Introduction
Pediatric speech therapy services play a crucial role in addressing communication disorders among children, offering tailored interventions that cater to individual needs. With a focus on enhancing speech articulation, language development, and social communication, speech-language pathologists (SLPs) collaborate with families and educators to create a supportive therapeutic environment.
This article delves into the various aspects of pediatric speech therapy, including:
- The importance of recognizing speech delays
- Understanding the evaluation process
- The diverse therapy techniques available, from traditional methods to augmentative and alternative communication (AAC)
By exploring these elements, caregivers can gain valuable insights into how to effectively support their child's communication journey and the significant impact of early intervention on overall development.
1. An Overview of Pediatric Speech Therapy Services
Pediatric speech therapy includes a wide array of interventions designed to help children with language disorders. These services typically include both individual and group sessions tailored to address specific needs such as:
- Pediatric speech therapy
- Speech articulation
- Language development
- Social communication
- Feeding difficulties
Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) often engage in consultation with families and collaborate closely with educators to ensure a holistic approach to therapy.
This collaboration is crucial in creating a supportive environment conducive to the individual's progress. SLPs also provide valuable resources and strategies to empower caregivers, enabling them to foster effective communication skills at home. It is essential for caregivers to comprehend these services, as they play a crucial role in making informed choices about their child's treatment journey.
Recent insights emphasize that 68% of surveyed communication specialists are contemplating adopting telehealth services, which could further improve access to essential treatments. Furthermore, prominent firms in the U.S. communication support sector, like Kindred Healthcare, LLC, Genesis Rehab Services, and Benchmark Physical Rehabilitation Institute, are set to capitalize on these expanding market prospects, illustrating the changing environment of pediatric communication assistance. Expert statements from SLPs highlight the significance of pediatric speech therapy, asserting, 'Prompt pediatric speech therapy can greatly influence a young person's abilities and overall growth.'
The incorporation of these elements highlights the considerable influence of language therapy on young people's communication disorders and overall development.
2. Recognizing Speech Delays: Milestones and Warning Signs
Caregivers must be vigilant in recognizing essential developmental milestones in communication, particularly for kids aged 4 to 5 years. At this stage, young individuals are expected to:
- Answer 'why' questions
- Categorize items
- Grasp more abstract spatial concepts
They begin employing irregular past tense verbs and are capable of describing processes, indicating a significant progression in their language skills.
According to the case study titled 'Language Development in 4 to 5 Years,' while youngsters' verbal expressions are generally comprehensible, they may struggle with articulating longer or more complex words. Warning signs that may indicate potential speech delays include:
- A lack of response to their name
- A limited vocabulary
- Difficulty maintaining eye contact
- Trouble forming sentences
These signs can often be addressed through pediatric speech therapy. The identification of these 'red flags' is crucial, as they suggest a high prevalence of persistent disorders that may require pediatric speech therapy evaluation.
As noted by Kid Sense Child Development, recent modifications in educational frameworks, such as the Australian Curriculum, emphasize the necessity for children to meet specific functional requirements, which can sometimes misalign with standardized research findings. Recognizing these signs is essential; caregivers should seek professional evaluation, particularly pediatric speech therapy, if such indicators are observed. Early intervention through pediatric speech therapy has been demonstrated to improve language abilities and encourage overall developmental progress.
3. Understanding the Speech Therapy Evaluation Process
The pediatric speech therapy evaluation process is initiated with a thorough assessment conducted by a speech-language pathologist (SLP). This comprehensive evaluation for pediatric speech therapy often incorporates:
- Standardized tests
- Observational data
- Interviews with caregivers
All aimed at collecting vital information regarding the child's expressive skills. Key areas of focus in pediatric speech therapy include:
- Articulation
- Language comprehension
- Expressiveness
- Social communication skills
Recent findings indicate that among standardized measures, tools such as the CELF-4, CELF-5, CELF-P, RAPT, and SPAT are frequently employed by SLPs, showcasing a standardization in practices that enhances the quality of language assessment and intervention. Notably, only 3.0% of SLPs reported using the YARC, highlighting the varying adoption of different assessment tools. Additionally, language sampling techniques are increasingly utilized to elicit spontaneous language in different contexts, providing complementary data to standardized assessments.
