Introduction
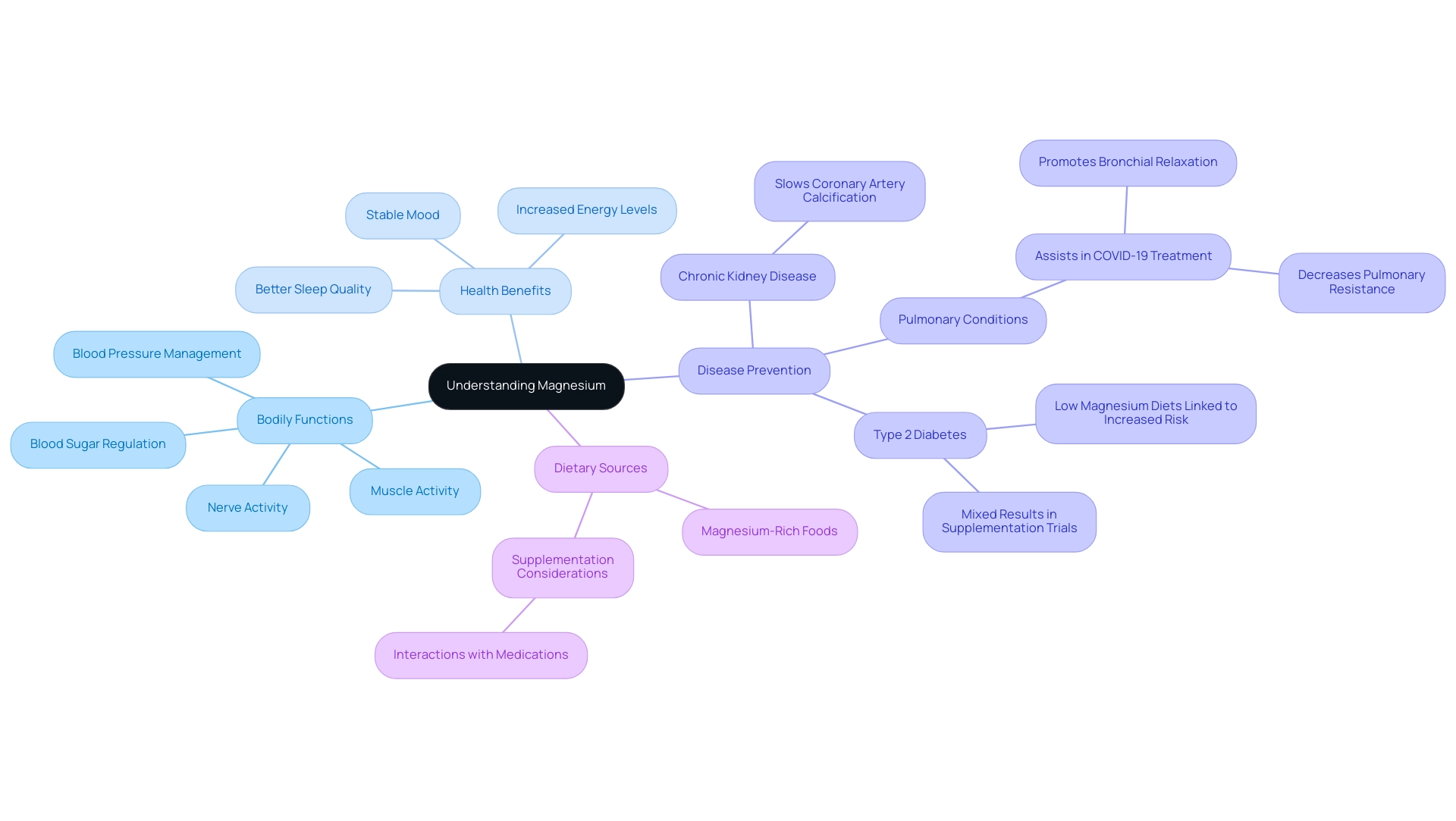
Magnesium is often referred to as the unsung hero of essential minerals, playing a crucial role in numerous bodily functions that are vital for maintaining overall health. This mineral not only supports muscle and nerve function but also regulates blood sugar levels and blood pressure, contributing to a well-balanced physiological state. With research linking adequate magnesium intake to improved energy, better sleep quality, and enhanced mood stability, understanding its importance becomes paramount.
