Introduction
1. The Essential Role of Speech Therapy in Autism Spectrum Disorder
- 1.8 times as high among Hispanic youth
- 1.6 times as high among non-Hispanic Black individuals
2. Effective Speech Therapy Techniques for Enhancing Communication Skills in Autism
-
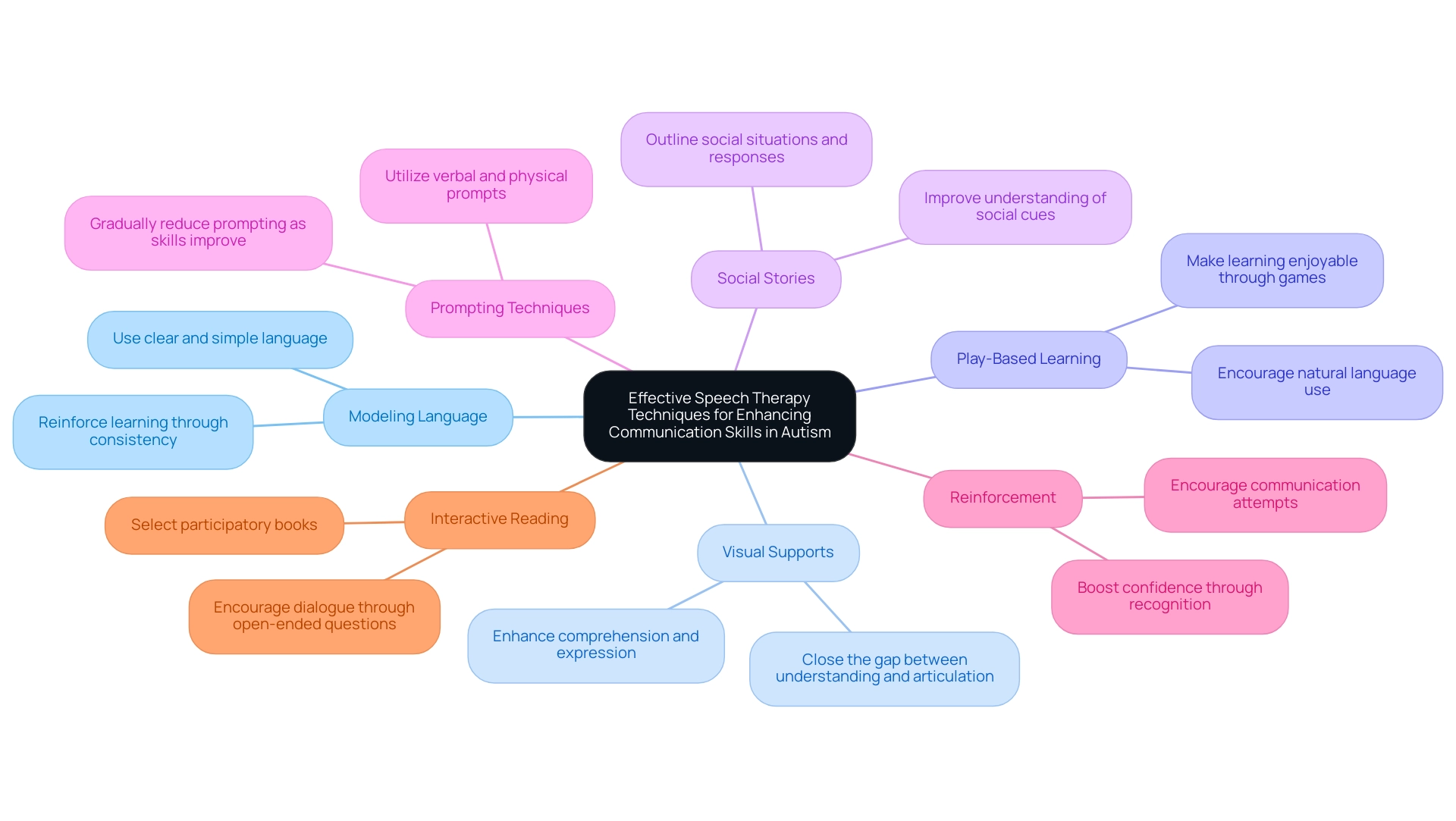
Modeling Language: To promote successful interaction, it is crucial to use clear and simple language when engaging with young individuals. Consistency and repetition are crucial; modeling phrases and vocabulary during daily routines reinforces learning and comprehension.
