Introduction
The significance of fish oil in promoting health has garnered considerable attention, particularly due to its rich content of omega-3 fatty acids, which play a pivotal role in various bodily functions. Extracted primarily from oily fish such as salmon and mackerel, fish oil serves as a vital source of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), essential for maintaining cardiovascular health and cognitive function.
However, with the growing popularity of fish oil supplements, consumers must navigate the complexities of quality, dosage, and potential side effects. This article delves into the composition and sources of fish oil, explores its health benefits, and provides guidance on selecting quality supplements while addressing the associated risks and recommended consumption practices.
Understanding these aspects is crucial for individuals looking to enhance their well-being through omega-3 supplementation.
1. Understanding Fish Oil: Composition and Sources
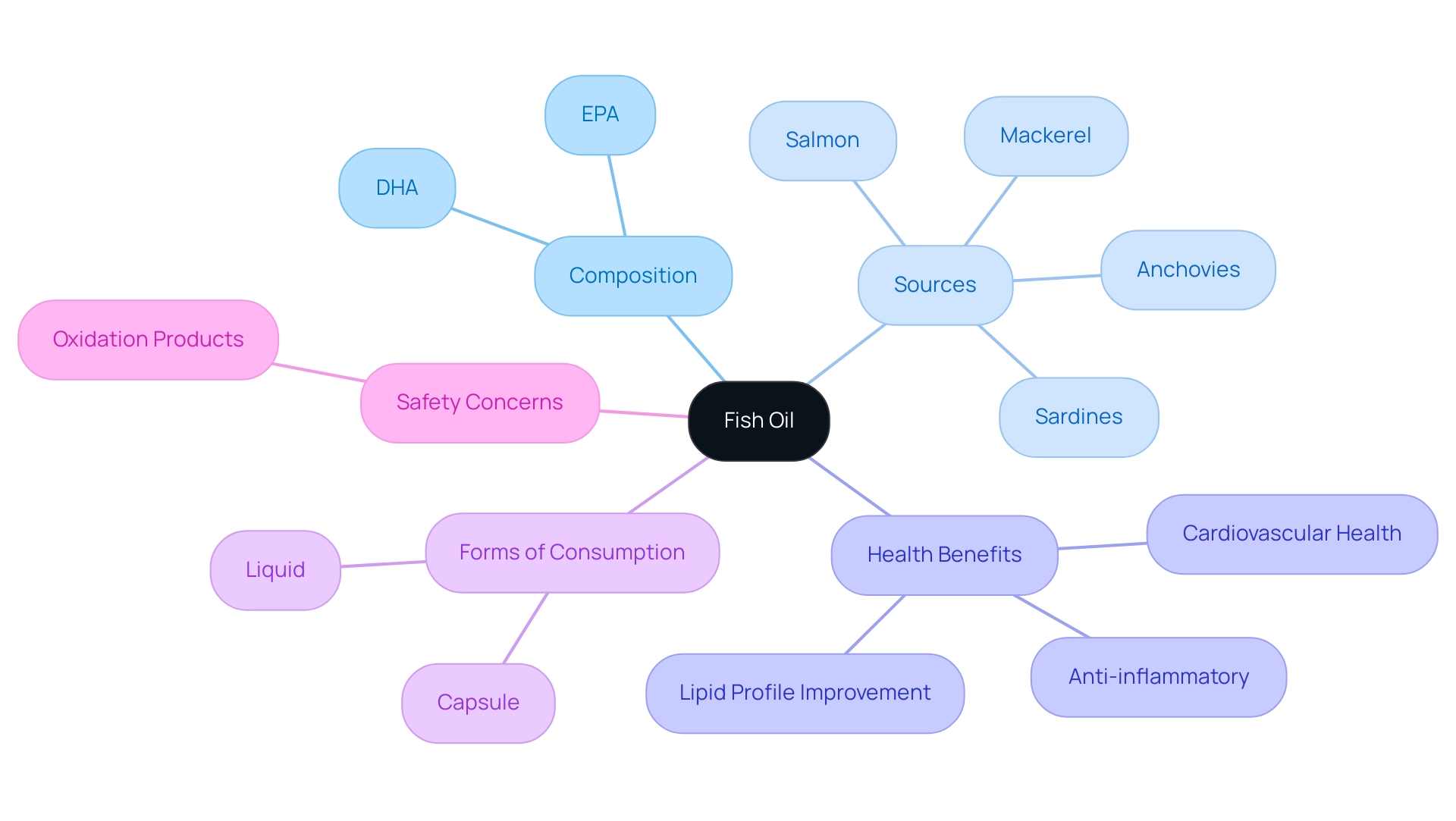
Fish oil, derived from the tissues of fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies, is a significant source of essential fatty acids, primarily eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These fatty acids are essential for numerous physiological functions, including cellular well-being and inflammatory response modulation. Since essential fatty acids cannot be synthesized by the human body, they must be ingested through
dietary sources or supplements.