Furthermore, magnesium's potential protective effects against chronic diseases, including its role in managing conditions like diabetes and heart disease, highlight the need for individuals to evaluate their dietary sources of this essential nutrient.
This article delves into the critical benefits of magnesium, identifies top food sources, and offers practical tips for incorporating magnesium-rich foods into daily meals, all while emphasizing the significant health risks associated with magnesium deficiency.
1. Understanding Magnesium: Importance and Benefits
Magnesium is an indispensable mineral that significantly contributes to various bodily functions, encompassing muscle and nerve activity, blood sugar regulation, and blood pressure management. Its role extends to the synthesis of proteins and the development of bones, making it essential for overall health. Sufficient intake of this mineral is linked to increased energy levels, better sleep quality, and a more stable mood.
Research indicates that this mineral may play a protective role against chronic diseases; for example, a randomized clinical trial demonstrated that oral supplementation can slow the progression of coronary artery calcification among non-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. Additionally, sulfate may assist in treating pulmonary conditions associated with COVID-19 by promoting bronchial relaxation and decreasing pulmonary resistance. Magnesium also assists enzymes crucial for
regulating blood sugar and insulin activity, highlighting its potential in diabetes management.
Despite some mixed results from clinical trials regarding the supplement's effectiveness, prospective cohort studies suggest that low diets of this mineral correlate with an elevated risk of type 2 diabetes. As Chinta Sidharthan observes, 'Researchers explain why a diet high in this mineral is crucial for your well-being.' Given these findings, it becomes evident that incorporating magnesium rich foods into one's diet is vital for promoting wellness and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
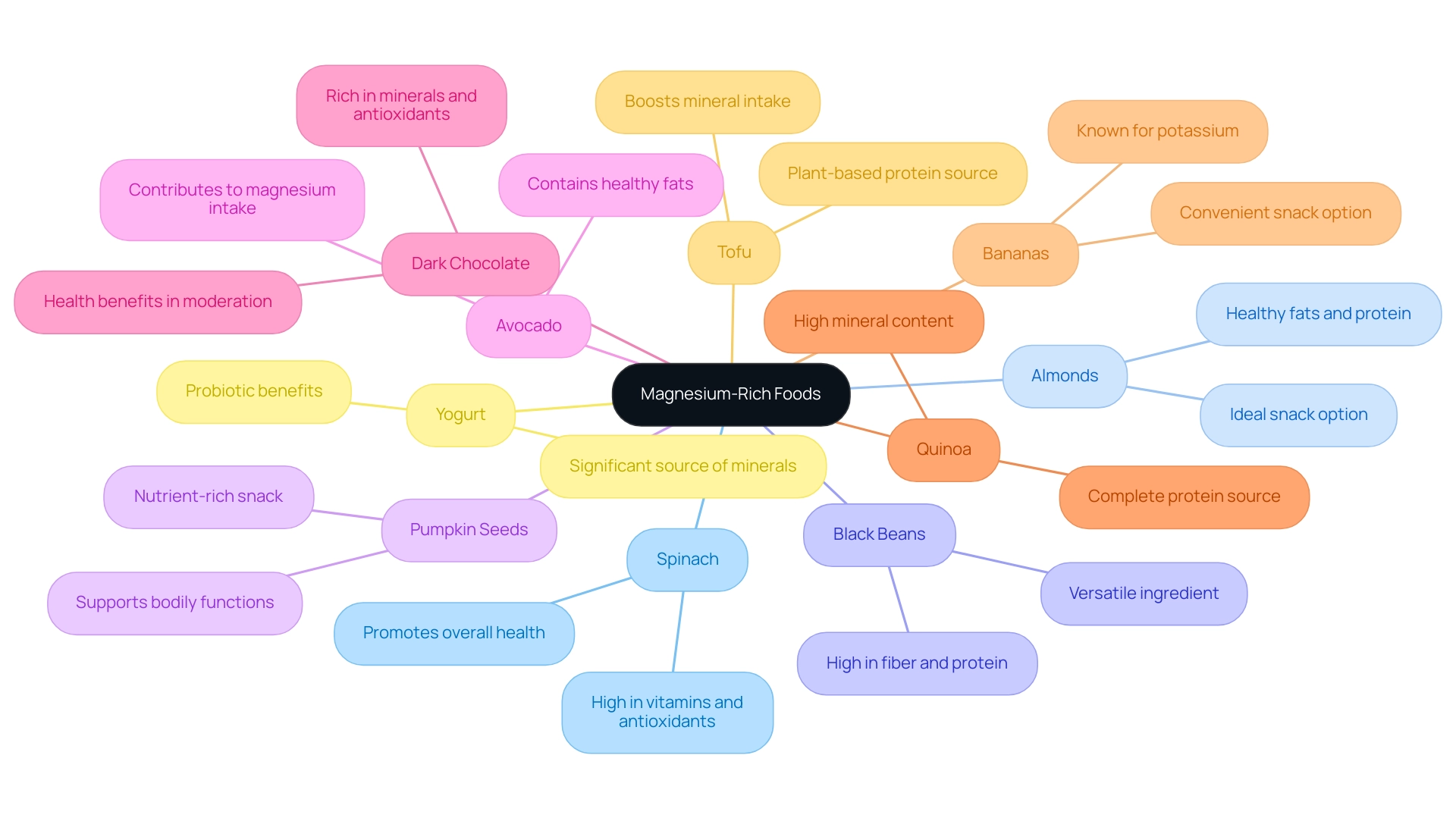
2. Top 10 Magnesium-Rich Foods to Incorporate into Your Diet
-
Spinach: This leafy green vegetable stands out as an exceptional source of this vital mineral, offering not just this essential nutrient but also a rich array of vitamins and antioxidants. Recent nutritional studies have highlighted spinach's role in promoting overall health and its notable mineral content. Considering that 25% of cases reviewed by the FDA found that supplements did not elevate levels of the mineral in patients taking proton pump inhibitors, it's essential to concentrate on food sources like spinach for sufficient intake of this nutrient.
