovascular events, thereby supporting the overall health benefits of a low carb diet.
4. Meal Planning and Preparation Tips
Successfully following a low carb diet involves strategic food preparation, enhanced by personalized nutrition support from Certified Nutritionists at Awesome Health Club. Here are key approaches to ensure you stay on track:
-
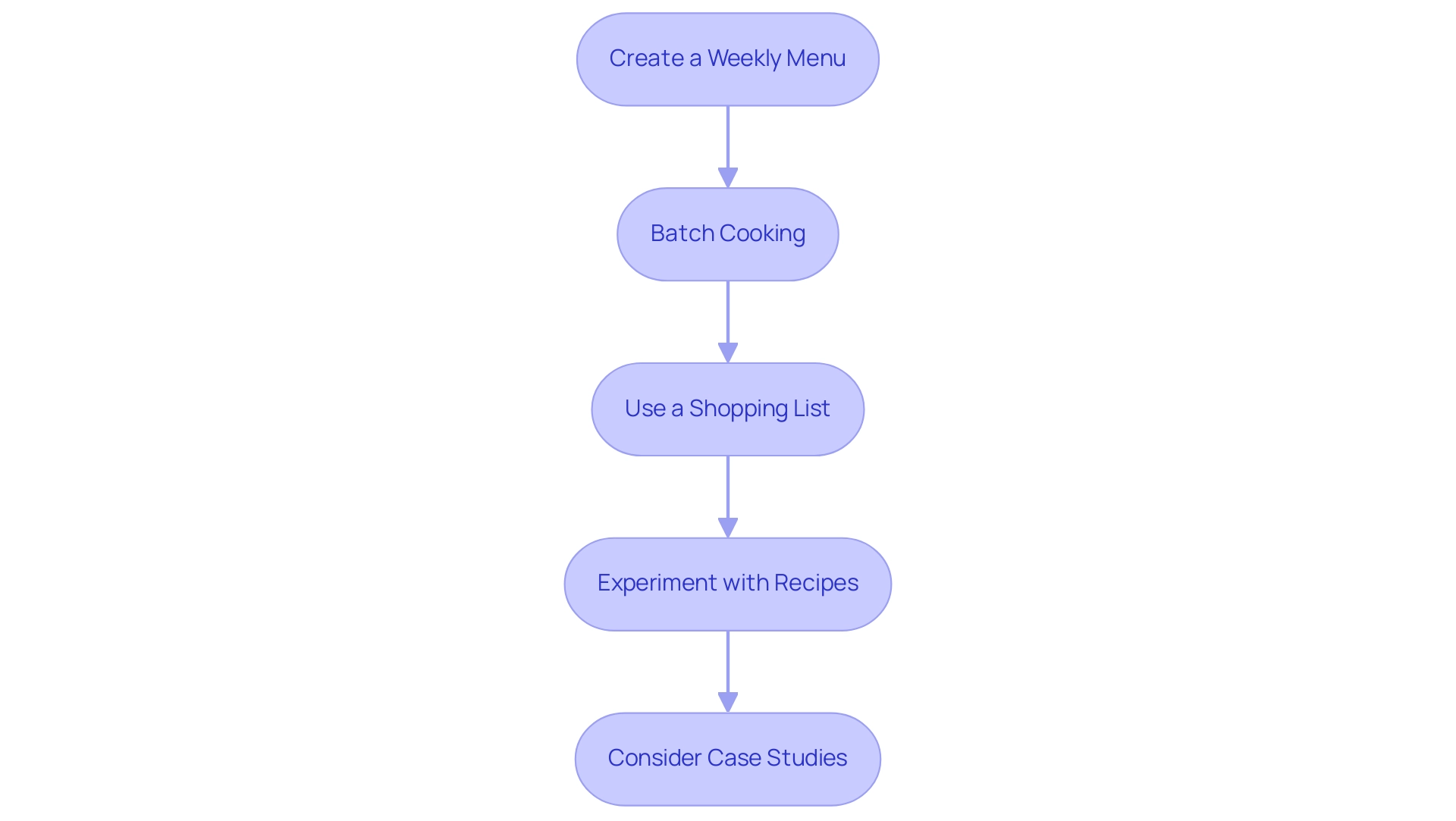
Create a Weekly Menu: Draft a detailed menu for each day, encompassing breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks. This not only enhances organization but also minimizes the temptation to stray from your diet. Studies indicate that most individuals who
plan their food intake participate in this activity at least once a week, highlighting its effectiveness in sustaining nutritional focus. Additionally, studies indicate that exercise planning also plays a role, with an estimate of -3.389 and a standard error of 0.757 highlighting the importance of structured planning in food adherence.