Fish oil is available in both liquid and capsule forms, offering flexibility for consumption. However, it is important to note that recent statistics indicate that primary, secondary, and total oxidation products in some dietary supplements have exceeded maximum levels established by international standards, raising safety concerns regarding their use. Acknowledged for its notable anti-inflammatory attributes, the fish oil benefits from aquatic sources have attracted interest for their possible wellness advantages, which encompass enhancing lipid profiles and promoting cardiovascular well-being.
A 2016 review of 143 studies found that fatty acid supplementation during pregnancy slightly increased babies' birth weight but did not change the risk of low birth weight or premature birth. Moreover, a randomized study named 'Comparison of Supplements and Fresh Seafood' examined the impacts of supplements and fresh seafood on lipid profiles, demonstrating that both sources significantly improve lipid profiles, highlighting the significance of these fatty acids in preserving overall well-being.
2. Exploring the Health Benefits of Fish Oil
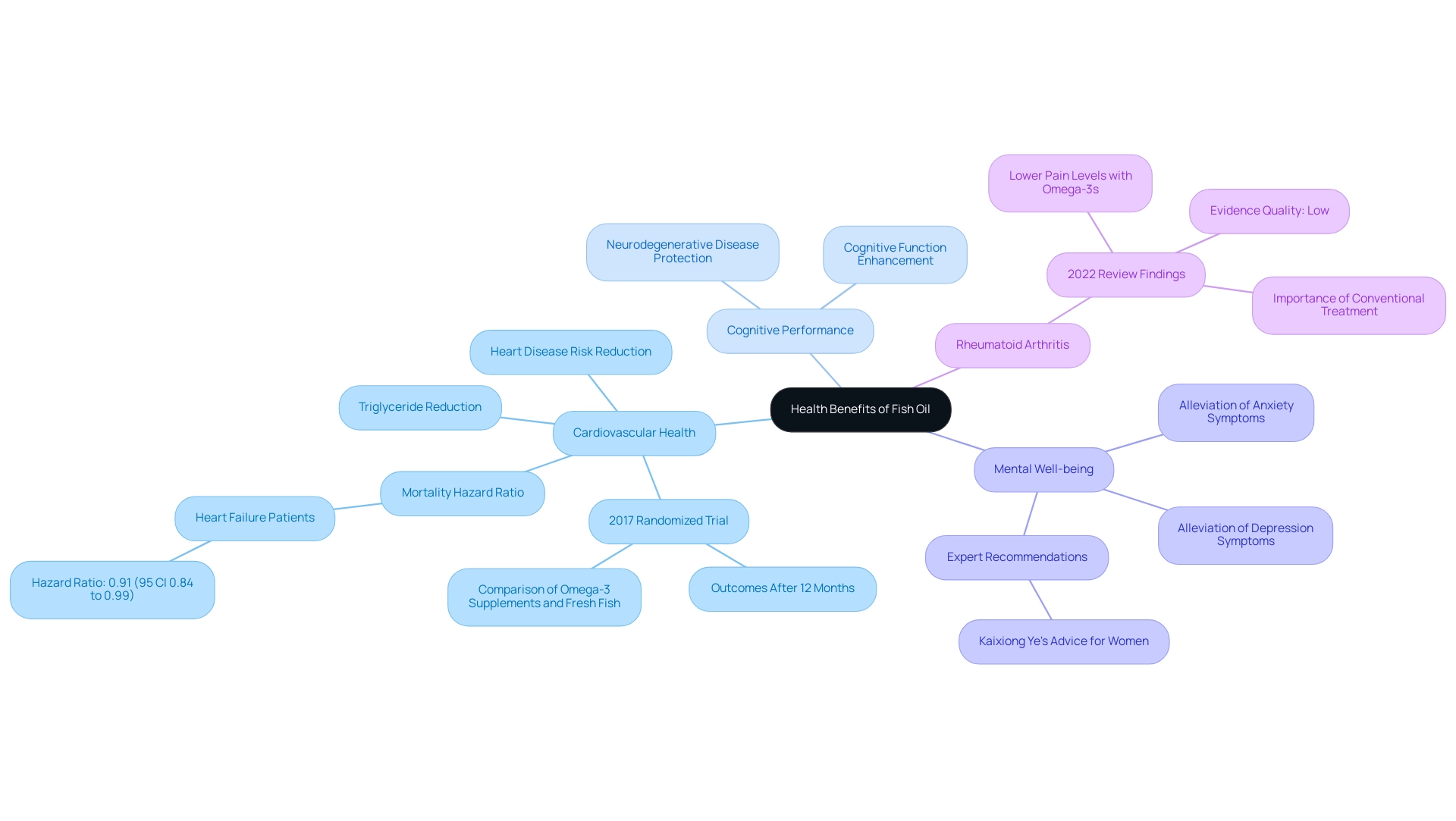
The intake of seafood oil, rich in essential fatty acids, offers various fish oil benefits, particularly for cardiovascular fitness and cognitive performance. Research indicates that these fatty acids can significantly lower triglyceride levels, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease. In a notable 2017 randomized trial published in Nutrition & Diabetes, the effects of fish oil supplements were compared to those of fresh fish on lipid profiles, revealing that both options provide significant fish oil benefits for heart health.
Importantly, after 12 months, outcomes didn’t differ between the two groups, suggesting comparable effectiveness. Furthermore, the
hazard ratio for mortality in patients with heart failure was determined to be 0.91 (95% CI 0.84 to 0.99), emphasizing the possible life-extending effects associated with fish oil benefits. Health experts, including Kaixiong Ye, strongly recommend that women enhance their intake of essential fatty acids because of these cardiovascular advantages.
Beyond heart health, the fish oil benefits, particularly from fatty acids, also show promise in supporting mental well-being by potentially alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety. Additionally, there is evidence suggesting that the fish oil benefits include enhancing cognitive function and may protect against neurodegenerative diseases, making it particularly beneficial for aging populations. A 2022 review highlighted that diets rich in omega-3s resulted in lower pain levels among rheumatoid arthritis patients; however, it noted that the evidence was low and that conventional medical treatment remains essential for effective management.
Overall, incorporating fish oil benefits from aquatic sources into one's daily regimen can lead to notable improvements in both physical and mental health.