-
Visual Supports: The integration of visual aids—such as pictures, symbols, or written words—serves to enhance both comprehension and expression. Visual aids serve a crucial function in closing the divide between comprehension and effective expression, thus equipping youngsters with the resources they require to articulate themselves.
-
Play-Based Learning: Engaging in play activities that promote language development is highly beneficial. Utilizing toys and games that encourage turn-taking, sharing, and conversation not only makes learning enjoyable but also fosters natural language use in a playful context.
-
Social Stories: Crafting social narratives that outline specific social situations and suitable responses can significantly assist young individuals in understanding social cues and expectations. These narratives enhance understanding and improve social interactions by providing clear examples of acceptable behavior.
-
Prompting Techniques: Utilizing prompting strategies can effectively foster interaction. This method may involve verbal prompts (hints) or physical prompts (such as guiding a hand to point). It is important to gradually reduce the level of prompting as the individual becomes more adept and independent in their communication.
-
Reinforcement: Positive reinforcement is essential when a young one attempts to communicate, whether through verbal expressions, gestures, or alternative forms. Recognizing these efforts not only boosts the individual's confidence but also encourages further attempts, fostering an environment conducive to learning.
-
Interactive Reading: Selecting books that promote participation can enhance language skills during reading sessions. Asking open-ended questions encourages dialogue and comprehension, allowing young individuals to actively engage with the material and express their thoughts.
3. Creating a Structured Communication Environment
-
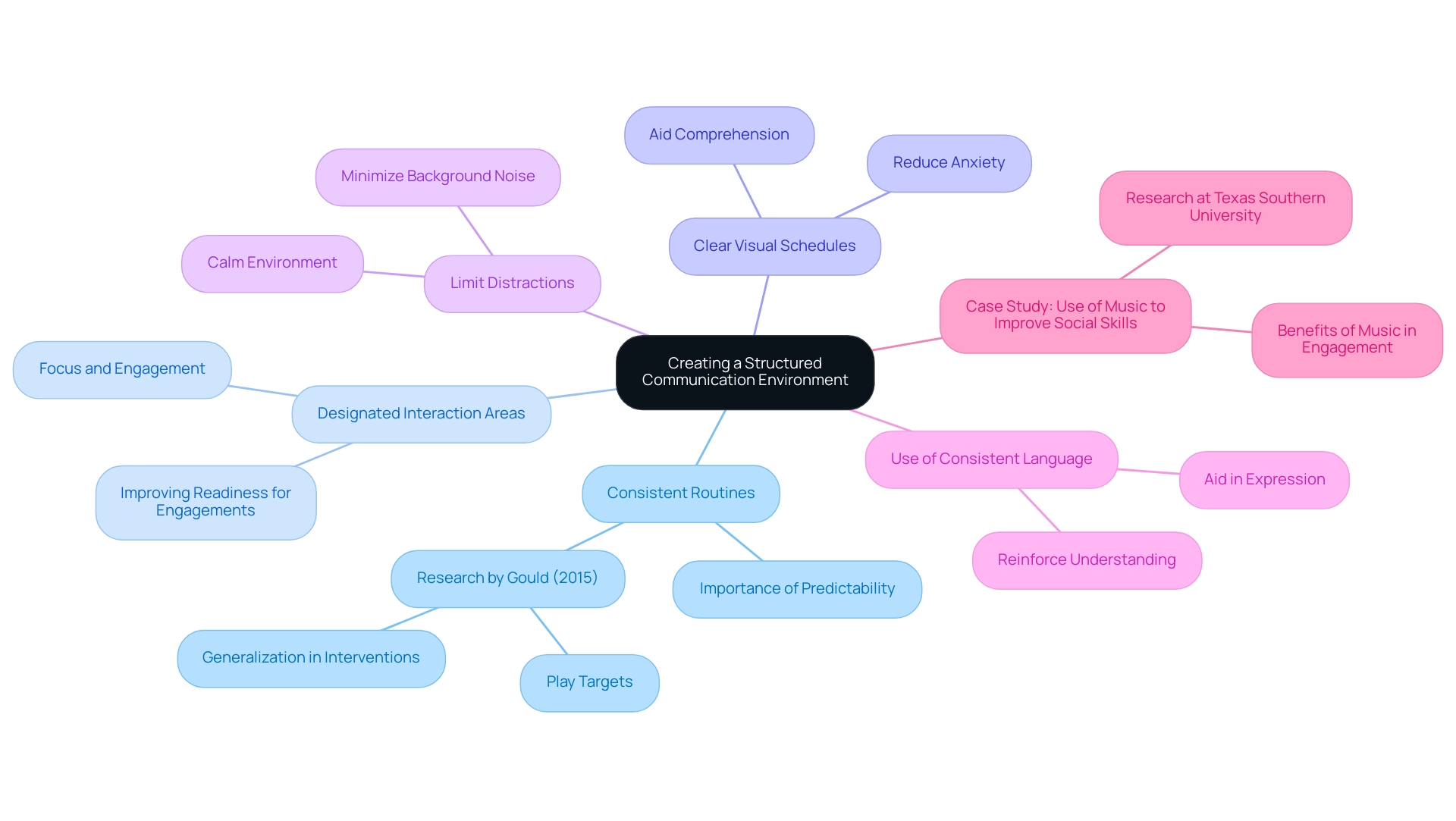