-
Almonds: A handful of almonds provides a significant amount of minerals, along with healthy fats and protein, making them an ideal snack option. Dietitians emphasize the importance of incorporating magnesium rich foods like almonds into daily diets for optimal health. The
2020–2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans state that nutritional needs should be met primarily through foods, highlighting almonds as an excellent choice.
-
Black Beans: Known for their high fiber and protein content, black beans serve as a superb source of an essential mineral. Their versatility allows for easy inclusion in various dishes, contributing to a balanced and nutritious diet.
-
Pumpkin Seeds: Frequently viewed as a nutrient-rich choice, pumpkin seeds are a tasty snack alternative that can improve salads and various dishes. Their high mineral content supports various bodily functions, making them a dietary staple for health enthusiasts.
-
Avocado: This creamy fruit is not only a culinary favorite but also offers a considerable amount of essential minerals along with fiber and healthy fats. Incorporating magnesium rich foods like avocados into meals can contribute to achieving the recommended dietary intake of magnesium.
-
Dark Chocolate: A delightful treat, dark chocolate with high cocoa content is remarkably rich in minerals and antioxidants. Consuming dark chocolate in moderation can offer health benefits while satisfying sweet cravings.
-
Quinoa: As a complete protein, quinoa is highly versatile and offers a significant quantity of mineral content per serving. Incorporating magnesium rich foods into meals can aid in meeting the dietary needs for this essential mineral.
-
Bananas: While best recognized for their potassium content, bananas also have other minerals, making them an excellent snack option that supports a balanced diet. Their accessibility and convenience make them a popular option for health-conscious individuals.
-
Tofu: A fantastic source of plant-based protein, tofu is abundant in minerals and can be utilized in a variety of dishes. This makes it an ideal ingredient for those seeking to boost their mineral intake through vegetarian or vegan diets.
-
Yogurt: Beyond its probiotic advantages for digestive wellness, yogurt, especially Greek yogurt, acts as a significant source of a vital mineral. Incorporating yogurt into the diet can assist in achieving the suggested amounts of this essential mineral while offering extra wellness advantages.
Moreover, research has indicated that increased dietary intake of magnesium rich foods may reduce the likelihood of cardiovascular illnesses, highlighting the significance of magnesium rich foods for heart wellness.