3. Choosing Quality Fish Oil Supplements: What to Look For
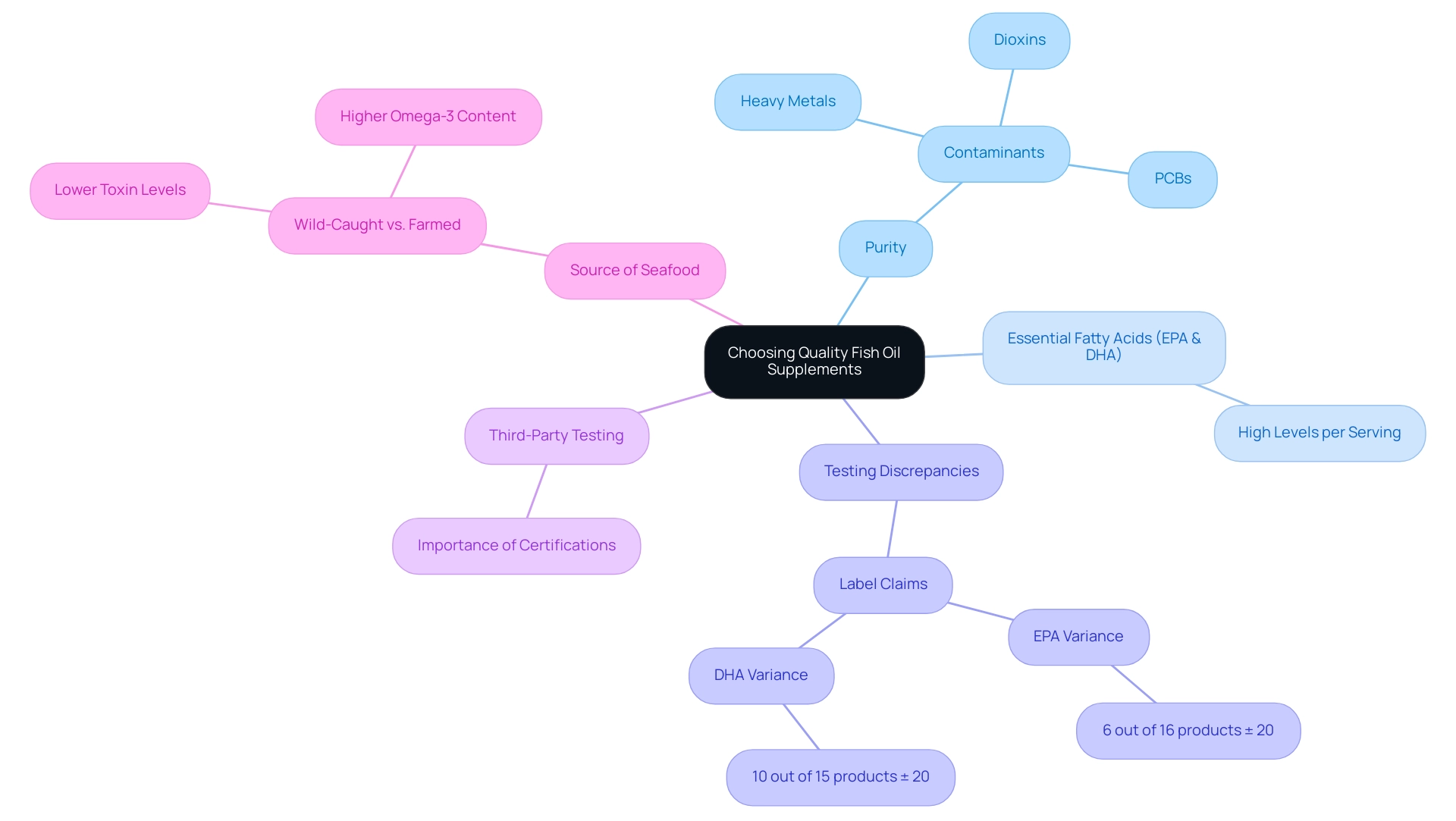
When selecting supplements that provide fish oil benefits, several critical factors must be taken into account to ensure quality and efficacy. Purity is paramount; consumers should actively seek products that have undergone rigorous testing for contaminants such as heavy metals, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), dioxins, and also consider the fish oil benefits. Rakesh Satyal emphasizes the importance of these tests, stating, "The
Quantitation of EPA and DHA in Fish Oil Dietary Supplements Sold in the United States highlights the need for stringent quality assessments in this industry."
Furthermore, the fish oil benefits include a high level of essential fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which should be high per serving. In a study examining oil dietary supplements sold in the United States, significant discrepancies were found between label claims and actual EPA and DHA content. Specifically, out of 16 products tested:
- Six were ± 20% outside of their EPA label claims.
- Ten out of 15 were similarly inconsistent with their DHA claims, a variance that could mislead consumers about their intake.
This highlights the necessity of third-party testing certifications as a reliable indicator of quality. Furthermore, purification processes are essential for producing high-quality omega-3 supplements, and it is advisable to verify the source of the seafood used in the oil, as the fish oil benefits of wild-caught options are generally superior to those of farmed varieties due to their lower levels of toxins and higher omega-3 content. In 2024, adherence to these guidelines will be essential for selecting high-quality oil supplements that meet consumer health needs.