Consistent Routines: Establishing daily schedules that incorporate specific times for interaction activities is crucial. Predictability in routines not only helps young ones feel secure but also encourages them to participate more willingly in interaction exercises. Research, such as Gould's PhD thesis completed at the University of California in 2015, highlights the importance of play targets and generalization in interventions for individuals with autism, underscoring the value of consistent routines.
-
Designated Interaction Areas: Establishing particular spaces within the home or classroom devoted to interaction activities can improve focus and engagement. Linking these areas with interaction can assist young individuals in improving their readiness for engagements.
-
Clear Visual Schedules: Implementing visual schedules to outline daily activities aids comprehension and allows children to anticipate subsequent events. This proactive method can significantly lessen anxiety linked to transitions, promoting a more productive interaction experience.
-
Limit Distractions: Creating a calm environment by minimizing background noise and visual disruptions is essential during interaction activities. A peaceful environment allows young individuals to focus entirely on the task before them, which is essential for successful learning.
-
Use of Consistent Language: Maintaining consistency in phrases and terminology is vital. Repeatedly using the same expressions reinforces understanding and aids in expression, making interaction more effective.
4. Collaborating with Speech-Language Pathologists
-
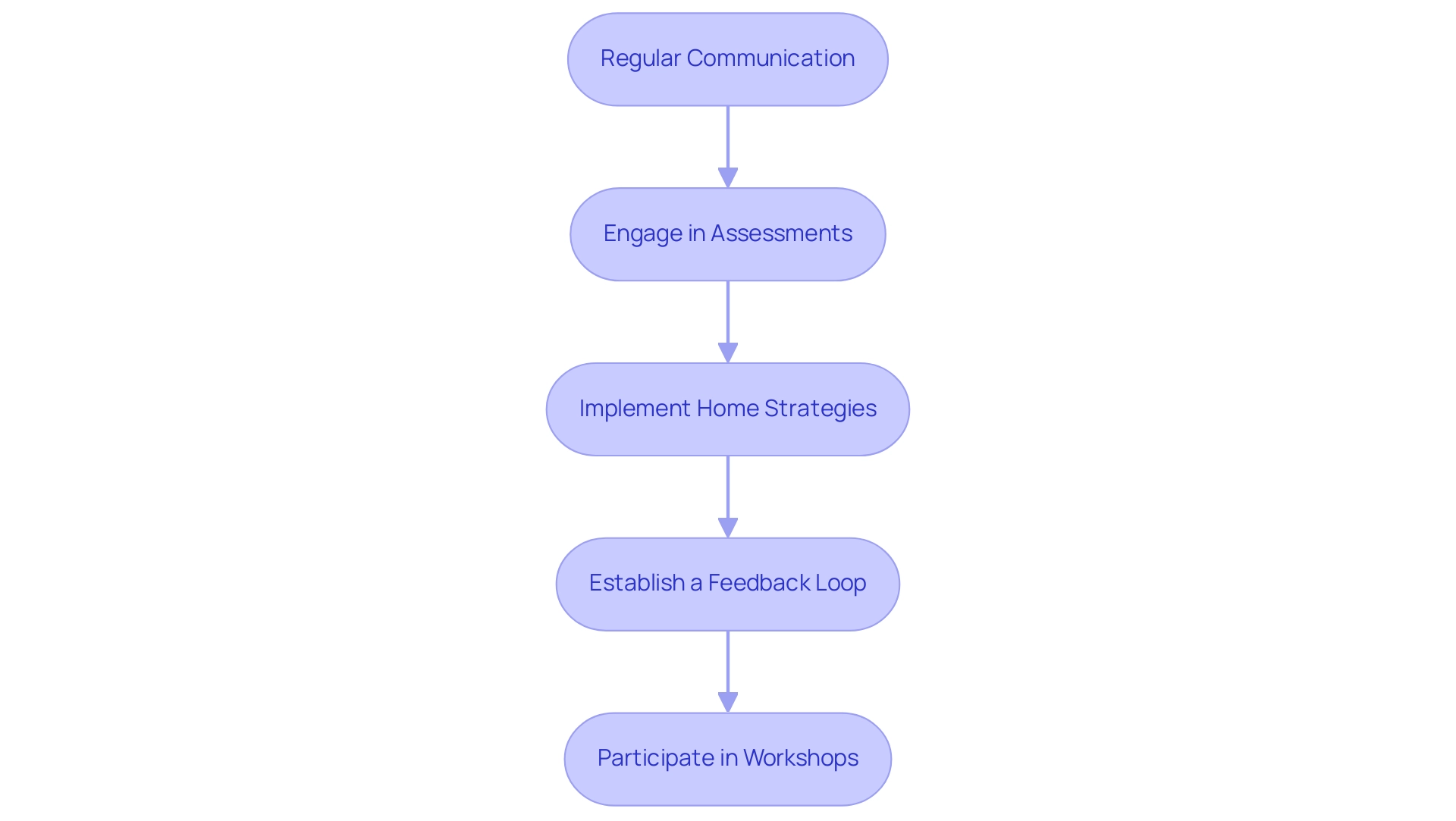
Regular Communication: Establish and maintain consistent communication with the SLP. Frequent updates about the young one's progress and any difficulties encountered can assist in making prompt modifications to treatment plans.
-