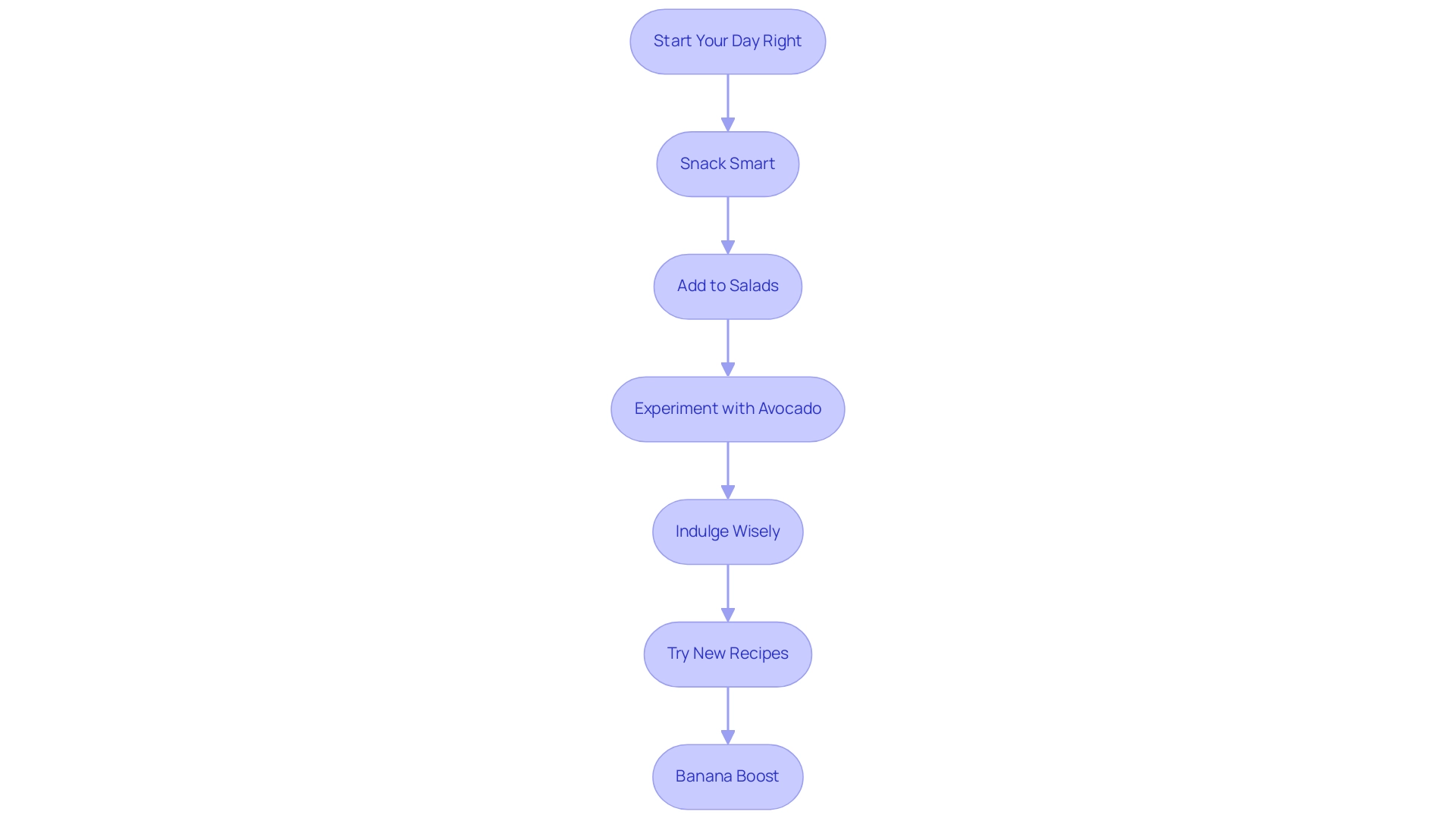
3. How to Easily Add Magnesium-Rich Foods to Your Daily Meals
-
Start Your Day Right: Begin your morning with a nutrient-packed smoothie by adding spinach or kale. These leafy greens are not only abundant in nutrients but provide vital vitamins and minerals for overall health.
-
Snack Smart: Keep a supply of almonds or pumpkin seeds at your desk. Both magnesium rich foods are excellent sources of this mineral and provide healthy, convenient snacks that can help maintain energy levels throughout the day.
-
Add to Salads: Enhance your salads by incorporating black beans or quinoa. These ingredients, which are magnesium rich foods, not only enhance texture but significantly increase the mineral content of your meal, aligning with the recommendation that at least two-thirds of grain foods consumed should be whole grains.