The concentration of monounsaturated fatty acids in supplements typically ranges from 1.87 to 43.36 grams, further underscoring the importance of careful selection.
4. Potential Risks and Side Effects of Fish Oil
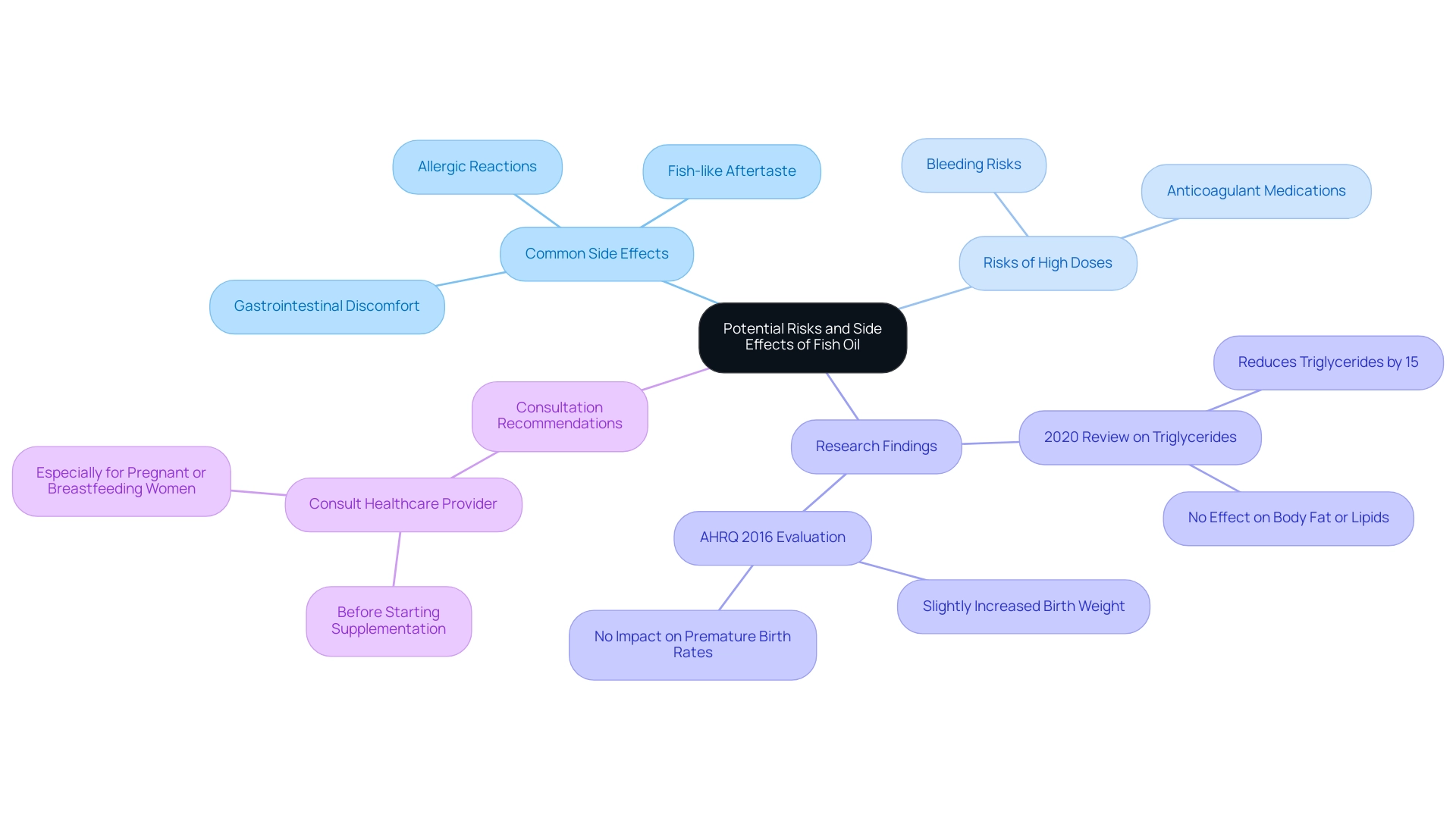
Fish oil benefits are widely recognized as a beneficial supplement; however, it is essential to recognize that it may lead to side effects in some individuals. Common complaints include:
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
- A persistent fish-like aftertaste
- Allergic reactions, particularly in those with sensitivities to seafood
High doses of marine oil have been linked to a heightened risk of bleeding, especially in patients who are on anticoagulant medications.