Following the assessment, the SLP compiles a comprehensive report that details the findings and provides customized suggestions for pediatric speech therapy treatment. This report acts as an essential resource for caregivers, offering insight into their offspring's needs and the suggested intervention strategies, in line with the necessity for efficient evaluation methods in communication support. As noted by Roberts et al., only 25% of the articles published in ASHA journals over the past decade focus on clinical practice research, underscoring the importance of ongoing evaluation and adaptation of assessment techniques in improving clinical outcomes.
4. The Role of Speech-Language Pathologists in Therapy
Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) are highly trained professionals dedicated to diagnosing and treating a range of disorders through pediatric speech therapy. They employ a range of methods customized specifically to each young person's unique requirements, including:
- Pediatric speech therapy
- Play-based interventions
- Structured exercises
- Interactive activities that promote engagement and learning
Notably, productions with only vowel distortion errors achieved an average of 30% interrater agreement, highlighting the assessment challenges SLPs face.
Collaboration with families is a cornerstone of effective treatment in pediatric speech therapy, where SLPs work closely with parents and caregivers to set personalized goals and develop strategies that can be reinforced at home. This collaboration not only improves the therapeutic process but also enables families to assist their offspring's development in interaction. A case study titled "Diagnosis and Early Intervention" illustrates the significance of early diagnosis by SLPs, who utilize play-based activities and verbal tasks for assessment.
Prompt intervention, as illustrated in this case study, significantly enhances results in therapy. The expertise of SLPs in pediatric speech therapy is crucial in navigating these challenges, ensuring that children not only receive appropriate interventions but also develop essential language skills within a nurturing environment. As noted by Klein et al., "correct productions may be easier for SLP listeners to judge than distortions/close approximations and inaccurate productions," emphasizing the complexities involved in verbal assessment.
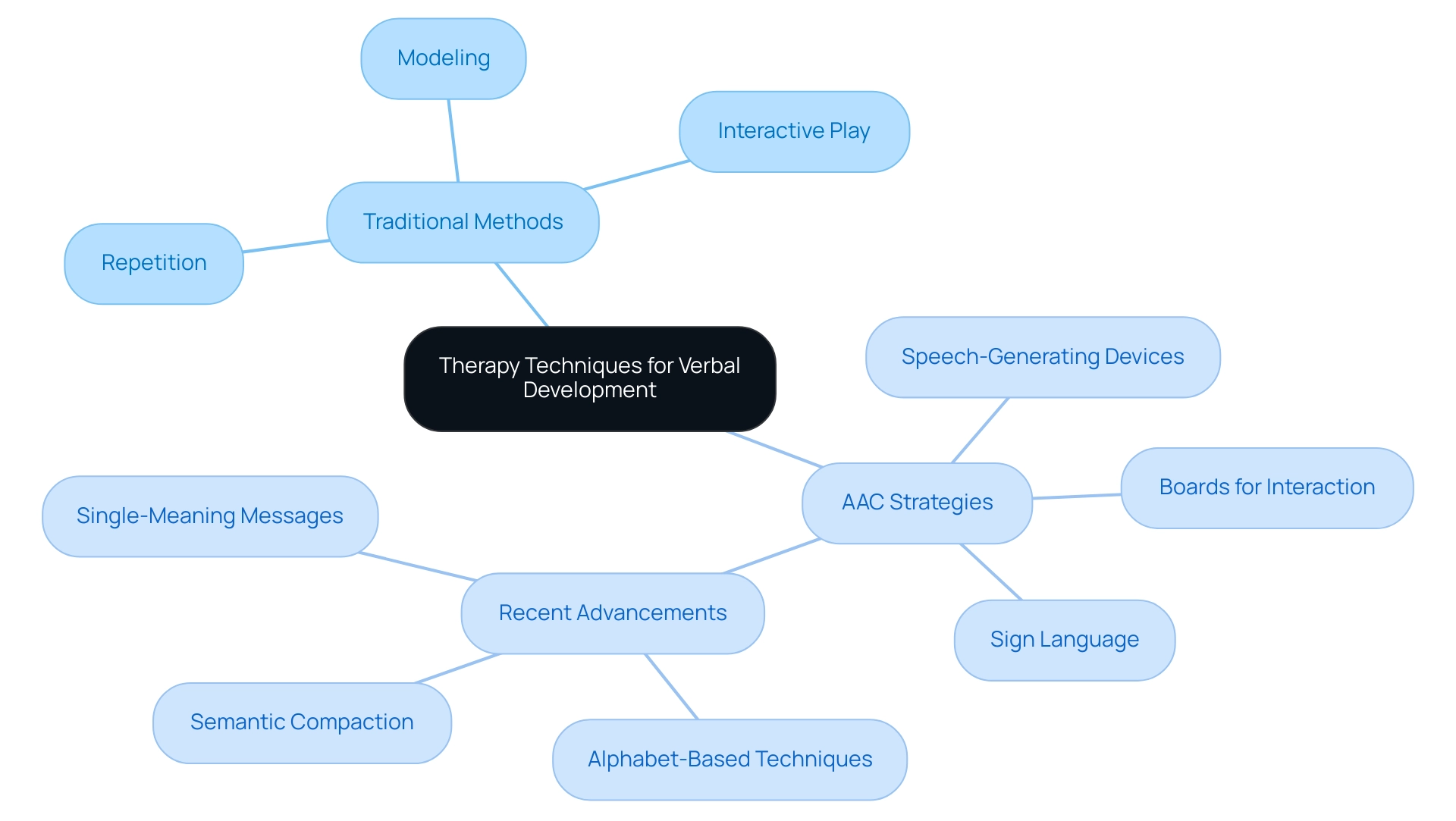
5. Exploring Therapy Techniques: From Traditional to AAC
Therapy techniques for verbal development are varied, including both conventional language therapy methods and augmentative and alternative interaction (AAC) systems. Traditional approaches typically prioritize articulation and language development through techniques such as:
- Repetition
- Modeling
- Interactive play
All aimed at enhancing an individual's speech skills. In contrast, AAC strategies offer vital options for individuals who encounter difficulties with verbal expression.
These strategies may include the use of:
- Boards for interaction
- Speech-generating devices
- Sign language