-
Batch Cooking: Prepare larger portions of meals for a low carb diet and store them in individual containers for convenient access throughout the week. This strategy not only saves time but also supports consistency in food adherence. According to recent statistics, individuals who engage in batch cooking tend to experience enhanced nutritional compliance and better health outcomes.
-
Use a Shopping List: Before grocery shopping, create a list based on your dining plan to avoid the pitfalls of purchasing high-carb items. It is advisable to navigate the store’s perimeter, where fresh produce and proteins are typically located, to ensure that your selections align with your dietary goals.
-
Experiment with Recipes: Keep your dishes engaging by trying out new recipes for a low carb diet. The abundance of resources accessible online can spark creativity in your food planning, making it easier to adhere to your diet. Notably, most participants in planning studies organized dishes according to their personal recipe repertoire or the ingredients available during grocery shopping, showcasing the importance of adaptability in preparation.
-
Consider Case Studies: The study titled "Influence of Meal and Exercise Planning on BMI" examined the impact of meal and exercise planning on BMI trajectories, revealing that individuals who planned their meals and exercise routines experienced a decrease in BMI over time, particularly older individuals who saw a steeper decline compared to their younger counterparts.
By embracing these strategies and connecting with a Certified Nutritionist for personalized support, you can streamline your low carb diet journey, ensuring that healthy options are readily available and enjoyable. Schedule your free consultation today with one of our Certified Nutritionists at Awesome Health Club to get started on your path to optimal wellness!
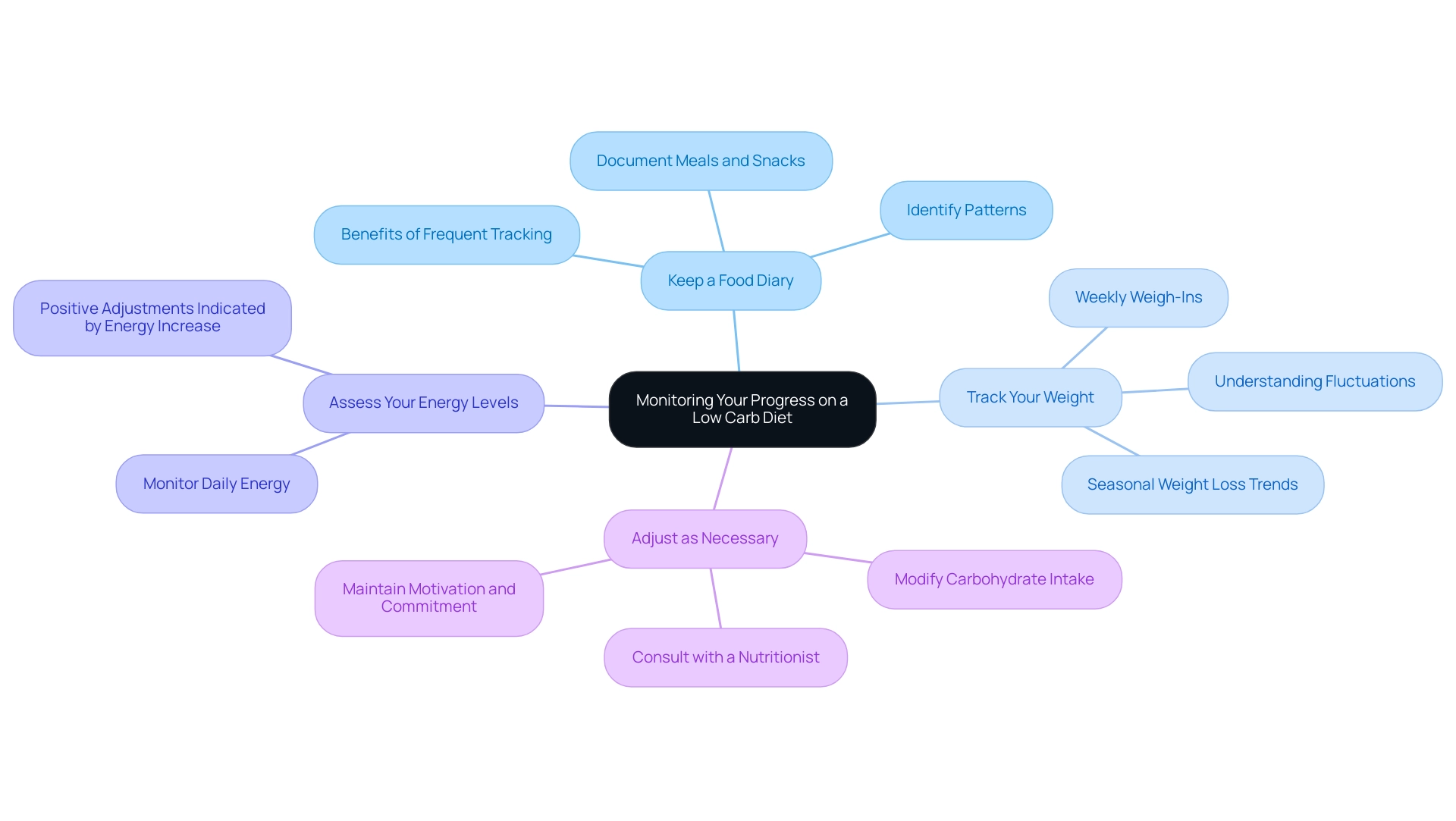
5. Monitoring Your Progress and Adjusting Your Diet
Monitoring your progress on a low carb diet is crucial for achieving long-term success. Employing effective tracking methods can significantly enhance your weight loss efforts. Consider the following strategies:
-
Keep a Food Diary: Maintaining a detailed food diary allows you to document your meals and snacks, thereby identifying patterns and areas for improvement.
-
Track Your Weight: Weighing yourself on a weekly basis enables you to monitor changes in your weight. It's important to remember that weight loss may not follow a linear path; fluctuations are a normal part of the process.