The importance of consulting with a healthcare provider prior to initiating any new supplementation, especially for those with existing health conditions or who are pregnant or breastfeeding, cannot be overstated. Current research highlights the necessity of being cautious with high-dose fish oil benefits consumption, as it may exacerbate bleeding risks. A 2020 review indicated that while essential fatty acids, specifically EPA and DHA, can reduce triglyceride levels by approximately 15%, they do not significantly influence body fat or other lipid levels.
Additionally, an extensive evaluation of 143 studies by AHRQ in 2016 observed that while supplementation of fatty acids during pregnancy resulted in slightly increased birth weights, it had no impact on premature birth rates or other maternal and infant well-being outcomes. This review concluded that fatty acids did not significantly affect the risk of low birth weight or other medical outcomes for mothers and infants. Additionally, a randomized trial compared the effects of omega-3 supplements and fresh seafood on lipid profiles, providing further insight into the efficacy of these sources of omega-3s.
These discoveries highlight the significance of comprehending the
dangers linked to fish oil benefits, enabling individuals to make informed choices when considering its inclusion in their wellness routines.
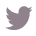
5. Guidelines for Fish Oil Dosage and Consumption
The suggested dosage of marine oil varies considerably based on personal wellness requirements and eating patterns. For healthy adults, a daily intake of 250-500 mg of combined EPA and DHA is generally suggested. However, those with specific health conditions may require higher dosages.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before exceeding these amounts to ensure safety and efficacy. Notably, the FDA recommends an additional 200–300 mg of DHA during pregnancy and nursing, highlighting the tailored approach required for different life stages. This recommendation is particularly important as women in the highest tertiles of dietary DHA plus EPA intake had a 38% lower risk of developing
age-related macular degeneration (AMD) during an average of 10 years of follow-up compared to those in the lowest tertile.
Furthermore, to enhance the absorption of fish oil benefits and mitigate gastrointestinal discomfort, it is ideal to take fish oil with meals. Spreading the dosage throughout the day, rather than consuming it all at once, may also minimize potential side effects. Consumers should also be aware of the variability in EPA and DHA amounts in omega-3 supplements, as highlighted in the case study 'Understanding Omega-3 Supplement Labels.'
This practice aligns with the latest guidelines, which emphasize the importance of adherence to recommended dosages for optimal health benefits.
Conclusion
The exploration of fish oil highlights its significant role in enhancing health, primarily through its omega-3 fatty acids, EPA and DHA. These essential fatty acids contribute to various physiological functions, including cardiovascular health and cognitive function. Research consistently supports the benefits of fish oil, with studies demonstrating its effectiveness in improving lipid profiles and reducing the risk of heart disease. Additionally, the potential mental health benefits, such as alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety, further establish fish oil as a valuable supplement for overall well-being.
However, the selection of quality fish oil supplements is paramount. Consumers must be vigilant about purity and concentration, ensuring that products have undergone thorough testing for contaminants and accurately reflect their omega-3 content. The presence of third-party testing certifications can serve as a reliable indicator of product quality, guiding consumers towards safe and effective options.
While fish oil is generally well-tolerated, awareness of potential side effects is crucial. Gastrointestinal discomfort and increased bleeding risks are notable concerns, particularly at high doses. Consulting with healthcare professionals before starting supplementation is essential, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or specific dietary needs.
In conclusion, integrating fish oil into a health regimen can yield numerous benefits, provided that consumers are informed and cautious in their choices. By understanding the composition, selecting quality supplements, and adhering to recommended dosages, individuals can harness the advantages of omega-3 fatty acids to enhance their health and well-being.