-
Experiment with Avocado: Use avocado as a creamy spread on whole grain toast or as a delicious side to your meals. The mineral content of magnesium rich foods and their beneficial fats can help support cardiovascular health.
-
Indulge Wisely: When it comes to dessert, choose dark chocolate with at least 70% cocoa. This treat not only fulfills your sweet desires but also provides a rich source of minerals, particularly magnesium rich foods.
-
Try New Recipes: Diversify your meals by exploring recipes that feature tofu or yogurt as main ingredients. Both options are abundant in minerals, especially magnesium rich foods, and can easily be included in various dishes, making them ideal for meal planning.
-
Banana Boost: Keep bananas on hand for a quick, on-the-go snack that also satisfies your sweet tooth. This fruit is an excellent source of magnesium rich foods and can be enjoyed alone or included in smoothies and cereals.
By including magnesium rich foods that are abundant in minerals in your daily meals, you can greatly enhance your overall well-being, as emphasized by specialists such as Razzaque, M. S., who highlight the significance of sufficient mineral intake for optimal body function. Additionally, the FDA has issued a safety communication regarding low mineral levels associated with long-term PPI use, underscoring the necessity of maintaining sufficient intake of magnesium rich foods. As Razzaque (2018) notes, `
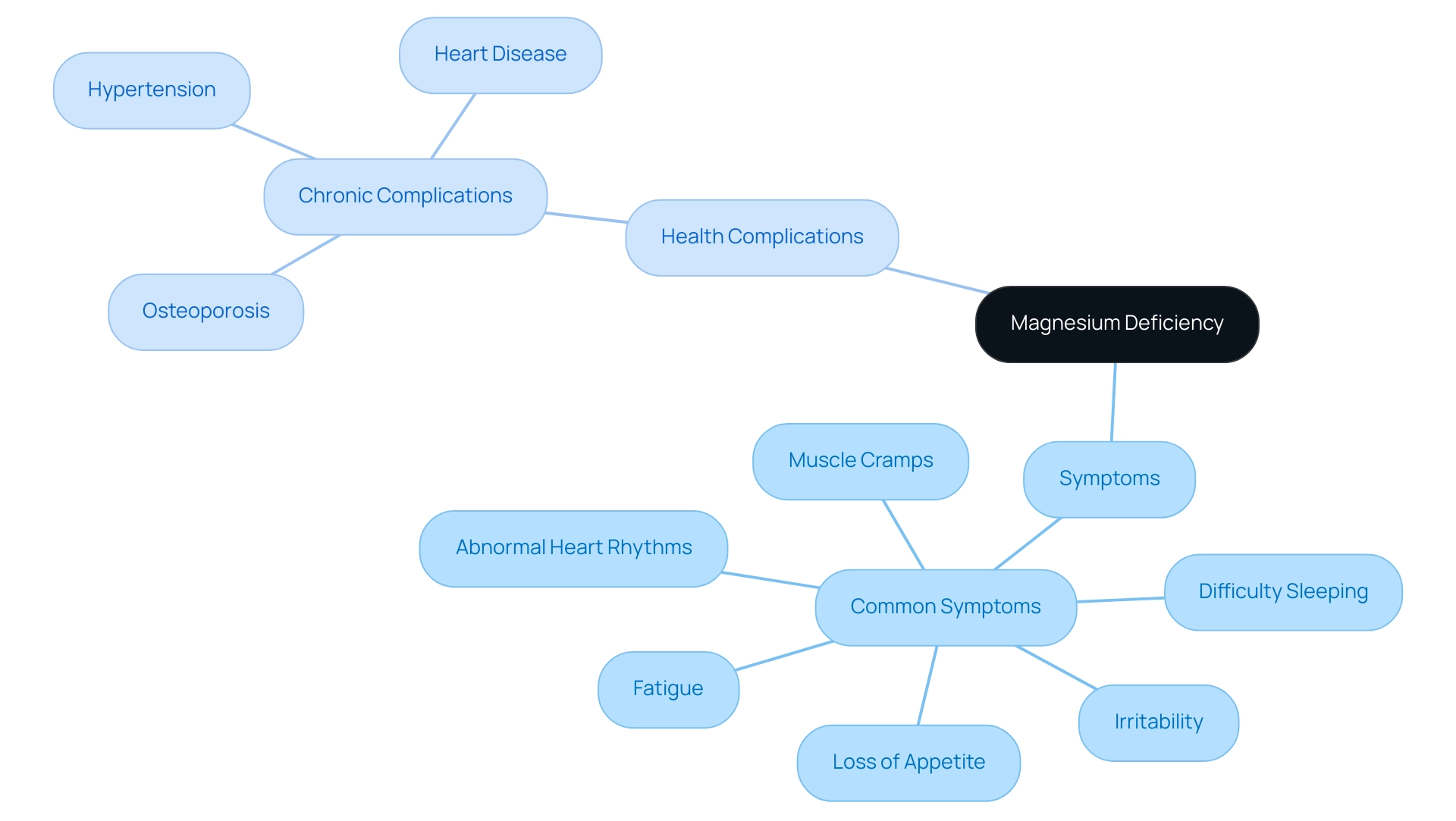
4. Recognizing Magnesium Deficiency: Signs and Symptoms
Magnesium deficiency presents a spectrum of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Common manifestations include:
- Muscle cramps
- Fatigue
- Irritability
Additionally, individuals may experience:
- Difficulty sleeping
- Loss of appetite
- Abnormal heart rhythms
Chronic deficiency of this essential mineral is particularly concerning, as it can lead to serious health complications such as:
- Osteoporosis
- Hypertension
- Heart disease
Numerous studies conducted over the past 30 years have established a clear link between chronic mineral deficiency and the exacerbation of major disorders. As healthcare professionals emphasize, recognizing these symptoms is crucial.