Interestingly, studies show that more weight is typically lost during the summer months compared to the holiday season, which highlights the importance of consistent tracking throughout the year.
-
Assess Your Energy Levels: Being aware of your energy levels throughout the day can offer insight into how well your body is adjusting to a low carb diet. An increase in energy often signifies positive adjustments.
-
Adjust as Necessary: If you're not observing the desired results, consider modifying your carbohydrate intake or consult with a nutritionist for tailored advice. By actively monitoring your progress and making informed adjustments, you can maintain motivation and commitment to your low carb diet.
Nicholas Rizzo, Fitness Research Director, emphasizes the value of collaboration with industry leaders to enhance the effectiveness of nutritional approaches, stating,
Along the way, collaborating with industry leaders like Michael Yessis, Mark Rippetoe, Carlo Buzzichelli, Dave Tate, Ray Williams, and Joel Seedman.
This underscores the importance of integrating expert insights into your dietary strategy. Furthermore, with 40% of Gen X women focusing solely on dieting, understanding effective monitoring techniques is crucial for anyone looking to achieve their weight loss goals.
Conclusion
Embarking on a low-carbohydrate diet can lead to significant improvements in weight management and overall health. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods—such as proteins, healthy fats, and low-carb vegetables—individuals can effectively shift their metabolism to burn fat for energy rather than relying on glucose. The article outlines essential strategies for starting this dietary journey, including:
- Meal planning
- Food tracking
- Gradual carbohydrate reduction to ease the transition
Practical steps such as creating a weekly menu, engaging in batch cooking, and utilizing a shopping list are crucial for maintaining adherence to a low-carb lifestyle. Monitoring progress through a food diary and regular weight checks enables individuals to stay accountable and make necessary adjustments to their diet. By combining these strategies with professional guidance from nutritionists, individuals can enhance their chances of success and sustain their commitment to a low-carb regimen.
Ultimately, a low-carbohydrate diet offers a structured approach to healthier eating that can lead to weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and better overall well-being. By making informed choices and embracing a comprehensive plan, individuals can empower themselves to achieve their health goals and enjoy the numerous benefits associated with a low-carb lifestyle.