Enabling kids to express themselves more effectively. Research indicates that all participants in aided AAC modeling exhibited improvements in expressive interaction, highlighting the efficacy of these methods. Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) work closely with caregivers to identify the most effective techniques tailored to the individual's unique needs and preferences.
By understanding the spectrum of available options, caregivers can better navigate and support their child’s expression journey. Moreover, recent advancements in AAC, such as language representation methods that include:
- Alphabet-based techniques
- Single-meaning messages
- Semantic compaction
Have further enhanced the potential for effective interaction in pediatric speech therapy settings. As Schwartz and Baer noted, observing peers of the same age as AAC users and gathering language samples in various contexts can yield more ecologically valid interaction targets and vocabulary.
Additionally, Østvik et al. (2017) emphasized the significance of friendships between youth using AAC and their peers, which can positively impact social dynamics and communication skills. This multifaceted approach highlights the significance of adjusting treatment techniques in pediatric speech therapy to enhance results for children facing speech challenges.
Moreover, the case study titled 'Quality of Study Characteristics' demonstrates that reliability or interobserver agreement was measured in 53 studies, with generalization of targeted behavior assessed in 28% of studies, further emphasizing the effectiveness and social validity of AAC methods in therapy.
Conclusion
Pediatric speech therapy services are essential for addressing communication disorders in children, providing targeted interventions that cater to individual needs. Recognizing speech delays early is crucial, as timely intervention can significantly impact a child's development. Caregivers play a vital role in this process by familiarizing themselves with developmental milestones and seeking professional evaluation when warning signs arise.
The evaluation process conducted by speech-language pathologists (SLPs) is comprehensive, employing a variety of assessment tools and techniques to gain a thorough understanding of a child’s communication abilities. This ensures that the therapy provided is tailored to each child's specific needs. The collaboration between SLPs and families is fundamental, as it empowers caregivers to support their child's communication development effectively.
Various therapy techniques, from traditional methods to augmentative and alternative communication (AAC), demonstrate the adaptability of interventions available. By utilizing a combination of these strategies, SLPs can enhance communication skills and overall social interaction for children facing challenges.
Ultimately, understanding the significance of pediatric speech therapy, recognizing the early signs of speech delays, and engaging in the evaluation process are critical steps in facilitating a child's communication journey. The collective effort of families, educators, and SLPs can yield profound benefits, ensuring that children receive the support they need to thrive in their communication skills and overall development.




