Abbas Ismail, a consultant rheumatologist, raises an important question:
If acknowledged, should oral mineral supplements be provided to restore body stores?
This inquiry emphasizes the necessity for individuals, particularly those with medical conditions leading to mineral depletion, to pursue dietary modifications or consult healthcare specialists regarding the intake of
magnesium-rich foods or supplements containing this essential nutrient. Furthermore, effective management of hypomagnesemia requires collaboration among healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive care, as highlighted in a case study on interprofessional collaboration in hypomagnesemia management.
Prompt action can be crucial in averting the advancement of deficiency-related medical problems.
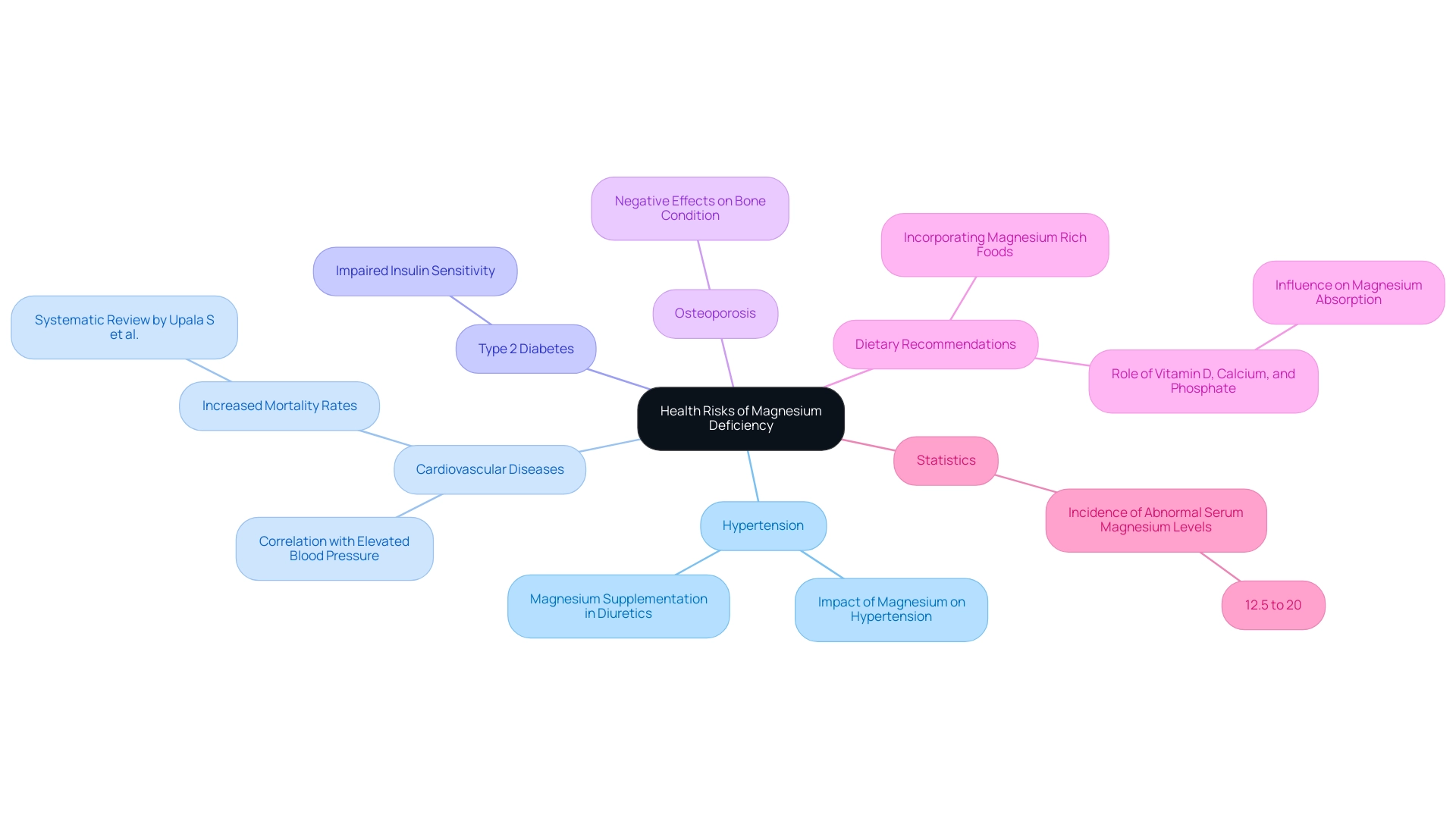
5. Health Risks of Magnesium Deficiency: Why You Should Care
Reduced amounts of this mineral are linked to various serious health hazards. Studies indicate that the
incidence of abnormal serum mineral levels ranges from 12.5% to 20%, highlighting a prevalent issue. Inadequate levels of this mineral are associated with elevated blood pressure, which can lead to hypertension and heighten the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
As mentioned in the case study titled 'Impact of Magnesium on Hypertension,' the mineral status affects vascular smooth muscle relaxation and the regulation of blood pressure. Magnesium supplementation in patients on diuretics has been shown to significantly reduce blood pressure, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent for hypertension. Additionally, a systematic review and meta-analysis by Upala S et al. revealed that hypomagnesemia is correlated with increased mortality rates in intensive care unit patients, underscoring the critical nature of maintaining adequate levels of the mineral.
Furthermore, a deficiency in this mineral impairs insulin sensitivity, raising the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes—a condition that affects millions globally. Along with metabolic issues, insufficient levels of this mineral can negatively affect bone condition, leading to an increased risk of osteoporosis.