Engage in Assessments: Actively participate in assessments conducted by the SLP. A comprehensive grasp of the assessment process allows caregivers to better assist the individual's specific needs and promotes a more customized approach to treatment.
-
Implement Home Strategies: Collaborate with the SLP to create strategies that can be seamlessly integrated into home routines. Consistency between treatment sessions and home practice is crucial for reinforcing newly acquired skills.
-
Establish a Feedback Loop: Provide the SLP with feedback regarding which techniques resonate with the youth. This mutual exchange permits the personalization of treatment to match the individual's distinct preferences and strengths, thereby improving involvement in the learning process.
-
Participate in Workshops: If available, attend any workshops or training sessions offered by the SLP. Such opportunities can deepen caregivers' understanding of effective communication strategies and equip them with additional tools to support their offspring's development.
further emphasizing the importance of integrating diverse perspectives into effective service delivery models.
5. Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Techniques
-
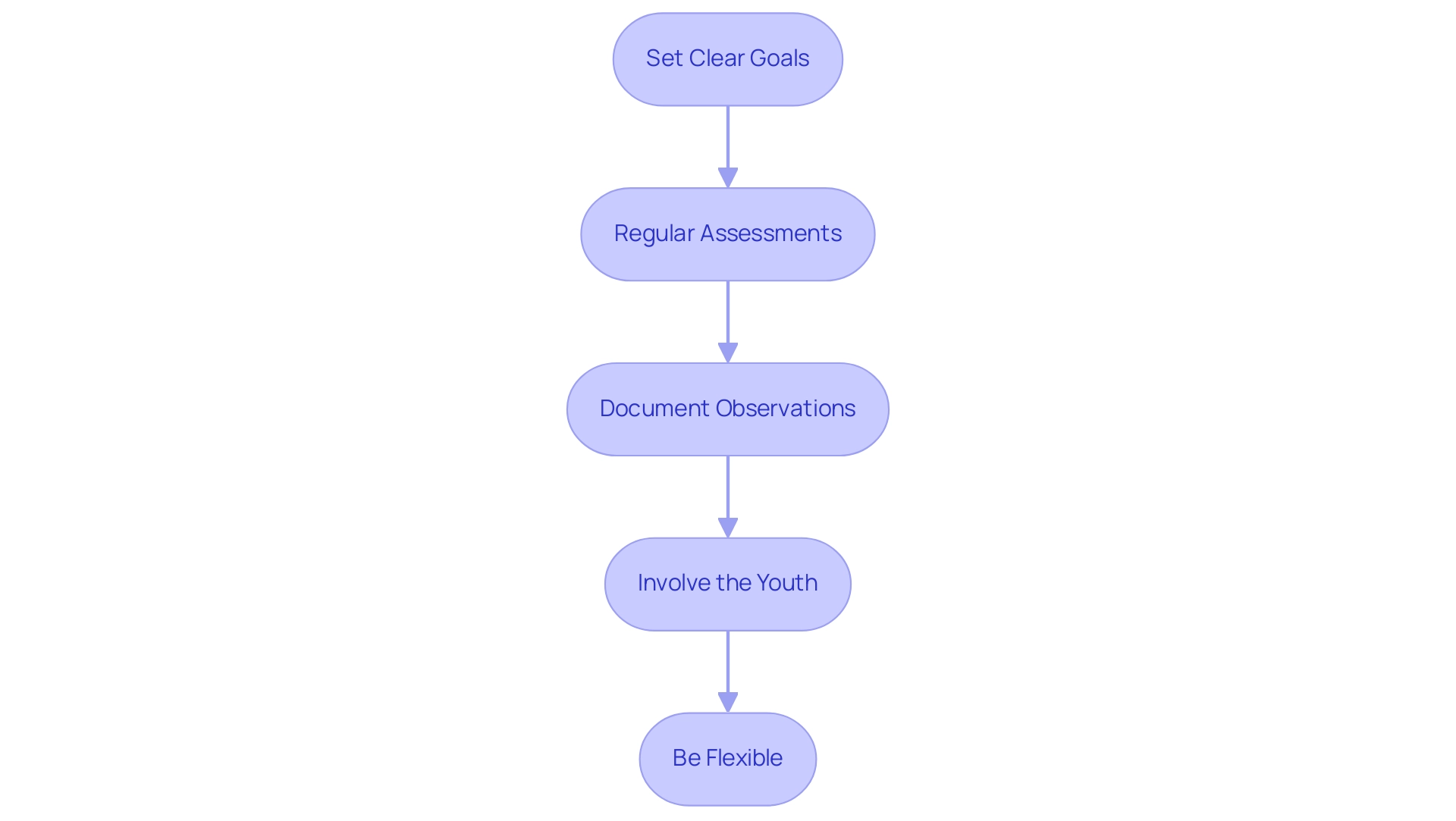
Set Clear Goals: It is crucial to establish specific, measurable objectives for interpersonal skills at the outset of therapy. This practice not only establishes a clear standard for evaluating progress but also aligns with expert recommendations that highlight the significance of setting measurable goals in therapy.
-
Regular Assessments: Schedule consistent assessments with a Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP) to evaluate the child’s progress. Structured evaluations, such as the 15- to 25-min structured observation designed to measure nonverbal interaction skills (Mundy et al.), provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the current strategies and inform necessary adjustments to therapy techniques. Recent findings suggest that investing time in evaluating intentional interactions and joint attention can yield more accurate predictions of expressive language outcomes.
-
Document Observations: Keeping a detailed log of the individual's communication attempts and successes is essential. Documenting these observations not only helps identify patterns but also highlights areas that require additional focus for improvement. This ongoing documentation is vital for tracking progress over time and adjusting goals as needed.
-
Involve the youth: Actively encourage them to express their feelings regarding the techniques being utilized. Their feedback provides invaluable insights into what methods resonate best with them, which can lead to more successful treatment outcomes.
-
Be Flexible: Adaptability is key in the therapeutic process. Be ready to modify methods according to the young person's progress and input, guaranteeing that the treatment stays impactful and engaging. This approach is particularly important given the significant increase in demand for certified ABA therapists (5,852% from 2010 to 2021), highlighting the need for responsive and tailored therapeutic interventions. Furthermore, it is essential to consider the financial aspects of treatment, as many families face challenges accessing specialized healthcare services due to substantial costs. The cost of the SLP Toolkit is a concern for users, highlighting the need for accessible and affordable speech therapy for autism spectrum disorder options. By diligently monitoring progress and demonstrating a willingness to adapt techniques, caregivers can better support children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in their communication development, ensuring they receive the most effective interventions tailored to their unique needs.
Conclusion
- Modeling language
- Utilizing visual supports
- Engaging in play-based learning






