Hardwick et al. (1991) discussed the mechanisms of magnesium absorption and the influence of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate, emphasizing the importance of these nutrients in maintaining magnesium levels. As noted by Leiva-Salinas C., improving diagnosis and treatment of hypomagnesemia is essential for mitigating these risks.
Understanding these health implications underscores the necessity of incorporating magnesium rich foods into daily diets, promoting long-term health and well-being.
Conclusion
Incorporating adequate magnesium into the diet is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing chronic diseases. This mineral plays a vital role in:
- Muscle and nerve function
- Blood sugar regulation
- Blood pressure management
The benefits of magnesium extend beyond basic bodily functions, as research indicates its potential to enhance energy levels, improve sleep quality, and stabilize mood. Furthermore, magnesium's protective effects against chronic conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, underscore the importance of ensuring sufficient intake through dietary sources.
The article highlights a variety of magnesium-rich foods, including:
- Spinach
- Almonds
- Black beans
- Pumpkin seeds
These can easily be integrated into daily meals. Simple strategies, such as starting the day with a nutrient-packed smoothie or snacking on magnesium-rich nuts, can significantly boost overall magnesium consumption. Recognizing the signs of magnesium deficiency, such as muscle cramps and fatigue, is crucial for individuals to take proactive steps toward improving their health through dietary adjustments.
Overall, maintaining adequate magnesium levels is not merely a health recommendation; it is a critical component of long-term wellness. By prioritizing magnesium-rich foods, individuals can enhance their quality of life and reduce the risk of serious health complications. The imperative to evaluate and improve magnesium intake cannot be overstated, as this essential mineral is foundational to sustaining health and preventing disease.